Constants in C++
Constants in C++ are identifiers whose values cannot be altered during the execution of a program. They are used to represent fixed values that remain unchanged throughout the program's execution. Constants provide a way to make code more readable, maintainable, and self-documenting by giving meaningful names to important values.
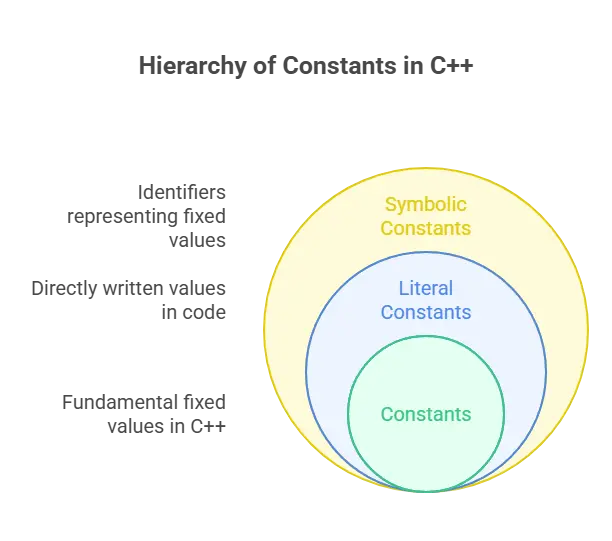
Types of Constants
In C++, constants can be categorized into two main types:
Literal Constants
Literal constants are fixed values that are directly written into the code. They are also known as literal values. There are several types of literal constants in C++:
- Integer Constants: Whole numbers without fractional parts, such as
10,-5,1000. - Floating-point Constants: Numbers with decimal points or exponents, such as
3.14,1.0e-5. - Character Constants: Single characters enclosed in single quotes, such as
'A','x','7'. - String Constants: Sequences of characters enclosed in double quotes, such as
"Hello","C++","123". - Boolean Constants: Represent true or false values,
trueorfalse.
Symbolic Constants
Symbolic constants are identifiers that represent fixed values. They are declared using the const keyword followed by the data type and the value. Symbolic constants provide meaningful names to important values, making the code more readable and maintainable.
Using Symbolic Constants
Symbolic constants are typically declared at the beginning of a program or within a specific scope where they are used. They follow the naming conventions for variables and are often written in uppercase letters to distinguish them from variables.
#include <iostream>
int main() {
// Declaration of symbolic constants
const double PI = 3.14159;
const int MAX_VALUE = 100;
// Using symbolic constants in calculations
double radius = 5.0;
double area = PI * radius * radius;
// Output the calculated area
std::cout << "Area of the circle: " << area << std::endl;
return 0;
}
// output //
Area of the circle: 78.5397
Explanation:
- We declare symbolic constants
PIandMAX_VALUEusing theconstkeyword. - We use these constants in calculations to find the area of a circle.
- We output the calculated area using
std::cout.
In this example, PI and MAX_VALUE are symbolic constants representing the value of pi and the maximum value, respectively. By using symbolic constants, the code becomes more readable, and if the value needs to be changed later, it can be done at a single location in the code.
Advantages of Using Constants
Using constants in C++ offers several advantages:
Readability: Constants provide meaningful names to fixed values, making the code more readable and self-explanatory.
Maintainability: By using symbolic constants, if a value needs to be changed later, it can be done at a single location in the code, reducing the chances of errors and simplifying maintenance.
Debugging: Constants help in debugging by providing descriptive names to important values, making it easier to identify and understand the purpose of variables and expressions.
Constants in C++ are essential for representing fixed values that remain unchanged during the program's execution. By using both literal and symbolic constants, you can make your code more readable, maintainable, and self-documenting. Understanding and effectively using constants is a fundamental aspect of writing clean and efficient C++ code.Happy coding! ❤️
