Structure of C++ Program
Welcome to the exploration of the structure of C++ programs. In this chapter, we will dissect the various components that make up a C++ program, from basic syntax to advanced concepts, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of how to structure your code effectively.
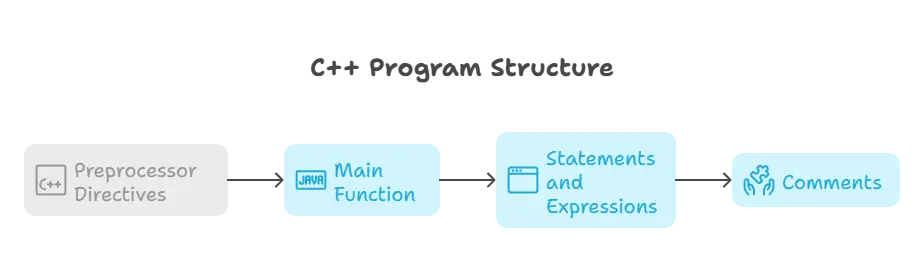
C++ Program Structure
At its core, a C++ program consists of several essential components:
Preprocessor Directives: Preprocessor directives provide instructions to the compiler before the actual compilation process begins. They typically start with a
#symbol. Common preprocessor directives include#includefor including header files and#definefor defining constants and macros.Main Function: Every C++ program must have a
main()function, which serves as the entry point of the program. Execution of the program begins from themain()function.Statements and Expressions: Statements are individual instructions that perform specific tasks, while expressions are combinations of operators and operands that produce a value. C++ programs consist of a sequence of statements and expressions.
Comments: Comments are used to add explanatory notes within the code. They are ignored by the compiler and serve to improve code readability and maintainability.
Now, let’s look at a basic example of a C++ program
#include <iostream> // Preprocessor directive
int main() { // Main function
// Statement
std::cout << "Hello, World!" << std::endl; // Expression
return 0; // Statement
}
Explanation:
#include <iostream>: This preprocessor directive includes the input/output stream library, allowing us to perform input and output operations.int main() { ... }: This is the main function of our program, where the execution begins. It returns an integer value to indicate the status of the program.std::cout << "Hello, World!" << std::endl;: This statement uses thestd::coutobject to output the text “Hello, World!” to the standard output stream.return 0;: This statement indicates that the program executed successfully and returns an exit status of 0 to the operating system.
// output //
Hello, World!
Understanding the structure of a C++ program is crucial for writing efficient and maintainable code. Stay tuned for further exploration of advanced C++ topics in the upcoming chapters. Happy coding!❤️
