Pointer declaration and initialization
Pointers are fundamental concepts in C++ programming that allow you to store and manipulate memory addresses. They provide a way to directly interact with memory, offering a powerful tool for managing data and optimizing performance in your programs.
Basics of Pointers
In C++, a pointer is a variable that holds the memory address of another variable. It allows indirect access to the memory location it points to. To declare a pointer, you use the asterisk (*) symbol followed by the data type of the variable it points to. Here’s a basic example:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int num = 5;
int* ptr; // Declares a pointer to an integer
ptr = # // Assigns the address of 'num' to 'ptr'
// Output the value of 'num' and the value pointed to by 'ptr'
cout << "Value of num: " << num << endl;
cout << "Value pointed to by ptr: " << *ptr << endl;
return 0;
}
// output //
Value of num: 5
Value pointed to by ptr: 5
Explanation:
- We declare an integer variable
numand initialize it with the value 5. - Then, we declare a pointer
ptrto an integer. - We assign the address of
numto the pointerptr. - Finally, we output the value of
numand the value pointed to byptr. Sinceptrholds the address ofnum,*ptrdereferences the pointer and gives us the value stored innum.
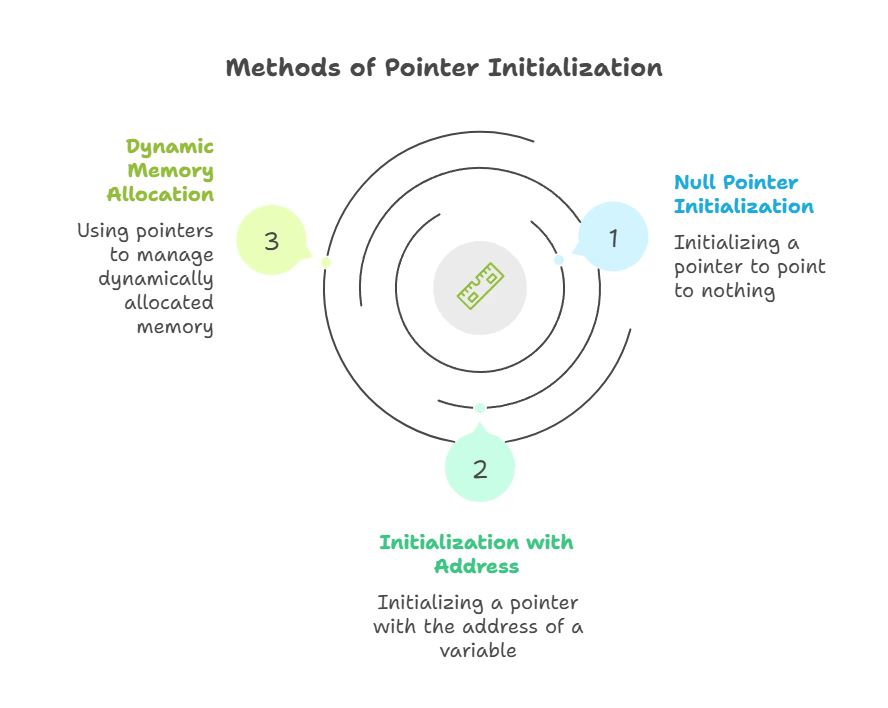
Initialization of Pointers
Pointers can be initialized in several ways:
Null Pointer Initialization
You can initialize a pointer to point to nothing using the nullptr keyword or NULL macro.
int* ptr = nullptr; // or int* ptr = NULL;
Initialization with Address
You can initialize a pointer with the address of another variable.
int x = 10;
int* ptr = &x; // ptr now holds the address of x
Dynamic Memory Allocation
Pointers are commonly used to manage dynamically allocated memory using the new keyword.
int* ptr = new int; // Allocates memory for an integer
Code Example
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// Null pointer initialization
int* ptr1 = nullptr;
cout << "Null pointer: " << ptr1 << endl;
// Initialization with address
int x = 10;
int* ptr2 = &x;
cout << "Address of x: " << &x << endl;
cout << "Pointer ptr2: " << ptr2 << endl;
// Dynamic memory allocation
int* ptr3 = new int(20);
cout << "Dynamic allocation: " << *ptr3 << endl;
delete ptr3; // Free memory allocated by new
return 0;
}
// output //
Null pointer: 0
Address of x: 0x7ffdf33dc51c
Pointer ptr2: 0x7ffdf33dc51c
Dynamic allocation: 20
Explanation:
- We initialize
ptr1as a null pointer usingnullptr. ptr2is initialized with the address ofx.- We dynamically allocate memory for an integer using
newand initializeptr3with the address of the allocated memory. - After usage, we deallocate the memory allocated for
ptr3usingdelete.
In conclusion, understanding pointers is crucial for mastering C++ programming. They offer powerful capabilities for memory management and manipulation. By learning how to declare, initialize, and work with pointers, you can enhance the efficiency and flexibility of your code. Practice and experimentation are key to becoming proficient with pointers in C++.Happy coding !❤️
