Load method in JQuery
The .load() method in jQuery is a powerful and convenient way to load data from the server and insert it into the DOM without requiring a full page refresh. This chapter will provide a comprehensive overview of the .load() method, from basic to advanced usage, including detailed examples and explanations.
Load method
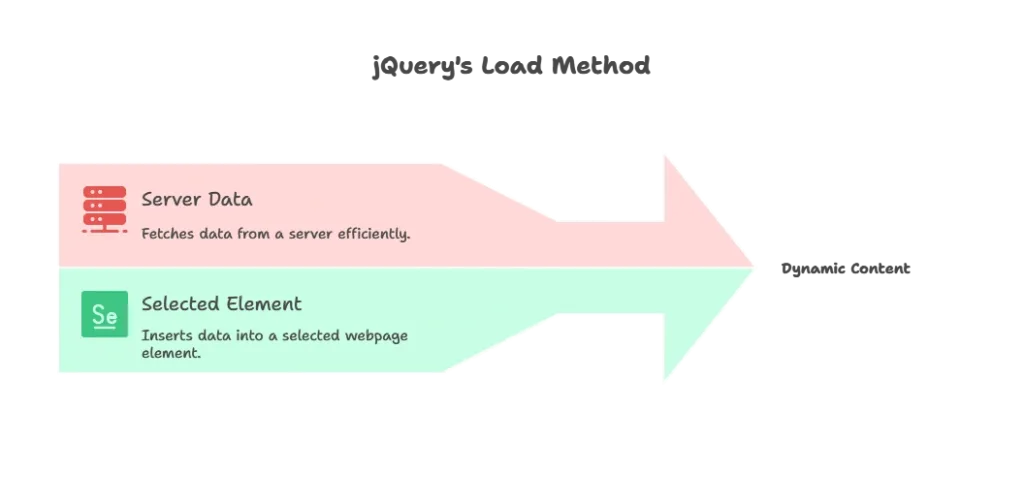
The .load() method is one of jQuery‘s simplest and most commonly used Ajax methods. It allows you to fetch data from a server and insert it directly into a selected element on the webpage. This method is highly useful for creating dynamic content without reloading the entire page.
Basic Syntax
The basic syntax of the .load() method is:
$(selector).load(url, [data], [callback]);
selector: The element where the loaded data will be inserted.url: The URL of the server-side resource to fetch data from.data(optional): Data to be sent to the server (in key-value pairs).callback(optional): A function to execute after the load operation completes.
Basic Usage Examples
Example 1: Loading HTML Content
Suppose you have an HTML file named content.html that you want to load into a div with the ID #content.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Load Method Example</title> <script type="litespeed/javascript" data-src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.6.0.min.js"></script> </head>
<body>
<div id="content">Loading...</div> <script type="litespeed/javascript">$(document).ready(function(){$('#content').load('content.html')})</script> <script data-no-optimize="1">window.lazyLoadOptions=Object.assign({},{threshold:300},window.lazyLoadOptions||{});!function(t,e){"object"==typeof exports&&"undefined"!=typeof module?module.exports=e():"function"==typeof define&&define.amd?define(e):(t="undefined"!=typeof globalThis?globalThis:t||self).LazyLoad=e()}(this,function(){"use strict";function e(){return(e=Object.assign||function(t){for(var e=1;e<arguments.length;e++){var n,a=arguments[e];for(n in a)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(a,n)&&(t[n]=a[n])}return t}).apply(this,arguments)}function o(t){return e({},at,t)}function l(t,e){return t.getAttribute(gt+e)}function c(t){return l(t,vt)}function s(t,e){return function(t,e,n){e=gt+e;null!==n?t.setAttribute(e,n):t.removeAttribute(e)}(t,vt,e)}function i(t){return s(t,null),0}function r(t){return null===c(t)}function u(t){return c(t)===_t}function d(t,e,n,a){t&&(void 0===a?void 0===n?t(e):t(e,n):t(e,n,a))}function f(t,e){et?t.classList.add(e):t.className+=(t.className?" ":"")+e}function _(t,e){et?t.classList.remove(e):t.className=t.className.replace(new RegExp("(^|\\s+)"+e+"(\\s+|$)")," ").replace(/^\s+/,"").replace(/\s+$/,"")}function g(t){return t.llTempImage}function v(t,e){!e||(e=e._observer)&&e.unobserve(t)}function b(t,e){t&&(t.loadingCount+=e)}function p(t,e){t&&(t.toLoadCount=e)}function n(t){for(var e,n=[],a=0;e=t.children[a];a+=1)"SOURCE"===e.tagName&&n.push(e);return n}function h(t,e){(t=t.parentNode)&&"PICTURE"===t.tagName&&n(t).forEach(e)}function a(t,e){n(t).forEach(e)}function m(t){return!!t[lt]}function E(t){return t[lt]}function I(t){return delete t[lt]}function y(e,t){var n;m(e)||(n={},t.forEach(function(t){n[t]=e.getAttribute(t)}),e[lt]=n)}function L(a,t){var o;m(a)&&(o=E(a),t.forEach(function(t){var e,n;e=a,(t=o[n=t])?e.setAttribute(n,t):e.removeAttribute(n)}))}function k(t,e,n){f(t,e.class_loading),s(t,st),n&&(b(n,1),d(e.callback_loading,t,n))}function A(t,e,n){n&&t.setAttribute(e,n)}function O(t,e){A(t,rt,l(t,e.data_sizes)),A(t,it,l(t,e.data_srcset)),A(t,ot,l(t,e.data_src))}function w(t,e,n){var a=l(t,e.data_bg_multi),o=l(t,e.data_bg_multi_hidpi);(a=nt&&o?o:a)&&(t.style.backgroundImage=a,n=n,f(t=t,(e=e).class_applied),s(t,dt),n&&(e.unobserve_completed&&v(t,e),d(e.callback_applied,t,n)))}function x(t,e){!e||0<e.loadingCount||0<e.toLoadCount||d(t.callback_finish,e)}function M(t,e,n){t.addEventListener(e,n),t.llEvLisnrs[e]=n}function N(t){return!!t.llEvLisnrs}function z(t){if(N(t)){var e,n,a=t.llEvLisnrs;for(e in a){var o=a[e];n=e,o=o,t.removeEventListener(n,o)}delete t.llEvLisnrs}}function C(t,e,n){var a;delete t.llTempImage,b(n,-1),(a=n)&&--a.toLoadCount,_(t,e.class_loading),e.unobserve_completed&&v(t,n)}function R(i,r,c){var l=g(i)||i;N(l)||function(t,e,n){N(t)||(t.llEvLisnrs={});var a="VIDEO"===t.tagName?"loadeddata":"load";M(t,a,e),M(t,"error",n)}(l,function(t){var e,n,a,o;n=r,a=c,o=u(e=i),C(e,n,a),f(e,n.class_loaded),s(e,ut),d(n.callback_loaded,e,a),o||x(n,a),z(l)},function(t){var e,n,a,o;n=r,a=c,o=u(e=i),C(e,n,a),f(e,n.class_error),s(e,ft),d(n.callback_error,e,a),o||x(n,a),z(l)})}function T(t,e,n){var a,o,i,r,c;t.llTempImage=document.createElement("IMG"),R(t,e,n),m(c=t)||(c[lt]={backgroundImage:c.style.backgroundImage}),i=n,r=l(a=t,(o=e).data_bg),c=l(a,o.data_bg_hidpi),(r=nt&&c?c:r)&&(a.style.backgroundImage='url("'.concat(r,'")'),g(a).setAttribute(ot,r),k(a,o,i)),w(t,e,n)}function G(t,e,n){var a;R(t,e,n),a=e,e=n,(t=Et[(n=t).tagName])&&(t(n,a),k(n,a,e))}function D(t,e,n){var a;a=t,(-1<It.indexOf(a.tagName)?G:T)(t,e,n)}function S(t,e,n){var a;t.setAttribute("loading","lazy"),R(t,e,n),a=e,(e=Et[(n=t).tagName])&&e(n,a),s(t,_t)}function V(t){t.removeAttribute(ot),t.removeAttribute(it),t.removeAttribute(rt)}function j(t){h(t,function(t){L(t,mt)}),L(t,mt)}function F(t){var e;(e=yt[t.tagName])?e(t):m(e=t)&&(t=E(e),e.style.backgroundImage=t.backgroundImage)}function P(t,e){var n;F(t),n=e,r(e=t)||u(e)||(_(e,n.class_entered),_(e,n.class_exited),_(e,n.class_applied),_(e,n.class_loading),_(e,n.class_loaded),_(e,n.class_error)),i(t),I(t)}function U(t,e,n,a){var o;n.cancel_on_exit&&(c(t)!==st||"IMG"===t.tagName&&(z(t),h(o=t,function(t){V(t)}),V(o),j(t),_(t,n.class_loading),b(a,-1),i(t),d(n.callback_cancel,t,e,a)))}function $(t,e,n,a){var o,i,r=(i=t,0<=bt.indexOf(c(i)));s(t,"entered"),f(t,n.class_entered),_(t,n.class_exited),o=t,i=a,n.unobserve_entered&&v(o,i),d(n.callback_enter,t,e,a),r||D(t,n,a)}function q(t){return t.use_native&&"loading"in HTMLImageElement.prototype}function H(t,o,i){t.forEach(function(t){return(a=t).isIntersecting||0<a.intersectionRatio?$(t.target,t,o,i):(e=t.target,n=t,a=o,t=i,void(r(e)||(f(e,a.class_exited),U(e,n,a,t),d(a.callback_exit,e,n,t))));var e,n,a})}function B(e,n){var t;tt&&!q(e)&&(n._observer=new IntersectionObserver(function(t){H(t,e,n)},{root:(t=e).container===document?null:t.container,rootMargin:t.thresholds||t.threshold+"px"}))}function J(t){return Array.prototype.slice.call(t)}function K(t){return t.container.querySelectorAll(t.elements_selector)}function Q(t){return c(t)===ft}function W(t,e){return e=t||K(e),J(e).filter(r)}function X(e,t){var n;(n=K(e),J(n).filter(Q)).forEach(function(t){_(t,e.class_error),i(t)}),t.update()}function t(t,e){var n,a,t=o(t);this._settings=t,this.loadingCount=0,B(t,this),n=t,a=this,Y&&window.addEventListener("online",function(){X(n,a)}),this.update(e)}var Y="undefined"!=typeof window,Z=Y&&!("onscroll"in window)||"undefined"!=typeof navigator&&/(gle|ing|ro)bot|crawl|spider/i.test(navigator.userAgent),tt=Y&&"IntersectionObserver"in window,et=Y&&"classList"in document.createElement("p"),nt=Y&&1<window.devicePixelRatio,at={elements_selector:".lazy",container:Z||Y?document:null,threshold:300,thresholds:null,data_src:"src",data_srcset:"srcset",data_sizes:"sizes",data_bg:"bg",data_bg_hidpi:"bg-hidpi",data_bg_multi:"bg-multi",data_bg_multi_hidpi:"bg-multi-hidpi",data_poster:"poster",class_applied:"applied",class_loading:"litespeed-loading",class_loaded:"litespeed-loaded",class_error:"error",class_entered:"entered",class_exited:"exited",unobserve_completed:!0,unobserve_entered:!1,cancel_on_exit:!0,callback_enter:null,callback_exit:null,callback_applied:null,callback_loading:null,callback_loaded:null,callback_error:null,callback_finish:null,callback_cancel:null,use_native:!1},ot="src",it="srcset",rt="sizes",ct="poster",lt="llOriginalAttrs",st="loading",ut="loaded",dt="applied",ft="error",_t="native",gt="data-",vt="ll-status",bt=[st,ut,dt,ft],pt=[ot],ht=[ot,ct],mt=[ot,it,rt],Et={IMG:function(t,e){h(t,function(t){y(t,mt),O(t,e)}),y(t,mt),O(t,e)},IFRAME:function(t,e){y(t,pt),A(t,ot,l(t,e.data_src))},VIDEO:function(t,e){a(t,function(t){y(t,pt),A(t,ot,l(t,e.data_src))}),y(t,ht),A(t,ct,l(t,e.data_poster)),A(t,ot,l(t,e.data_src)),t.load()}},It=["IMG","IFRAME","VIDEO"],yt={IMG:j,IFRAME:function(t){L(t,pt)},VIDEO:function(t){a(t,function(t){L(t,pt)}),L(t,ht),t.load()}},Lt=["IMG","IFRAME","VIDEO"];return t.prototype={update:function(t){var e,n,a,o=this._settings,i=W(t,o);{if(p(this,i.length),!Z&&tt)return q(o)?(e=o,n=this,i.forEach(function(t){-1!==Lt.indexOf(t.tagName)&&S(t,e,n)}),void p(n,0)):(t=this._observer,o=i,t.disconnect(),a=t,void o.forEach(function(t){a.observe(t)}));this.loadAll(i)}},destroy:function(){this._observer&&this._observer.disconnect(),K(this._settings).forEach(function(t){I(t)}),delete this._observer,delete this._settings,delete this.loadingCount,delete this.toLoadCount},loadAll:function(t){var e=this,n=this._settings;W(t,n).forEach(function(t){v(t,e),D(t,n,e)})},restoreAll:function(){var e=this._settings;K(e).forEach(function(t){P(t,e)})}},t.load=function(t,e){e=o(e);D(t,e)},t.resetStatus=function(t){i(t)},t}),function(t,e){"use strict";function n(){e.body.classList.add("litespeed_lazyloaded")}function a(){console.log("[LiteSpeed] Start Lazy Load"),o=new LazyLoad(Object.assign({},t.lazyLoadOptions||{},{elements_selector:"[data-lazyloaded]",callback_finish:n})),i=function(){o.update()},t.MutationObserver&&new MutationObserver(i).observe(e.documentElement,{childList:!0,subtree:!0,attributes:!0})}var o,i;t.addEventListener?t.addEventListener("load",a,!1):t.attachEvent("onload",a)}(window,document);</script><script data-no-optimize="1">window.litespeed_ui_events=window.litespeed_ui_events||["mouseover","click","keydown","wheel","touchmove","touchstart"];var urlCreator=window.URL||window.webkitURL;function litespeed_load_delayed_js_force(){console.log("[LiteSpeed] Start Load JS Delayed"),litespeed_ui_events.forEach(e=>{window.removeEventListener(e,litespeed_load_delayed_js_force,{passive:!0})}),document.querySelectorAll("iframe[data-litespeed-src]").forEach(e=>{e.setAttribute("src",e.getAttribute("data-litespeed-src"))}),"loading"==document.readyState?window.addEventListener("DOMContentLoaded",litespeed_load_delayed_js):litespeed_load_delayed_js()}litespeed_ui_events.forEach(e=>{window.addEventListener(e,litespeed_load_delayed_js_force,{passive:!0})});async function litespeed_load_delayed_js(){let t=[];for(var d in document.querySelectorAll('script[type="litespeed/javascript"]').forEach(e=>{t.push(e)}),t)await new Promise(e=>litespeed_load_one(t[d],e));document.dispatchEvent(new Event("DOMContentLiteSpeedLoaded")),window.dispatchEvent(new Event("DOMContentLiteSpeedLoaded"))}function litespeed_load_one(t,e){console.log("[LiteSpeed] Load ",t);var d=document.createElement("script");d.addEventListener("load",e),d.addEventListener("error",e),t.getAttributeNames().forEach(e=>{"type"!=e&&d.setAttribute("data-src"==e?"src":e,t.getAttribute(e))});let a=!(d.type="text/javascript");!d.src&&t.textContent&&(d.src=litespeed_inline2src(t.textContent),a=!0),t.after(d),t.remove(),a&&e()}function litespeed_inline2src(t){try{var d=urlCreator.createObjectURL(new Blob([t.replace(/^(?:<!--)?(.*?)(?:-->)?$/gm,"$1")],{type:"text/javascript"}))}catch(e){d="data:text/javascript;base64,"+btoa(t.replace(/^(?:<!--)?(.*?)(?:-->)?$/gm,"$1"))}return d}</script><script data-no-optimize="1">var litespeed_vary=document.cookie.replace(/(?:(?:^|.*;\s*)_lscache_vary\s*\=\s*([^;]*).*$)|^.*$/,"");litespeed_vary||fetch("/wp-content/plugins/litespeed-cache/guest.vary.php",{method:"POST",cache:"no-cache",redirect:"follow"}).then(e=>e.json()).then(e=>{console.log(e),e.hasOwnProperty("reload")&&"yes"==e.reload&&(sessionStorage.setItem("litespeed_docref",document.referrer),window.location.reload(!0))});</script><script data-optimized="1" type="litespeed/javascript" data-src="https://diginode.in/wp-content/litespeed/js/5ad5da7e80e1ecf64f3d75c5dab7ddb4.js?ver=da7aa"></script></body>
</html>
Explanation:
- The script loads the content of
content.htmlinto the#contentdiv when the document is ready.
Output:
- The content of
content.htmlis loaded into the#contentdiv, replacing the “Loading…” text.
Example 2: Loading Content with Parameters
You can also pass data to the server when making the request. For example, if you want to load user information based on a user ID:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Load Method with Parameters</title> <script type="litespeed/javascript" data-src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.6.0.min.js"></script> </head>
<body>
<div id="user-info">Loading user information...</div> <script type="litespeed/javascript">$(document).ready(function(){var userId=123;$('#user-info').load('user.php',{id:userId})})</script> <script data-no-optimize="1">window.lazyLoadOptions=Object.assign({},{threshold:300},window.lazyLoadOptions||{});!function(t,e){"object"==typeof exports&&"undefined"!=typeof module?module.exports=e():"function"==typeof define&&define.amd?define(e):(t="undefined"!=typeof globalThis?globalThis:t||self).LazyLoad=e()}(this,function(){"use strict";function e(){return(e=Object.assign||function(t){for(var e=1;e<arguments.length;e++){var n,a=arguments[e];for(n in a)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(a,n)&&(t[n]=a[n])}return t}).apply(this,arguments)}function o(t){return e({},at,t)}function l(t,e){return t.getAttribute(gt+e)}function c(t){return l(t,vt)}function s(t,e){return function(t,e,n){e=gt+e;null!==n?t.setAttribute(e,n):t.removeAttribute(e)}(t,vt,e)}function i(t){return s(t,null),0}function r(t){return null===c(t)}function u(t){return c(t)===_t}function d(t,e,n,a){t&&(void 0===a?void 0===n?t(e):t(e,n):t(e,n,a))}function f(t,e){et?t.classList.add(e):t.className+=(t.className?" ":"")+e}function _(t,e){et?t.classList.remove(e):t.className=t.className.replace(new RegExp("(^|\\s+)"+e+"(\\s+|$)")," ").replace(/^\s+/,"").replace(/\s+$/,"")}function g(t){return t.llTempImage}function v(t,e){!e||(e=e._observer)&&e.unobserve(t)}function b(t,e){t&&(t.loadingCount+=e)}function p(t,e){t&&(t.toLoadCount=e)}function n(t){for(var e,n=[],a=0;e=t.children[a];a+=1)"SOURCE"===e.tagName&&n.push(e);return n}function h(t,e){(t=t.parentNode)&&"PICTURE"===t.tagName&&n(t).forEach(e)}function a(t,e){n(t).forEach(e)}function m(t){return!!t[lt]}function E(t){return t[lt]}function I(t){return delete t[lt]}function y(e,t){var n;m(e)||(n={},t.forEach(function(t){n[t]=e.getAttribute(t)}),e[lt]=n)}function L(a,t){var o;m(a)&&(o=E(a),t.forEach(function(t){var e,n;e=a,(t=o[n=t])?e.setAttribute(n,t):e.removeAttribute(n)}))}function k(t,e,n){f(t,e.class_loading),s(t,st),n&&(b(n,1),d(e.callback_loading,t,n))}function A(t,e,n){n&&t.setAttribute(e,n)}function O(t,e){A(t,rt,l(t,e.data_sizes)),A(t,it,l(t,e.data_srcset)),A(t,ot,l(t,e.data_src))}function w(t,e,n){var a=l(t,e.data_bg_multi),o=l(t,e.data_bg_multi_hidpi);(a=nt&&o?o:a)&&(t.style.backgroundImage=a,n=n,f(t=t,(e=e).class_applied),s(t,dt),n&&(e.unobserve_completed&&v(t,e),d(e.callback_applied,t,n)))}function x(t,e){!e||0<e.loadingCount||0<e.toLoadCount||d(t.callback_finish,e)}function M(t,e,n){t.addEventListener(e,n),t.llEvLisnrs[e]=n}function N(t){return!!t.llEvLisnrs}function z(t){if(N(t)){var e,n,a=t.llEvLisnrs;for(e in a){var o=a[e];n=e,o=o,t.removeEventListener(n,o)}delete t.llEvLisnrs}}function C(t,e,n){var a;delete t.llTempImage,b(n,-1),(a=n)&&--a.toLoadCount,_(t,e.class_loading),e.unobserve_completed&&v(t,n)}function R(i,r,c){var l=g(i)||i;N(l)||function(t,e,n){N(t)||(t.llEvLisnrs={});var a="VIDEO"===t.tagName?"loadeddata":"load";M(t,a,e),M(t,"error",n)}(l,function(t){var e,n,a,o;n=r,a=c,o=u(e=i),C(e,n,a),f(e,n.class_loaded),s(e,ut),d(n.callback_loaded,e,a),o||x(n,a),z(l)},function(t){var e,n,a,o;n=r,a=c,o=u(e=i),C(e,n,a),f(e,n.class_error),s(e,ft),d(n.callback_error,e,a),o||x(n,a),z(l)})}function T(t,e,n){var a,o,i,r,c;t.llTempImage=document.createElement("IMG"),R(t,e,n),m(c=t)||(c[lt]={backgroundImage:c.style.backgroundImage}),i=n,r=l(a=t,(o=e).data_bg),c=l(a,o.data_bg_hidpi),(r=nt&&c?c:r)&&(a.style.backgroundImage='url("'.concat(r,'")'),g(a).setAttribute(ot,r),k(a,o,i)),w(t,e,n)}function G(t,e,n){var a;R(t,e,n),a=e,e=n,(t=Et[(n=t).tagName])&&(t(n,a),k(n,a,e))}function D(t,e,n){var a;a=t,(-1<It.indexOf(a.tagName)?G:T)(t,e,n)}function S(t,e,n){var a;t.setAttribute("loading","lazy"),R(t,e,n),a=e,(e=Et[(n=t).tagName])&&e(n,a),s(t,_t)}function V(t){t.removeAttribute(ot),t.removeAttribute(it),t.removeAttribute(rt)}function j(t){h(t,function(t){L(t,mt)}),L(t,mt)}function F(t){var e;(e=yt[t.tagName])?e(t):m(e=t)&&(t=E(e),e.style.backgroundImage=t.backgroundImage)}function P(t,e){var n;F(t),n=e,r(e=t)||u(e)||(_(e,n.class_entered),_(e,n.class_exited),_(e,n.class_applied),_(e,n.class_loading),_(e,n.class_loaded),_(e,n.class_error)),i(t),I(t)}function U(t,e,n,a){var o;n.cancel_on_exit&&(c(t)!==st||"IMG"===t.tagName&&(z(t),h(o=t,function(t){V(t)}),V(o),j(t),_(t,n.class_loading),b(a,-1),i(t),d(n.callback_cancel,t,e,a)))}function $(t,e,n,a){var o,i,r=(i=t,0<=bt.indexOf(c(i)));s(t,"entered"),f(t,n.class_entered),_(t,n.class_exited),o=t,i=a,n.unobserve_entered&&v(o,i),d(n.callback_enter,t,e,a),r||D(t,n,a)}function q(t){return t.use_native&&"loading"in HTMLImageElement.prototype}function H(t,o,i){t.forEach(function(t){return(a=t).isIntersecting||0<a.intersectionRatio?$(t.target,t,o,i):(e=t.target,n=t,a=o,t=i,void(r(e)||(f(e,a.class_exited),U(e,n,a,t),d(a.callback_exit,e,n,t))));var e,n,a})}function B(e,n){var t;tt&&!q(e)&&(n._observer=new IntersectionObserver(function(t){H(t,e,n)},{root:(t=e).container===document?null:t.container,rootMargin:t.thresholds||t.threshold+"px"}))}function J(t){return Array.prototype.slice.call(t)}function K(t){return t.container.querySelectorAll(t.elements_selector)}function Q(t){return c(t)===ft}function W(t,e){return e=t||K(e),J(e).filter(r)}function X(e,t){var n;(n=K(e),J(n).filter(Q)).forEach(function(t){_(t,e.class_error),i(t)}),t.update()}function t(t,e){var n,a,t=o(t);this._settings=t,this.loadingCount=0,B(t,this),n=t,a=this,Y&&window.addEventListener("online",function(){X(n,a)}),this.update(e)}var Y="undefined"!=typeof window,Z=Y&&!("onscroll"in window)||"undefined"!=typeof navigator&&/(gle|ing|ro)bot|crawl|spider/i.test(navigator.userAgent),tt=Y&&"IntersectionObserver"in window,et=Y&&"classList"in document.createElement("p"),nt=Y&&1<window.devicePixelRatio,at={elements_selector:".lazy",container:Z||Y?document:null,threshold:300,thresholds:null,data_src:"src",data_srcset:"srcset",data_sizes:"sizes",data_bg:"bg",data_bg_hidpi:"bg-hidpi",data_bg_multi:"bg-multi",data_bg_multi_hidpi:"bg-multi-hidpi",data_poster:"poster",class_applied:"applied",class_loading:"litespeed-loading",class_loaded:"litespeed-loaded",class_error:"error",class_entered:"entered",class_exited:"exited",unobserve_completed:!0,unobserve_entered:!1,cancel_on_exit:!0,callback_enter:null,callback_exit:null,callback_applied:null,callback_loading:null,callback_loaded:null,callback_error:null,callback_finish:null,callback_cancel:null,use_native:!1},ot="src",it="srcset",rt="sizes",ct="poster",lt="llOriginalAttrs",st="loading",ut="loaded",dt="applied",ft="error",_t="native",gt="data-",vt="ll-status",bt=[st,ut,dt,ft],pt=[ot],ht=[ot,ct],mt=[ot,it,rt],Et={IMG:function(t,e){h(t,function(t){y(t,mt),O(t,e)}),y(t,mt),O(t,e)},IFRAME:function(t,e){y(t,pt),A(t,ot,l(t,e.data_src))},VIDEO:function(t,e){a(t,function(t){y(t,pt),A(t,ot,l(t,e.data_src))}),y(t,ht),A(t,ct,l(t,e.data_poster)),A(t,ot,l(t,e.data_src)),t.load()}},It=["IMG","IFRAME","VIDEO"],yt={IMG:j,IFRAME:function(t){L(t,pt)},VIDEO:function(t){a(t,function(t){L(t,pt)}),L(t,ht),t.load()}},Lt=["IMG","IFRAME","VIDEO"];return t.prototype={update:function(t){var e,n,a,o=this._settings,i=W(t,o);{if(p(this,i.length),!Z&&tt)return q(o)?(e=o,n=this,i.forEach(function(t){-1!==Lt.indexOf(t.tagName)&&S(t,e,n)}),void p(n,0)):(t=this._observer,o=i,t.disconnect(),a=t,void o.forEach(function(t){a.observe(t)}));this.loadAll(i)}},destroy:function(){this._observer&&this._observer.disconnect(),K(this._settings).forEach(function(t){I(t)}),delete this._observer,delete this._settings,delete this.loadingCount,delete this.toLoadCount},loadAll:function(t){var e=this,n=this._settings;W(t,n).forEach(function(t){v(t,e),D(t,n,e)})},restoreAll:function(){var e=this._settings;K(e).forEach(function(t){P(t,e)})}},t.load=function(t,e){e=o(e);D(t,e)},t.resetStatus=function(t){i(t)},t}),function(t,e){"use strict";function n(){e.body.classList.add("litespeed_lazyloaded")}function a(){console.log("[LiteSpeed] Start Lazy Load"),o=new LazyLoad(Object.assign({},t.lazyLoadOptions||{},{elements_selector:"[data-lazyloaded]",callback_finish:n})),i=function(){o.update()},t.MutationObserver&&new MutationObserver(i).observe(e.documentElement,{childList:!0,subtree:!0,attributes:!0})}var o,i;t.addEventListener?t.addEventListener("load",a,!1):t.attachEvent("onload",a)}(window,document);</script><script data-no-optimize="1">window.litespeed_ui_events=window.litespeed_ui_events||["mouseover","click","keydown","wheel","touchmove","touchstart"];var urlCreator=window.URL||window.webkitURL;function litespeed_load_delayed_js_force(){console.log("[LiteSpeed] Start Load JS Delayed"),litespeed_ui_events.forEach(e=>{window.removeEventListener(e,litespeed_load_delayed_js_force,{passive:!0})}),document.querySelectorAll("iframe[data-litespeed-src]").forEach(e=>{e.setAttribute("src",e.getAttribute("data-litespeed-src"))}),"loading"==document.readyState?window.addEventListener("DOMContentLoaded",litespeed_load_delayed_js):litespeed_load_delayed_js()}litespeed_ui_events.forEach(e=>{window.addEventListener(e,litespeed_load_delayed_js_force,{passive:!0})});async function litespeed_load_delayed_js(){let t=[];for(var d in document.querySelectorAll('script[type="litespeed/javascript"]').forEach(e=>{t.push(e)}),t)await new Promise(e=>litespeed_load_one(t[d],e));document.dispatchEvent(new Event("DOMContentLiteSpeedLoaded")),window.dispatchEvent(new Event("DOMContentLiteSpeedLoaded"))}function litespeed_load_one(t,e){console.log("[LiteSpeed] Load ",t);var d=document.createElement("script");d.addEventListener("load",e),d.addEventListener("error",e),t.getAttributeNames().forEach(e=>{"type"!=e&&d.setAttribute("data-src"==e?"src":e,t.getAttribute(e))});let a=!(d.type="text/javascript");!d.src&&t.textContent&&(d.src=litespeed_inline2src(t.textContent),a=!0),t.after(d),t.remove(),a&&e()}function litespeed_inline2src(t){try{var d=urlCreator.createObjectURL(new Blob([t.replace(/^(?:<!--)?(.*?)(?:-->)?$/gm,"$1")],{type:"text/javascript"}))}catch(e){d="data:text/javascript;base64,"+btoa(t.replace(/^(?:<!--)?(.*?)(?:-->)?$/gm,"$1"))}return d}</script><script data-optimized="1" type="litespeed/javascript" data-src="https://diginode.in/wp-content/litespeed/js/5ad5da7e80e1ecf64f3d75c5dab7ddb4.js?ver=da7aa"></script></body>
</html>
Explanation:
- The script sends a request to
user.php, passing{ id: 123 }as parameters. The response is loaded into the#user-infodiv.
Output:
- The user information returned by
user.phpfor the user with ID 123 is loaded into the#user-infodiv.
Advanced Techniques
Using Callback Functions
The .load() method can accept a callback function that executes after the content is loaded. This allows for additional processing or error handling.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Load Method with Callback</title> <script type="litespeed/javascript" data-src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.6.0.min.js"></script> </head>
<body>
<div id="content">Loading content...</div> <script type="litespeed/javascript">$(document).ready(function(){$('#content').load('content.html',function(response,status,xhr){if(status=="success"){console.log('Content loaded successfully!')}else{console.error('Error loading content:',status,xhr.statusText)}})})</script> <script data-no-optimize="1">window.lazyLoadOptions=Object.assign({},{threshold:300},window.lazyLoadOptions||{});!function(t,e){"object"==typeof exports&&"undefined"!=typeof module?module.exports=e():"function"==typeof define&&define.amd?define(e):(t="undefined"!=typeof globalThis?globalThis:t||self).LazyLoad=e()}(this,function(){"use strict";function e(){return(e=Object.assign||function(t){for(var e=1;e<arguments.length;e++){var n,a=arguments[e];for(n in a)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(a,n)&&(t[n]=a[n])}return t}).apply(this,arguments)}function o(t){return e({},at,t)}function l(t,e){return t.getAttribute(gt+e)}function c(t){return l(t,vt)}function s(t,e){return function(t,e,n){e=gt+e;null!==n?t.setAttribute(e,n):t.removeAttribute(e)}(t,vt,e)}function i(t){return s(t,null),0}function r(t){return null===c(t)}function u(t){return c(t)===_t}function d(t,e,n,a){t&&(void 0===a?void 0===n?t(e):t(e,n):t(e,n,a))}function f(t,e){et?t.classList.add(e):t.className+=(t.className?" ":"")+e}function _(t,e){et?t.classList.remove(e):t.className=t.className.replace(new RegExp("(^|\\s+)"+e+"(\\s+|$)")," ").replace(/^\s+/,"").replace(/\s+$/,"")}function g(t){return t.llTempImage}function v(t,e){!e||(e=e._observer)&&e.unobserve(t)}function b(t,e){t&&(t.loadingCount+=e)}function p(t,e){t&&(t.toLoadCount=e)}function n(t){for(var e,n=[],a=0;e=t.children[a];a+=1)"SOURCE"===e.tagName&&n.push(e);return n}function h(t,e){(t=t.parentNode)&&"PICTURE"===t.tagName&&n(t).forEach(e)}function a(t,e){n(t).forEach(e)}function m(t){return!!t[lt]}function E(t){return t[lt]}function I(t){return delete t[lt]}function y(e,t){var n;m(e)||(n={},t.forEach(function(t){n[t]=e.getAttribute(t)}),e[lt]=n)}function L(a,t){var o;m(a)&&(o=E(a),t.forEach(function(t){var e,n;e=a,(t=o[n=t])?e.setAttribute(n,t):e.removeAttribute(n)}))}function k(t,e,n){f(t,e.class_loading),s(t,st),n&&(b(n,1),d(e.callback_loading,t,n))}function A(t,e,n){n&&t.setAttribute(e,n)}function O(t,e){A(t,rt,l(t,e.data_sizes)),A(t,it,l(t,e.data_srcset)),A(t,ot,l(t,e.data_src))}function w(t,e,n){var a=l(t,e.data_bg_multi),o=l(t,e.data_bg_multi_hidpi);(a=nt&&o?o:a)&&(t.style.backgroundImage=a,n=n,f(t=t,(e=e).class_applied),s(t,dt),n&&(e.unobserve_completed&&v(t,e),d(e.callback_applied,t,n)))}function x(t,e){!e||0<e.loadingCount||0<e.toLoadCount||d(t.callback_finish,e)}function M(t,e,n){t.addEventListener(e,n),t.llEvLisnrs[e]=n}function N(t){return!!t.llEvLisnrs}function z(t){if(N(t)){var e,n,a=t.llEvLisnrs;for(e in a){var o=a[e];n=e,o=o,t.removeEventListener(n,o)}delete t.llEvLisnrs}}function C(t,e,n){var a;delete t.llTempImage,b(n,-1),(a=n)&&--a.toLoadCount,_(t,e.class_loading),e.unobserve_completed&&v(t,n)}function R(i,r,c){var l=g(i)||i;N(l)||function(t,e,n){N(t)||(t.llEvLisnrs={});var a="VIDEO"===t.tagName?"loadeddata":"load";M(t,a,e),M(t,"error",n)}(l,function(t){var e,n,a,o;n=r,a=c,o=u(e=i),C(e,n,a),f(e,n.class_loaded),s(e,ut),d(n.callback_loaded,e,a),o||x(n,a),z(l)},function(t){var e,n,a,o;n=r,a=c,o=u(e=i),C(e,n,a),f(e,n.class_error),s(e,ft),d(n.callback_error,e,a),o||x(n,a),z(l)})}function T(t,e,n){var a,o,i,r,c;t.llTempImage=document.createElement("IMG"),R(t,e,n),m(c=t)||(c[lt]={backgroundImage:c.style.backgroundImage}),i=n,r=l(a=t,(o=e).data_bg),c=l(a,o.data_bg_hidpi),(r=nt&&c?c:r)&&(a.style.backgroundImage='url("'.concat(r,'")'),g(a).setAttribute(ot,r),k(a,o,i)),w(t,e,n)}function G(t,e,n){var a;R(t,e,n),a=e,e=n,(t=Et[(n=t).tagName])&&(t(n,a),k(n,a,e))}function D(t,e,n){var a;a=t,(-1<It.indexOf(a.tagName)?G:T)(t,e,n)}function S(t,e,n){var a;t.setAttribute("loading","lazy"),R(t,e,n),a=e,(e=Et[(n=t).tagName])&&e(n,a),s(t,_t)}function V(t){t.removeAttribute(ot),t.removeAttribute(it),t.removeAttribute(rt)}function j(t){h(t,function(t){L(t,mt)}),L(t,mt)}function F(t){var e;(e=yt[t.tagName])?e(t):m(e=t)&&(t=E(e),e.style.backgroundImage=t.backgroundImage)}function P(t,e){var n;F(t),n=e,r(e=t)||u(e)||(_(e,n.class_entered),_(e,n.class_exited),_(e,n.class_applied),_(e,n.class_loading),_(e,n.class_loaded),_(e,n.class_error)),i(t),I(t)}function U(t,e,n,a){var o;n.cancel_on_exit&&(c(t)!==st||"IMG"===t.tagName&&(z(t),h(o=t,function(t){V(t)}),V(o),j(t),_(t,n.class_loading),b(a,-1),i(t),d(n.callback_cancel,t,e,a)))}function $(t,e,n,a){var o,i,r=(i=t,0<=bt.indexOf(c(i)));s(t,"entered"),f(t,n.class_entered),_(t,n.class_exited),o=t,i=a,n.unobserve_entered&&v(o,i),d(n.callback_enter,t,e,a),r||D(t,n,a)}function q(t){return t.use_native&&"loading"in HTMLImageElement.prototype}function H(t,o,i){t.forEach(function(t){return(a=t).isIntersecting||0<a.intersectionRatio?$(t.target,t,o,i):(e=t.target,n=t,a=o,t=i,void(r(e)||(f(e,a.class_exited),U(e,n,a,t),d(a.callback_exit,e,n,t))));var e,n,a})}function B(e,n){var t;tt&&!q(e)&&(n._observer=new IntersectionObserver(function(t){H(t,e,n)},{root:(t=e).container===document?null:t.container,rootMargin:t.thresholds||t.threshold+"px"}))}function J(t){return Array.prototype.slice.call(t)}function K(t){return t.container.querySelectorAll(t.elements_selector)}function Q(t){return c(t)===ft}function W(t,e){return e=t||K(e),J(e).filter(r)}function X(e,t){var n;(n=K(e),J(n).filter(Q)).forEach(function(t){_(t,e.class_error),i(t)}),t.update()}function t(t,e){var n,a,t=o(t);this._settings=t,this.loadingCount=0,B(t,this),n=t,a=this,Y&&window.addEventListener("online",function(){X(n,a)}),this.update(e)}var Y="undefined"!=typeof window,Z=Y&&!("onscroll"in window)||"undefined"!=typeof navigator&&/(gle|ing|ro)bot|crawl|spider/i.test(navigator.userAgent),tt=Y&&"IntersectionObserver"in window,et=Y&&"classList"in document.createElement("p"),nt=Y&&1<window.devicePixelRatio,at={elements_selector:".lazy",container:Z||Y?document:null,threshold:300,thresholds:null,data_src:"src",data_srcset:"srcset",data_sizes:"sizes",data_bg:"bg",data_bg_hidpi:"bg-hidpi",data_bg_multi:"bg-multi",data_bg_multi_hidpi:"bg-multi-hidpi",data_poster:"poster",class_applied:"applied",class_loading:"litespeed-loading",class_loaded:"litespeed-loaded",class_error:"error",class_entered:"entered",class_exited:"exited",unobserve_completed:!0,unobserve_entered:!1,cancel_on_exit:!0,callback_enter:null,callback_exit:null,callback_applied:null,callback_loading:null,callback_loaded:null,callback_error:null,callback_finish:null,callback_cancel:null,use_native:!1},ot="src",it="srcset",rt="sizes",ct="poster",lt="llOriginalAttrs",st="loading",ut="loaded",dt="applied",ft="error",_t="native",gt="data-",vt="ll-status",bt=[st,ut,dt,ft],pt=[ot],ht=[ot,ct],mt=[ot,it,rt],Et={IMG:function(t,e){h(t,function(t){y(t,mt),O(t,e)}),y(t,mt),O(t,e)},IFRAME:function(t,e){y(t,pt),A(t,ot,l(t,e.data_src))},VIDEO:function(t,e){a(t,function(t){y(t,pt),A(t,ot,l(t,e.data_src))}),y(t,ht),A(t,ct,l(t,e.data_poster)),A(t,ot,l(t,e.data_src)),t.load()}},It=["IMG","IFRAME","VIDEO"],yt={IMG:j,IFRAME:function(t){L(t,pt)},VIDEO:function(t){a(t,function(t){L(t,pt)}),L(t,ht),t.load()}},Lt=["IMG","IFRAME","VIDEO"];return t.prototype={update:function(t){var e,n,a,o=this._settings,i=W(t,o);{if(p(this,i.length),!Z&&tt)return q(o)?(e=o,n=this,i.forEach(function(t){-1!==Lt.indexOf(t.tagName)&&S(t,e,n)}),void p(n,0)):(t=this._observer,o=i,t.disconnect(),a=t,void o.forEach(function(t){a.observe(t)}));this.loadAll(i)}},destroy:function(){this._observer&&this._observer.disconnect(),K(this._settings).forEach(function(t){I(t)}),delete this._observer,delete this._settings,delete this.loadingCount,delete this.toLoadCount},loadAll:function(t){var e=this,n=this._settings;W(t,n).forEach(function(t){v(t,e),D(t,n,e)})},restoreAll:function(){var e=this._settings;K(e).forEach(function(t){P(t,e)})}},t.load=function(t,e){e=o(e);D(t,e)},t.resetStatus=function(t){i(t)},t}),function(t,e){"use strict";function n(){e.body.classList.add("litespeed_lazyloaded")}function a(){console.log("[LiteSpeed] Start Lazy Load"),o=new LazyLoad(Object.assign({},t.lazyLoadOptions||{},{elements_selector:"[data-lazyloaded]",callback_finish:n})),i=function(){o.update()},t.MutationObserver&&new MutationObserver(i).observe(e.documentElement,{childList:!0,subtree:!0,attributes:!0})}var o,i;t.addEventListener?t.addEventListener("load",a,!1):t.attachEvent("onload",a)}(window,document);</script><script data-no-optimize="1">window.litespeed_ui_events=window.litespeed_ui_events||["mouseover","click","keydown","wheel","touchmove","touchstart"];var urlCreator=window.URL||window.webkitURL;function litespeed_load_delayed_js_force(){console.log("[LiteSpeed] Start Load JS Delayed"),litespeed_ui_events.forEach(e=>{window.removeEventListener(e,litespeed_load_delayed_js_force,{passive:!0})}),document.querySelectorAll("iframe[data-litespeed-src]").forEach(e=>{e.setAttribute("src",e.getAttribute("data-litespeed-src"))}),"loading"==document.readyState?window.addEventListener("DOMContentLoaded",litespeed_load_delayed_js):litespeed_load_delayed_js()}litespeed_ui_events.forEach(e=>{window.addEventListener(e,litespeed_load_delayed_js_force,{passive:!0})});async function litespeed_load_delayed_js(){let t=[];for(var d in document.querySelectorAll('script[type="litespeed/javascript"]').forEach(e=>{t.push(e)}),t)await new Promise(e=>litespeed_load_one(t[d],e));document.dispatchEvent(new Event("DOMContentLiteSpeedLoaded")),window.dispatchEvent(new Event("DOMContentLiteSpeedLoaded"))}function litespeed_load_one(t,e){console.log("[LiteSpeed] Load ",t);var d=document.createElement("script");d.addEventListener("load",e),d.addEventListener("error",e),t.getAttributeNames().forEach(e=>{"type"!=e&&d.setAttribute("data-src"==e?"src":e,t.getAttribute(e))});let a=!(d.type="text/javascript");!d.src&&t.textContent&&(d.src=litespeed_inline2src(t.textContent),a=!0),t.after(d),t.remove(),a&&e()}function litespeed_inline2src(t){try{var d=urlCreator.createObjectURL(new Blob([t.replace(/^(?:<!--)?(.*?)(?:-->)?$/gm,"$1")],{type:"text/javascript"}))}catch(e){d="data:text/javascript;base64,"+btoa(t.replace(/^(?:<!--)?(.*?)(?:-->)?$/gm,"$1"))}return d}</script><script data-optimized="1" type="litespeed/javascript" data-src="https://diginode.in/wp-content/litespeed/js/5ad5da7e80e1ecf64f3d75c5dab7ddb4.js?ver=da7aa"></script></body>
</html>
Explanation:
- The script loads
content.htmlinto the#contentdiv. The callback function logs a success message or an error message depending on the status.
Output:
- The content of
content.htmlis loaded into the#contentdiv. The console displays “Content loaded successfully!” or an error message if the load fails.
Loading Specific Elements
You can load specific elements from a remote HTML file by using jQuery selectors within the .load() method.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Load Specific Elements</title> <script type="litespeed/javascript" data-src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.6.0.min.js"></script> </head>
<body>
<div id="content">Loading specific content...</div> <script type="litespeed/javascript">$(document).ready(function(){$('#content').load('page.html #specific-element')})</script> <script data-no-optimize="1">window.lazyLoadOptions=Object.assign({},{threshold:300},window.lazyLoadOptions||{});!function(t,e){"object"==typeof exports&&"undefined"!=typeof module?module.exports=e():"function"==typeof define&&define.amd?define(e):(t="undefined"!=typeof globalThis?globalThis:t||self).LazyLoad=e()}(this,function(){"use strict";function e(){return(e=Object.assign||function(t){for(var e=1;e<arguments.length;e++){var n,a=arguments[e];for(n in a)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(a,n)&&(t[n]=a[n])}return t}).apply(this,arguments)}function o(t){return e({},at,t)}function l(t,e){return t.getAttribute(gt+e)}function c(t){return l(t,vt)}function s(t,e){return function(t,e,n){e=gt+e;null!==n?t.setAttribute(e,n):t.removeAttribute(e)}(t,vt,e)}function i(t){return s(t,null),0}function r(t){return null===c(t)}function u(t){return c(t)===_t}function d(t,e,n,a){t&&(void 0===a?void 0===n?t(e):t(e,n):t(e,n,a))}function f(t,e){et?t.classList.add(e):t.className+=(t.className?" ":"")+e}function _(t,e){et?t.classList.remove(e):t.className=t.className.replace(new RegExp("(^|\\s+)"+e+"(\\s+|$)")," ").replace(/^\s+/,"").replace(/\s+$/,"")}function g(t){return t.llTempImage}function v(t,e){!e||(e=e._observer)&&e.unobserve(t)}function b(t,e){t&&(t.loadingCount+=e)}function p(t,e){t&&(t.toLoadCount=e)}function n(t){for(var e,n=[],a=0;e=t.children[a];a+=1)"SOURCE"===e.tagName&&n.push(e);return n}function h(t,e){(t=t.parentNode)&&"PICTURE"===t.tagName&&n(t).forEach(e)}function a(t,e){n(t).forEach(e)}function m(t){return!!t[lt]}function E(t){return t[lt]}function I(t){return delete t[lt]}function y(e,t){var n;m(e)||(n={},t.forEach(function(t){n[t]=e.getAttribute(t)}),e[lt]=n)}function L(a,t){var o;m(a)&&(o=E(a),t.forEach(function(t){var e,n;e=a,(t=o[n=t])?e.setAttribute(n,t):e.removeAttribute(n)}))}function k(t,e,n){f(t,e.class_loading),s(t,st),n&&(b(n,1),d(e.callback_loading,t,n))}function A(t,e,n){n&&t.setAttribute(e,n)}function O(t,e){A(t,rt,l(t,e.data_sizes)),A(t,it,l(t,e.data_srcset)),A(t,ot,l(t,e.data_src))}function w(t,e,n){var a=l(t,e.data_bg_multi),o=l(t,e.data_bg_multi_hidpi);(a=nt&&o?o:a)&&(t.style.backgroundImage=a,n=n,f(t=t,(e=e).class_applied),s(t,dt),n&&(e.unobserve_completed&&v(t,e),d(e.callback_applied,t,n)))}function x(t,e){!e||0<e.loadingCount||0<e.toLoadCount||d(t.callback_finish,e)}function M(t,e,n){t.addEventListener(e,n),t.llEvLisnrs[e]=n}function N(t){return!!t.llEvLisnrs}function z(t){if(N(t)){var e,n,a=t.llEvLisnrs;for(e in a){var o=a[e];n=e,o=o,t.removeEventListener(n,o)}delete t.llEvLisnrs}}function C(t,e,n){var a;delete t.llTempImage,b(n,-1),(a=n)&&--a.toLoadCount,_(t,e.class_loading),e.unobserve_completed&&v(t,n)}function R(i,r,c){var l=g(i)||i;N(l)||function(t,e,n){N(t)||(t.llEvLisnrs={});var a="VIDEO"===t.tagName?"loadeddata":"load";M(t,a,e),M(t,"error",n)}(l,function(t){var e,n,a,o;n=r,a=c,o=u(e=i),C(e,n,a),f(e,n.class_loaded),s(e,ut),d(n.callback_loaded,e,a),o||x(n,a),z(l)},function(t){var e,n,a,o;n=r,a=c,o=u(e=i),C(e,n,a),f(e,n.class_error),s(e,ft),d(n.callback_error,e,a),o||x(n,a),z(l)})}function T(t,e,n){var a,o,i,r,c;t.llTempImage=document.createElement("IMG"),R(t,e,n),m(c=t)||(c[lt]={backgroundImage:c.style.backgroundImage}),i=n,r=l(a=t,(o=e).data_bg),c=l(a,o.data_bg_hidpi),(r=nt&&c?c:r)&&(a.style.backgroundImage='url("'.concat(r,'")'),g(a).setAttribute(ot,r),k(a,o,i)),w(t,e,n)}function G(t,e,n){var a;R(t,e,n),a=e,e=n,(t=Et[(n=t).tagName])&&(t(n,a),k(n,a,e))}function D(t,e,n){var a;a=t,(-1<It.indexOf(a.tagName)?G:T)(t,e,n)}function S(t,e,n){var a;t.setAttribute("loading","lazy"),R(t,e,n),a=e,(e=Et[(n=t).tagName])&&e(n,a),s(t,_t)}function V(t){t.removeAttribute(ot),t.removeAttribute(it),t.removeAttribute(rt)}function j(t){h(t,function(t){L(t,mt)}),L(t,mt)}function F(t){var e;(e=yt[t.tagName])?e(t):m(e=t)&&(t=E(e),e.style.backgroundImage=t.backgroundImage)}function P(t,e){var n;F(t),n=e,r(e=t)||u(e)||(_(e,n.class_entered),_(e,n.class_exited),_(e,n.class_applied),_(e,n.class_loading),_(e,n.class_loaded),_(e,n.class_error)),i(t),I(t)}function U(t,e,n,a){var o;n.cancel_on_exit&&(c(t)!==st||"IMG"===t.tagName&&(z(t),h(o=t,function(t){V(t)}),V(o),j(t),_(t,n.class_loading),b(a,-1),i(t),d(n.callback_cancel,t,e,a)))}function $(t,e,n,a){var o,i,r=(i=t,0<=bt.indexOf(c(i)));s(t,"entered"),f(t,n.class_entered),_(t,n.class_exited),o=t,i=a,n.unobserve_entered&&v(o,i),d(n.callback_enter,t,e,a),r||D(t,n,a)}function q(t){return t.use_native&&"loading"in HTMLImageElement.prototype}function H(t,o,i){t.forEach(function(t){return(a=t).isIntersecting||0<a.intersectionRatio?$(t.target,t,o,i):(e=t.target,n=t,a=o,t=i,void(r(e)||(f(e,a.class_exited),U(e,n,a,t),d(a.callback_exit,e,n,t))));var e,n,a})}function B(e,n){var t;tt&&!q(e)&&(n._observer=new IntersectionObserver(function(t){H(t,e,n)},{root:(t=e).container===document?null:t.container,rootMargin:t.thresholds||t.threshold+"px"}))}function J(t){return Array.prototype.slice.call(t)}function K(t){return t.container.querySelectorAll(t.elements_selector)}function Q(t){return c(t)===ft}function W(t,e){return e=t||K(e),J(e).filter(r)}function X(e,t){var n;(n=K(e),J(n).filter(Q)).forEach(function(t){_(t,e.class_error),i(t)}),t.update()}function t(t,e){var n,a,t=o(t);this._settings=t,this.loadingCount=0,B(t,this),n=t,a=this,Y&&window.addEventListener("online",function(){X(n,a)}),this.update(e)}var Y="undefined"!=typeof window,Z=Y&&!("onscroll"in window)||"undefined"!=typeof navigator&&/(gle|ing|ro)bot|crawl|spider/i.test(navigator.userAgent),tt=Y&&"IntersectionObserver"in window,et=Y&&"classList"in document.createElement("p"),nt=Y&&1<window.devicePixelRatio,at={elements_selector:".lazy",container:Z||Y?document:null,threshold:300,thresholds:null,data_src:"src",data_srcset:"srcset",data_sizes:"sizes",data_bg:"bg",data_bg_hidpi:"bg-hidpi",data_bg_multi:"bg-multi",data_bg_multi_hidpi:"bg-multi-hidpi",data_poster:"poster",class_applied:"applied",class_loading:"litespeed-loading",class_loaded:"litespeed-loaded",class_error:"error",class_entered:"entered",class_exited:"exited",unobserve_completed:!0,unobserve_entered:!1,cancel_on_exit:!0,callback_enter:null,callback_exit:null,callback_applied:null,callback_loading:null,callback_loaded:null,callback_error:null,callback_finish:null,callback_cancel:null,use_native:!1},ot="src",it="srcset",rt="sizes",ct="poster",lt="llOriginalAttrs",st="loading",ut="loaded",dt="applied",ft="error",_t="native",gt="data-",vt="ll-status",bt=[st,ut,dt,ft],pt=[ot],ht=[ot,ct],mt=[ot,it,rt],Et={IMG:function(t,e){h(t,function(t){y(t,mt),O(t,e)}),y(t,mt),O(t,e)},IFRAME:function(t,e){y(t,pt),A(t,ot,l(t,e.data_src))},VIDEO:function(t,e){a(t,function(t){y(t,pt),A(t,ot,l(t,e.data_src))}),y(t,ht),A(t,ct,l(t,e.data_poster)),A(t,ot,l(t,e.data_src)),t.load()}},It=["IMG","IFRAME","VIDEO"],yt={IMG:j,IFRAME:function(t){L(t,pt)},VIDEO:function(t){a(t,function(t){L(t,pt)}),L(t,ht),t.load()}},Lt=["IMG","IFRAME","VIDEO"];return t.prototype={update:function(t){var e,n,a,o=this._settings,i=W(t,o);{if(p(this,i.length),!Z&&tt)return q(o)?(e=o,n=this,i.forEach(function(t){-1!==Lt.indexOf(t.tagName)&&S(t,e,n)}),void p(n,0)):(t=this._observer,o=i,t.disconnect(),a=t,void o.forEach(function(t){a.observe(t)}));this.loadAll(i)}},destroy:function(){this._observer&&this._observer.disconnect(),K(this._settings).forEach(function(t){I(t)}),delete this._observer,delete this._settings,delete this.loadingCount,delete this.toLoadCount},loadAll:function(t){var e=this,n=this._settings;W(t,n).forEach(function(t){v(t,e),D(t,n,e)})},restoreAll:function(){var e=this._settings;K(e).forEach(function(t){P(t,e)})}},t.load=function(t,e){e=o(e);D(t,e)},t.resetStatus=function(t){i(t)},t}),function(t,e){"use strict";function n(){e.body.classList.add("litespeed_lazyloaded")}function a(){console.log("[LiteSpeed] Start Lazy Load"),o=new LazyLoad(Object.assign({},t.lazyLoadOptions||{},{elements_selector:"[data-lazyloaded]",callback_finish:n})),i=function(){o.update()},t.MutationObserver&&new MutationObserver(i).observe(e.documentElement,{childList:!0,subtree:!0,attributes:!0})}var o,i;t.addEventListener?t.addEventListener("load",a,!1):t.attachEvent("onload",a)}(window,document);</script><script data-no-optimize="1">window.litespeed_ui_events=window.litespeed_ui_events||["mouseover","click","keydown","wheel","touchmove","touchstart"];var urlCreator=window.URL||window.webkitURL;function litespeed_load_delayed_js_force(){console.log("[LiteSpeed] Start Load JS Delayed"),litespeed_ui_events.forEach(e=>{window.removeEventListener(e,litespeed_load_delayed_js_force,{passive:!0})}),document.querySelectorAll("iframe[data-litespeed-src]").forEach(e=>{e.setAttribute("src",e.getAttribute("data-litespeed-src"))}),"loading"==document.readyState?window.addEventListener("DOMContentLoaded",litespeed_load_delayed_js):litespeed_load_delayed_js()}litespeed_ui_events.forEach(e=>{window.addEventListener(e,litespeed_load_delayed_js_force,{passive:!0})});async function litespeed_load_delayed_js(){let t=[];for(var d in document.querySelectorAll('script[type="litespeed/javascript"]').forEach(e=>{t.push(e)}),t)await new Promise(e=>litespeed_load_one(t[d],e));document.dispatchEvent(new Event("DOMContentLiteSpeedLoaded")),window.dispatchEvent(new Event("DOMContentLiteSpeedLoaded"))}function litespeed_load_one(t,e){console.log("[LiteSpeed] Load ",t);var d=document.createElement("script");d.addEventListener("load",e),d.addEventListener("error",e),t.getAttributeNames().forEach(e=>{"type"!=e&&d.setAttribute("data-src"==e?"src":e,t.getAttribute(e))});let a=!(d.type="text/javascript");!d.src&&t.textContent&&(d.src=litespeed_inline2src(t.textContent),a=!0),t.after(d),t.remove(),a&&e()}function litespeed_inline2src(t){try{var d=urlCreator.createObjectURL(new Blob([t.replace(/^(?:<!--)?(.*?)(?:-->)?$/gm,"$1")],{type:"text/javascript"}))}catch(e){d="data:text/javascript;base64,"+btoa(t.replace(/^(?:<!--)?(.*?)(?:-->)?$/gm,"$1"))}return d}</script><script data-optimized="1" type="litespeed/javascript" data-src="https://diginode.in/wp-content/litespeed/js/5ad5da7e80e1ecf64f3d75c5dab7ddb4.js?ver=da7aa"></script></body>
</html>
Explanation:
- The script loads only the content inside the
#specific-elementfrompage.htmlinto the#contentdiv.
Output:
- Only the content inside the
#specific-elementfrompage.htmlis loaded into the#contentdiv.
Handling Errors
It’s important to handle errors gracefully when loading content. The .load() method allows you to manage errors using the callback function.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Handling Errors with Load</title> <script type="litespeed/javascript" data-src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.6.0.min.js"></script> </head>
<body>
<div id="content">Loading content...</div> <script type="litespeed/javascript">$(document).ready(function(){$('#content').load('nonexistent.html',function(response,status,xhr){if(status=="error"){$('#content').html('An error occurred: '+xhr.status+' '+xhr.statusText)}})})</script> <script data-no-optimize="1">window.lazyLoadOptions=Object.assign({},{threshold:300},window.lazyLoadOptions||{});!function(t,e){"object"==typeof exports&&"undefined"!=typeof module?module.exports=e():"function"==typeof define&&define.amd?define(e):(t="undefined"!=typeof globalThis?globalThis:t||self).LazyLoad=e()}(this,function(){"use strict";function e(){return(e=Object.assign||function(t){for(var e=1;e<arguments.length;e++){var n,a=arguments[e];for(n in a)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(a,n)&&(t[n]=a[n])}return t}).apply(this,arguments)}function o(t){return e({},at,t)}function l(t,e){return t.getAttribute(gt+e)}function c(t){return l(t,vt)}function s(t,e){return function(t,e,n){e=gt+e;null!==n?t.setAttribute(e,n):t.removeAttribute(e)}(t,vt,e)}function i(t){return s(t,null),0}function r(t){return null===c(t)}function u(t){return c(t)===_t}function d(t,e,n,a){t&&(void 0===a?void 0===n?t(e):t(e,n):t(e,n,a))}function f(t,e){et?t.classList.add(e):t.className+=(t.className?" ":"")+e}function _(t,e){et?t.classList.remove(e):t.className=t.className.replace(new RegExp("(^|\\s+)"+e+"(\\s+|$)")," ").replace(/^\s+/,"").replace(/\s+$/,"")}function g(t){return t.llTempImage}function v(t,e){!e||(e=e._observer)&&e.unobserve(t)}function b(t,e){t&&(t.loadingCount+=e)}function p(t,e){t&&(t.toLoadCount=e)}function n(t){for(var e,n=[],a=0;e=t.children[a];a+=1)"SOURCE"===e.tagName&&n.push(e);return n}function h(t,e){(t=t.parentNode)&&"PICTURE"===t.tagName&&n(t).forEach(e)}function a(t,e){n(t).forEach(e)}function m(t){return!!t[lt]}function E(t){return t[lt]}function I(t){return delete t[lt]}function y(e,t){var n;m(e)||(n={},t.forEach(function(t){n[t]=e.getAttribute(t)}),e[lt]=n)}function L(a,t){var o;m(a)&&(o=E(a),t.forEach(function(t){var e,n;e=a,(t=o[n=t])?e.setAttribute(n,t):e.removeAttribute(n)}))}function k(t,e,n){f(t,e.class_loading),s(t,st),n&&(b(n,1),d(e.callback_loading,t,n))}function A(t,e,n){n&&t.setAttribute(e,n)}function O(t,e){A(t,rt,l(t,e.data_sizes)),A(t,it,l(t,e.data_srcset)),A(t,ot,l(t,e.data_src))}function w(t,e,n){var a=l(t,e.data_bg_multi),o=l(t,e.data_bg_multi_hidpi);(a=nt&&o?o:a)&&(t.style.backgroundImage=a,n=n,f(t=t,(e=e).class_applied),s(t,dt),n&&(e.unobserve_completed&&v(t,e),d(e.callback_applied,t,n)))}function x(t,e){!e||0<e.loadingCount||0<e.toLoadCount||d(t.callback_finish,e)}function M(t,e,n){t.addEventListener(e,n),t.llEvLisnrs[e]=n}function N(t){return!!t.llEvLisnrs}function z(t){if(N(t)){var e,n,a=t.llEvLisnrs;for(e in a){var o=a[e];n=e,o=o,t.removeEventListener(n,o)}delete t.llEvLisnrs}}function C(t,e,n){var a;delete t.llTempImage,b(n,-1),(a=n)&&--a.toLoadCount,_(t,e.class_loading),e.unobserve_completed&&v(t,n)}function R(i,r,c){var l=g(i)||i;N(l)||function(t,e,n){N(t)||(t.llEvLisnrs={});var a="VIDEO"===t.tagName?"loadeddata":"load";M(t,a,e),M(t,"error",n)}(l,function(t){var e,n,a,o;n=r,a=c,o=u(e=i),C(e,n,a),f(e,n.class_loaded),s(e,ut),d(n.callback_loaded,e,a),o||x(n,a),z(l)},function(t){var e,n,a,o;n=r,a=c,o=u(e=i),C(e,n,a),f(e,n.class_error),s(e,ft),d(n.callback_error,e,a),o||x(n,a),z(l)})}function T(t,e,n){var a,o,i,r,c;t.llTempImage=document.createElement("IMG"),R(t,e,n),m(c=t)||(c[lt]={backgroundImage:c.style.backgroundImage}),i=n,r=l(a=t,(o=e).data_bg),c=l(a,o.data_bg_hidpi),(r=nt&&c?c:r)&&(a.style.backgroundImage='url("'.concat(r,'")'),g(a).setAttribute(ot,r),k(a,o,i)),w(t,e,n)}function G(t,e,n){var a;R(t,e,n),a=e,e=n,(t=Et[(n=t).tagName])&&(t(n,a),k(n,a,e))}function D(t,e,n){var a;a=t,(-1<It.indexOf(a.tagName)?G:T)(t,e,n)}function S(t,e,n){var a;t.setAttribute("loading","lazy"),R(t,e,n),a=e,(e=Et[(n=t).tagName])&&e(n,a),s(t,_t)}function V(t){t.removeAttribute(ot),t.removeAttribute(it),t.removeAttribute(rt)}function j(t){h(t,function(t){L(t,mt)}),L(t,mt)}function F(t){var e;(e=yt[t.tagName])?e(t):m(e=t)&&(t=E(e),e.style.backgroundImage=t.backgroundImage)}function P(t,e){var n;F(t),n=e,r(e=t)||u(e)||(_(e,n.class_entered),_(e,n.class_exited),_(e,n.class_applied),_(e,n.class_loading),_(e,n.class_loaded),_(e,n.class_error)),i(t),I(t)}function U(t,e,n,a){var o;n.cancel_on_exit&&(c(t)!==st||"IMG"===t.tagName&&(z(t),h(o=t,function(t){V(t)}),V(o),j(t),_(t,n.class_loading),b(a,-1),i(t),d(n.callback_cancel,t,e,a)))}function $(t,e,n,a){var o,i,r=(i=t,0<=bt.indexOf(c(i)));s(t,"entered"),f(t,n.class_entered),_(t,n.class_exited),o=t,i=a,n.unobserve_entered&&v(o,i),d(n.callback_enter,t,e,a),r||D(t,n,a)}function q(t){return t.use_native&&"loading"in HTMLImageElement.prototype}function H(t,o,i){t.forEach(function(t){return(a=t).isIntersecting||0<a.intersectionRatio?$(t.target,t,o,i):(e=t.target,n=t,a=o,t=i,void(r(e)||(f(e,a.class_exited),U(e,n,a,t),d(a.callback_exit,e,n,t))));var e,n,a})}function B(e,n){var t;tt&&!q(e)&&(n._observer=new IntersectionObserver(function(t){H(t,e,n)},{root:(t=e).container===document?null:t.container,rootMargin:t.thresholds||t.threshold+"px"}))}function J(t){return Array.prototype.slice.call(t)}function K(t){return t.container.querySelectorAll(t.elements_selector)}function Q(t){return c(t)===ft}function W(t,e){return e=t||K(e),J(e).filter(r)}function X(e,t){var n;(n=K(e),J(n).filter(Q)).forEach(function(t){_(t,e.class_error),i(t)}),t.update()}function t(t,e){var n,a,t=o(t);this._settings=t,this.loadingCount=0,B(t,this),n=t,a=this,Y&&window.addEventListener("online",function(){X(n,a)}),this.update(e)}var Y="undefined"!=typeof window,Z=Y&&!("onscroll"in window)||"undefined"!=typeof navigator&&/(gle|ing|ro)bot|crawl|spider/i.test(navigator.userAgent),tt=Y&&"IntersectionObserver"in window,et=Y&&"classList"in document.createElement("p"),nt=Y&&1<window.devicePixelRatio,at={elements_selector:".lazy",container:Z||Y?document:null,threshold:300,thresholds:null,data_src:"src",data_srcset:"srcset",data_sizes:"sizes",data_bg:"bg",data_bg_hidpi:"bg-hidpi",data_bg_multi:"bg-multi",data_bg_multi_hidpi:"bg-multi-hidpi",data_poster:"poster",class_applied:"applied",class_loading:"litespeed-loading",class_loaded:"litespeed-loaded",class_error:"error",class_entered:"entered",class_exited:"exited",unobserve_completed:!0,unobserve_entered:!1,cancel_on_exit:!0,callback_enter:null,callback_exit:null,callback_applied:null,callback_loading:null,callback_loaded:null,callback_error:null,callback_finish:null,callback_cancel:null,use_native:!1},ot="src",it="srcset",rt="sizes",ct="poster",lt="llOriginalAttrs",st="loading",ut="loaded",dt="applied",ft="error",_t="native",gt="data-",vt="ll-status",bt=[st,ut,dt,ft],pt=[ot],ht=[ot,ct],mt=[ot,it,rt],Et={IMG:function(t,e){h(t,function(t){y(t,mt),O(t,e)}),y(t,mt),O(t,e)},IFRAME:function(t,e){y(t,pt),A(t,ot,l(t,e.data_src))},VIDEO:function(t,e){a(t,function(t){y(t,pt),A(t,ot,l(t,e.data_src))}),y(t,ht),A(t,ct,l(t,e.data_poster)),A(t,ot,l(t,e.data_src)),t.load()}},It=["IMG","IFRAME","VIDEO"],yt={IMG:j,IFRAME:function(t){L(t,pt)},VIDEO:function(t){a(t,function(t){L(t,pt)}),L(t,ht),t.load()}},Lt=["IMG","IFRAME","VIDEO"];return t.prototype={update:function(t){var e,n,a,o=this._settings,i=W(t,o);{if(p(this,i.length),!Z&&tt)return q(o)?(e=o,n=this,i.forEach(function(t){-1!==Lt.indexOf(t.tagName)&&S(t,e,n)}),void p(n,0)):(t=this._observer,o=i,t.disconnect(),a=t,void o.forEach(function(t){a.observe(t)}));this.loadAll(i)}},destroy:function(){this._observer&&this._observer.disconnect(),K(this._settings).forEach(function(t){I(t)}),delete this._observer,delete this._settings,delete this.loadingCount,delete this.toLoadCount},loadAll:function(t){var e=this,n=this._settings;W(t,n).forEach(function(t){v(t,e),D(t,n,e)})},restoreAll:function(){var e=this._settings;K(e).forEach(function(t){P(t,e)})}},t.load=function(t,e){e=o(e);D(t,e)},t.resetStatus=function(t){i(t)},t}),function(t,e){"use strict";function n(){e.body.classList.add("litespeed_lazyloaded")}function a(){console.log("[LiteSpeed] Start Lazy Load"),o=new LazyLoad(Object.assign({},t.lazyLoadOptions||{},{elements_selector:"[data-lazyloaded]",callback_finish:n})),i=function(){o.update()},t.MutationObserver&&new MutationObserver(i).observe(e.documentElement,{childList:!0,subtree:!0,attributes:!0})}var o,i;t.addEventListener?t.addEventListener("load",a,!1):t.attachEvent("onload",a)}(window,document);</script><script data-no-optimize="1">window.litespeed_ui_events=window.litespeed_ui_events||["mouseover","click","keydown","wheel","touchmove","touchstart"];var urlCreator=window.URL||window.webkitURL;function litespeed_load_delayed_js_force(){console.log("[LiteSpeed] Start Load JS Delayed"),litespeed_ui_events.forEach(e=>{window.removeEventListener(e,litespeed_load_delayed_js_force,{passive:!0})}),document.querySelectorAll("iframe[data-litespeed-src]").forEach(e=>{e.setAttribute("src",e.getAttribute("data-litespeed-src"))}),"loading"==document.readyState?window.addEventListener("DOMContentLoaded",litespeed_load_delayed_js):litespeed_load_delayed_js()}litespeed_ui_events.forEach(e=>{window.addEventListener(e,litespeed_load_delayed_js_force,{passive:!0})});async function litespeed_load_delayed_js(){let t=[];for(var d in document.querySelectorAll('script[type="litespeed/javascript"]').forEach(e=>{t.push(e)}),t)await new Promise(e=>litespeed_load_one(t[d],e));document.dispatchEvent(new Event("DOMContentLiteSpeedLoaded")),window.dispatchEvent(new Event("DOMContentLiteSpeedLoaded"))}function litespeed_load_one(t,e){console.log("[LiteSpeed] Load ",t);var d=document.createElement("script");d.addEventListener("load",e),d.addEventListener("error",e),t.getAttributeNames().forEach(e=>{"type"!=e&&d.setAttribute("data-src"==e?"src":e,t.getAttribute(e))});let a=!(d.type="text/javascript");!d.src&&t.textContent&&(d.src=litespeed_inline2src(t.textContent),a=!0),t.after(d),t.remove(),a&&e()}function litespeed_inline2src(t){try{var d=urlCreator.createObjectURL(new Blob([t.replace(/^(?:<!--)?(.*?)(?:-->)?$/gm,"$1")],{type:"text/javascript"}))}catch(e){d="data:text/javascript;base64,"+btoa(t.replace(/^(?:<!--)?(.*?)(?:-->)?$/gm,"$1"))}return d}</script><script data-optimized="1" type="litespeed/javascript" data-src="https://diginode.in/wp-content/litespeed/js/5ad5da7e80e1ecf64f3d75c5dab7ddb4.js?ver=da7aa"></script></body>
</html>
Explanation:
- The script attempts to load
nonexistent.html. If the load fails, an error message is displayed in the#contentdiv.
Output:
- If
nonexistent.htmldoes not exist, the#contentdiv displays “An error occurred: 404 Not Found” (or the appropriate error message).
Loading Other Content Types
The .load() method is not limited to HTML files. It can load various content types including plain text, XML, and JSON, although it is primarily used for HTML.
Example 1: Loading Plain Text
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Load Plain Text</title> <script type="litespeed/javascript" data-src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.6.0.min.js"></script> </head>
<body>
<div id="text-content">Loading text...</div> <script type="litespeed/javascript">$(document).ready(function(){$('#text-content').load('text.txt')})</script> <script data-no-optimize="1">window.lazyLoadOptions=Object.assign({},{threshold:300},window.lazyLoadOptions||{});!function(t,e){"object"==typeof exports&&"undefined"!=typeof module?module.exports=e():"function"==typeof define&&define.amd?define(e):(t="undefined"!=typeof globalThis?globalThis:t||self).LazyLoad=e()}(this,function(){"use strict";function e(){return(e=Object.assign||function(t){for(var e=1;e<arguments.length;e++){var n,a=arguments[e];for(n in a)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(a,n)&&(t[n]=a[n])}return t}).apply(this,arguments)}function o(t){return e({},at,t)}function l(t,e){return t.getAttribute(gt+e)}function c(t){return l(t,vt)}function s(t,e){return function(t,e,n){e=gt+e;null!==n?t.setAttribute(e,n):t.removeAttribute(e)}(t,vt,e)}function i(t){return s(t,null),0}function r(t){return null===c(t)}function u(t){return c(t)===_t}function d(t,e,n,a){t&&(void 0===a?void 0===n?t(e):t(e,n):t(e,n,a))}function f(t,e){et?t.classList.add(e):t.className+=(t.className?" ":"")+e}function _(t,e){et?t.classList.remove(e):t.className=t.className.replace(new RegExp("(^|\\s+)"+e+"(\\s+|$)")," ").replace(/^\s+/,"").replace(/\s+$/,"")}function g(t){return t.llTempImage}function v(t,e){!e||(e=e._observer)&&e.unobserve(t)}function b(t,e){t&&(t.loadingCount+=e)}function p(t,e){t&&(t.toLoadCount=e)}function n(t){for(var e,n=[],a=0;e=t.children[a];a+=1)"SOURCE"===e.tagName&&n.push(e);return n}function h(t,e){(t=t.parentNode)&&"PICTURE"===t.tagName&&n(t).forEach(e)}function a(t,e){n(t).forEach(e)}function m(t){return!!t[lt]}function E(t){return t[lt]}function I(t){return delete t[lt]}function y(e,t){var n;m(e)||(n={},t.forEach(function(t){n[t]=e.getAttribute(t)}),e[lt]=n)}function L(a,t){var o;m(a)&&(o=E(a),t.forEach(function(t){var e,n;e=a,(t=o[n=t])?e.setAttribute(n,t):e.removeAttribute(n)}))}function k(t,e,n){f(t,e.class_loading),s(t,st),n&&(b(n,1),d(e.callback_loading,t,n))}function A(t,e,n){n&&t.setAttribute(e,n)}function O(t,e){A(t,rt,l(t,e.data_sizes)),A(t,it,l(t,e.data_srcset)),A(t,ot,l(t,e.data_src))}function w(t,e,n){var a=l(t,e.data_bg_multi),o=l(t,e.data_bg_multi_hidpi);(a=nt&&o?o:a)&&(t.style.backgroundImage=a,n=n,f(t=t,(e=e).class_applied),s(t,dt),n&&(e.unobserve_completed&&v(t,e),d(e.callback_applied,t,n)))}function x(t,e){!e||0<e.loadingCount||0<e.toLoadCount||d(t.callback_finish,e)}function M(t,e,n){t.addEventListener(e,n),t.llEvLisnrs[e]=n}function N(t){return!!t.llEvLisnrs}function z(t){if(N(t)){var e,n,a=t.llEvLisnrs;for(e in a){var o=a[e];n=e,o=o,t.removeEventListener(n,o)}delete t.llEvLisnrs}}function C(t,e,n){var a;delete t.llTempImage,b(n,-1),(a=n)&&--a.toLoadCount,_(t,e.class_loading),e.unobserve_completed&&v(t,n)}function R(i,r,c){var l=g(i)||i;N(l)||function(t,e,n){N(t)||(t.llEvLisnrs={});var a="VIDEO"===t.tagName?"loadeddata":"load";M(t,a,e),M(t,"error",n)}(l,function(t){var e,n,a,o;n=r,a=c,o=u(e=i),C(e,n,a),f(e,n.class_loaded),s(e,ut),d(n.callback_loaded,e,a),o||x(n,a),z(l)},function(t){var e,n,a,o;n=r,a=c,o=u(e=i),C(e,n,a),f(e,n.class_error),s(e,ft),d(n.callback_error,e,a),o||x(n,a),z(l)})}function T(t,e,n){var a,o,i,r,c;t.llTempImage=document.createElement("IMG"),R(t,e,n),m(c=t)||(c[lt]={backgroundImage:c.style.backgroundImage}),i=n,r=l(a=t,(o=e).data_bg),c=l(a,o.data_bg_hidpi),(r=nt&&c?c:r)&&(a.style.backgroundImage='url("'.concat(r,'")'),g(a).setAttribute(ot,r),k(a,o,i)),w(t,e,n)}function G(t,e,n){var a;R(t,e,n),a=e,e=n,(t=Et[(n=t).tagName])&&(t(n,a),k(n,a,e))}function D(t,e,n){var a;a=t,(-1<It.indexOf(a.tagName)?G:T)(t,e,n)}function S(t,e,n){var a;t.setAttribute("loading","lazy"),R(t,e,n),a=e,(e=Et[(n=t).tagName])&&e(n,a),s(t,_t)}function V(t){t.removeAttribute(ot),t.removeAttribute(it),t.removeAttribute(rt)}function j(t){h(t,function(t){L(t,mt)}),L(t,mt)}function F(t){var e;(e=yt[t.tagName])?e(t):m(e=t)&&(t=E(e),e.style.backgroundImage=t.backgroundImage)}function P(t,e){var n;F(t),n=e,r(e=t)||u(e)||(_(e,n.class_entered),_(e,n.class_exited),_(e,n.class_applied),_(e,n.class_loading),_(e,n.class_loaded),_(e,n.class_error)),i(t),I(t)}function U(t,e,n,a){var o;n.cancel_on_exit&&(c(t)!==st||"IMG"===t.tagName&&(z(t),h(o=t,function(t){V(t)}),V(o),j(t),_(t,n.class_loading),b(a,-1),i(t),d(n.callback_cancel,t,e,a)))}function $(t,e,n,a){var o,i,r=(i=t,0<=bt.indexOf(c(i)));s(t,"entered"),f(t,n.class_entered),_(t,n.class_exited),o=t,i=a,n.unobserve_entered&&v(o,i),d(n.callback_enter,t,e,a),r||D(t,n,a)}function q(t){return t.use_native&&"loading"in HTMLImageElement.prototype}function H(t,o,i){t.forEach(function(t){return(a=t).isIntersecting||0<a.intersectionRatio?$(t.target,t,o,i):(e=t.target,n=t,a=o,t=i,void(r(e)||(f(e,a.class_exited),U(e,n,a,t),d(a.callback_exit,e,n,t))));var e,n,a})}function B(e,n){var t;tt&&!q(e)&&(n._observer=new IntersectionObserver(function(t){H(t,e,n)},{root:(t=e).container===document?null:t.container,rootMargin:t.thresholds||t.threshold+"px"}))}function J(t){return Array.prototype.slice.call(t)}function K(t){return t.container.querySelectorAll(t.elements_selector)}function Q(t){return c(t)===ft}function W(t,e){return e=t||K(e),J(e).filter(r)}function X(e,t){var n;(n=K(e),J(n).filter(Q)).forEach(function(t){_(t,e.class_error),i(t)}),t.update()}function t(t,e){var n,a,t=o(t);this._settings=t,this.loadingCount=0,B(t,this),n=t,a=this,Y&&window.addEventListener("online",function(){X(n,a)}),this.update(e)}var Y="undefined"!=typeof window,Z=Y&&!("onscroll"in window)||"undefined"!=typeof navigator&&/(gle|ing|ro)bot|crawl|spider/i.test(navigator.userAgent),tt=Y&&"IntersectionObserver"in window,et=Y&&"classList"in document.createElement("p"),nt=Y&&1<window.devicePixelRatio,at={elements_selector:".lazy",container:Z||Y?document:null,threshold:300,thresholds:null,data_src:"src",data_srcset:"srcset",data_sizes:"sizes",data_bg:"bg",data_bg_hidpi:"bg-hidpi",data_bg_multi:"bg-multi",data_bg_multi_hidpi:"bg-multi-hidpi",data_poster:"poster",class_applied:"applied",class_loading:"litespeed-loading",class_loaded:"litespeed-loaded",class_error:"error",class_entered:"entered",class_exited:"exited",unobserve_completed:!0,unobserve_entered:!1,cancel_on_exit:!0,callback_enter:null,callback_exit:null,callback_applied:null,callback_loading:null,callback_loaded:null,callback_error:null,callback_finish:null,callback_cancel:null,use_native:!1},ot="src",it="srcset",rt="sizes",ct="poster",lt="llOriginalAttrs",st="loading",ut="loaded",dt="applied",ft="error",_t="native",gt="data-",vt="ll-status",bt=[st,ut,dt,ft],pt=[ot],ht=[ot,ct],mt=[ot,it,rt],Et={IMG:function(t,e){h(t,function(t){y(t,mt),O(t,e)}),y(t,mt),O(t,e)},IFRAME:function(t,e){y(t,pt),A(t,ot,l(t,e.data_src))},VIDEO:function(t,e){a(t,function(t){y(t,pt),A(t,ot,l(t,e.data_src))}),y(t,ht),A(t,ct,l(t,e.data_poster)),A(t,ot,l(t,e.data_src)),t.load()}},It=["IMG","IFRAME","VIDEO"],yt={IMG:j,IFRAME:function(t){L(t,pt)},VIDEO:function(t){a(t,function(t){L(t,pt)}),L(t,ht),t.load()}},Lt=["IMG","IFRAME","VIDEO"];return t.prototype={update:function(t){var e,n,a,o=this._settings,i=W(t,o);{if(p(this,i.length),!Z&&tt)return q(o)?(e=o,n=this,i.forEach(function(t){-1!==Lt.indexOf(t.tagName)&&S(t,e,n)}),void p(n,0)):(t=this._observer,o=i,t.disconnect(),a=t,void o.forEach(function(t){a.observe(t)}));this.loadAll(i)}},destroy:function(){this._observer&&this._observer.disconnect(),K(this._settings).forEach(function(t){I(t)}),delete this._observer,delete this._settings,delete this.loadingCount,delete this.toLoadCount},loadAll:function(t){var e=this,n=this._settings;W(t,n).forEach(function(t){v(t,e),D(t,n,e)})},restoreAll:function(){var e=this._settings;K(e).forEach(function(t){P(t,e)})}},t.load=function(t,e){e=o(e);D(t,e)},t.resetStatus=function(t){i(t)},t}),function(t,e){"use strict";function n(){e.body.classList.add("litespeed_lazyloaded")}function a(){console.log("[LiteSpeed] Start Lazy Load"),o=new LazyLoad(Object.assign({},t.lazyLoadOptions||{},{elements_selector:"[data-lazyloaded]",callback_finish:n})),i=function(){o.update()},t.MutationObserver&&new MutationObserver(i).observe(e.documentElement,{childList:!0,subtree:!0,attributes:!0})}var o,i;t.addEventListener?t.addEventListener("load",a,!1):t.attachEvent("onload",a)}(window,document);</script><script data-no-optimize="1">window.litespeed_ui_events=window.litespeed_ui_events||["mouseover","click","keydown","wheel","touchmove","touchstart"];var urlCreator=window.URL||window.webkitURL;function litespeed_load_delayed_js_force(){console.log("[LiteSpeed] Start Load JS Delayed"),litespeed_ui_events.forEach(e=>{window.removeEventListener(e,litespeed_load_delayed_js_force,{passive:!0})}),document.querySelectorAll("iframe[data-litespeed-src]").forEach(e=>{e.setAttribute("src",e.getAttribute("data-litespeed-src"))}),"loading"==document.readyState?window.addEventListener("DOMContentLoaded",litespeed_load_delayed_js):litespeed_load_delayed_js()}litespeed_ui_events.forEach(e=>{window.addEventListener(e,litespeed_load_delayed_js_force,{passive:!0})});async function litespeed_load_delayed_js(){let t=[];for(var d in document.querySelectorAll('script[type="litespeed/javascript"]').forEach(e=>{t.push(e)}),t)await new Promise(e=>litespeed_load_one(t[d],e));document.dispatchEvent(new Event("DOMContentLiteSpeedLoaded")),window.dispatchEvent(new Event("DOMContentLiteSpeedLoaded"))}function litespeed_load_one(t,e){console.log("[LiteSpeed] Load ",t);var d=document.createElement("script");d.addEventListener("load",e),d.addEventListener("error",e),t.getAttributeNames().forEach(e=>{"type"!=e&&d.setAttribute("data-src"==e?"src":e,t.getAttribute(e))});let a=!(d.type="text/javascript");!d.src&&t.textContent&&(d.src=litespeed_inline2src(t.textContent),a=!0),t.after(d),t.remove(),a&&e()}function litespeed_inline2src(t){try{var d=urlCreator.createObjectURL(new Blob([t.replace(/^(?:<!--)?(.*?)(?:-->)?$/gm,"$1")],{type:"text/javascript"}))}catch(e){d="data:text/javascript;base64,"+btoa(t.replace(/^(?:<!--)?(.*?)(?:-->)?$/gm,"$1"))}return d}</script><script data-optimized="1" type="litespeed/javascript" data-src="https://diginode.in/wp-content/litespeed/js/5ad5da7e80e1ecf64f3d75c5dab7ddb4.js?ver=da7aa"></script></body>
</html>
Explanation:
- This script loads the content of
text.txtinto the#text-contentdiv.
Output:
- The plain text from
text.txtis loaded into the#text-contentdiv.
Example 2: Loading XML Data
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Load XML Data</title> <script type="litespeed/javascript" data-src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.6.0.min.js"></script> </head>
<body>
<div id="xml-content">Loading XML data...</div> <script type="litespeed/javascript">$(document).ready(function(){$('#xml-content').load('data.xml',function(response,status,xhr){if(status=="success"){var xml=$(response);var items=xml.find('item');items.each(function(){var item=$(this);$('#xml-content').append('<p>'+item.text()+'</p>')})}else{console.error('Error loading XML:',xhr.statusText)}})})</script> <script data-no-optimize="1">window.lazyLoadOptions=Object.assign({},{threshold:300},window.lazyLoadOptions||{});!function(t,e){"object"==typeof exports&&"undefined"!=typeof module?module.exports=e():"function"==typeof define&&define.amd?define(e):(t="undefined"!=typeof globalThis?globalThis:t||self).LazyLoad=e()}(this,function(){"use strict";function e(){return(e=Object.assign||function(t){for(var e=1;e<arguments.length;e++){var n,a=arguments[e];for(n in a)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(a,n)&&(t[n]=a[n])}return t}).apply(this,arguments)}function o(t){return e({},at,t)}function l(t,e){return t.getAttribute(gt+e)}function c(t){return l(t,vt)}function s(t,e){return function(t,e,n){e=gt+e;null!==n?t.setAttribute(e,n):t.removeAttribute(e)}(t,vt,e)}function i(t){return s(t,null),0}function r(t){return null===c(t)}function u(t){return c(t)===_t}function d(t,e,n,a){t&&(void 0===a?void 0===n?t(e):t(e,n):t(e,n,a))}function f(t,e){et?t.classList.add(e):t.className+=(t.className?" ":"")+e}function _(t,e){et?t.classList.remove(e):t.className=t.className.replace(new RegExp("(^|\\s+)"+e+"(\\s+|$)")," ").replace(/^\s+/,"").replace(/\s+$/,"")}function g(t){return t.llTempImage}function v(t,e){!e||(e=e._observer)&&e.unobserve(t)}function b(t,e){t&&(t.loadingCount+=e)}function p(t,e){t&&(t.toLoadCount=e)}function n(t){for(var e,n=[],a=0;e=t.children[a];a+=1)"SOURCE"===e.tagName&&n.push(e);return n}function h(t,e){(t=t.parentNode)&&"PICTURE"===t.tagName&&n(t).forEach(e)}function a(t,e){n(t).forEach(e)}function m(t){return!!t[lt]}function E(t){return t[lt]}function I(t){return delete t[lt]}function y(e,t){var n;m(e)||(n={},t.forEach(function(t){n[t]=e.getAttribute(t)}),e[lt]=n)}function L(a,t){var o;m(a)&&(o=E(a),t.forEach(function(t){var e,n;e=a,(t=o[n=t])?e.setAttribute(n,t):e.removeAttribute(n)}))}function k(t,e,n){f(t,e.class_loading),s(t,st),n&&(b(n,1),d(e.callback_loading,t,n))}function A(t,e,n){n&&t.setAttribute(e,n)}function O(t,e){A(t,rt,l(t,e.data_sizes)),A(t,it,l(t,e.data_srcset)),A(t,ot,l(t,e.data_src))}function w(t,e,n){var a=l(t,e.data_bg_multi),o=l(t,e.data_bg_multi_hidpi);(a=nt&&o?o:a)&&(t.style.backgroundImage=a,n=n,f(t=t,(e=e).class_applied),s(t,dt),n&&(e.unobserve_completed&&v(t,e),d(e.callback_applied,t,n)))}function x(t,e){!e||0<e.loadingCount||0<e.toLoadCount||d(t.callback_finish,e)}function M(t,e,n){t.addEventListener(e,n),t.llEvLisnrs[e]=n}function N(t){return!!t.llEvLisnrs}function z(t){if(N(t)){var e,n,a=t.llEvLisnrs;for(e in a){var o=a[e];n=e,o=o,t.removeEventListener(n,o)}delete t.llEvLisnrs}}function C(t,e,n){var a;delete t.llTempImage,b(n,-1),(a=n)&&--a.toLoadCount,_(t,e.class_loading),e.unobserve_completed&&v(t,n)}function R(i,r,c){var l=g(i)||i;N(l)||function(t,e,n){N(t)||(t.llEvLisnrs={});var a="VIDEO"===t.tagName?"loadeddata":"load";M(t,a,e),M(t,"error",n)}(l,function(t){var e,n,a,o;n=r,a=c,o=u(e=i),C(e,n,a),f(e,n.class_loaded),s(e,ut),d(n.callback_loaded,e,a),o||x(n,a),z(l)},function(t){var e,n,a,o;n=r,a=c,o=u(e=i),C(e,n,a),f(e,n.class_error),s(e,ft),d(n.callback_error,e,a),o||x(n,a),z(l)})}function T(t,e,n){var a,o,i,r,c;t.llTempImage=document.createElement("IMG"),R(t,e,n),m(c=t)||(c[lt]={backgroundImage:c.style.backgroundImage}),i=n,r=l(a=t,(o=e).data_bg),c=l(a,o.data_bg_hidpi),(r=nt&&c?c:r)&&(a.style.backgroundImage='url("'.concat(r,'")'),g(a).setAttribute(ot,r),k(a,o,i)),w(t,e,n)}function G(t,e,n){var a;R(t,e,n),a=e,e=n,(t=Et[(n=t).tagName])&&(t(n,a),k(n,a,e))}function D(t,e,n){var a;a=t,(-1<It.indexOf(a.tagName)?G:T)(t,e,n)}function S(t,e,n){var a;t.setAttribute("loading","lazy"),R(t,e,n),a=e,(e=Et[(n=t).tagName])&&e(n,a),s(t,_t)}function V(t){t.removeAttribute(ot),t.removeAttribute(it),t.removeAttribute(rt)}function j(t){h(t,function(t){L(t,mt)}),L(t,mt)}function F(t){var e;(e=yt[t.tagName])?e(t):m(e=t)&&(t=E(e),e.style.backgroundImage=t.backgroundImage)}function P(t,e){var n;F(t),n=e,r(e=t)||u(e)||(_(e,n.class_entered),_(e,n.class_exited),_(e,n.class_applied),_(e,n.class_loading),_(e,n.class_loaded),_(e,n.class_error)),i(t),I(t)}function U(t,e,n,a){var o;n.cancel_on_exit&&(c(t)!==st||"IMG"===t.tagName&&(z(t),h(o=t,function(t){V(t)}),V(o),j(t),_(t,n.class_loading),b(a,-1),i(t),d(n.callback_cancel,t,e,a)))}function $(t,e,n,a){var o,i,r=(i=t,0<=bt.indexOf(c(i)));s(t,"entered"),f(t,n.class_entered),_(t,n.class_exited),o=t,i=a,n.unobserve_entered&&v(o,i),d(n.callback_enter,t,e,a),r||D(t,n,a)}function q(t){return t.use_native&&"loading"in HTMLImageElement.prototype}function H(t,o,i){t.forEach(function(t){return(a=t).isIntersecting||0<a.intersectionRatio?$(t.target,t,o,i):(e=t.target,n=t,a=o,t=i,void(r(e)||(f(e,a.class_exited),U(e,n,a,t),d(a.callback_exit,e,n,t))));var e,n,a})}function B(e,n){var t;tt&&!q(e)&&(n._observer=new IntersectionObserver(function(t){H(t,e,n)},{root:(t=e).container===document?null:t.container,rootMargin:t.thresholds||t.threshold+"px"}))}function J(t){return Array.prototype.slice.call(t)}function K(t){return t.container.querySelectorAll(t.elements_selector)}function Q(t){return c(t)===ft}function W(t,e){return e=t||K(e),J(e).filter(r)}function X(e,t){var n;(n=K(e),J(n).filter(Q)).forEach(function(t){_(t,e.class_error),i(t)}),t.update()}function t(t,e){var n,a,t=o(t);this._settings=t,this.loadingCount=0,B(t,this),n=t,a=this,Y&&window.addEventListener("online",function(){X(n,a)}),this.update(e)}var Y="undefined"!=typeof window,Z=Y&&!("onscroll"in window)||"undefined"!=typeof navigator&&/(gle|ing|ro)bot|crawl|spider/i.test(navigator.userAgent),tt=Y&&"IntersectionObserver"in window,et=Y&&"classList"in document.createElement("p"),nt=Y&&1<window.devicePixelRatio,at={elements_selector:".lazy",container:Z||Y?document:null,threshold:300,thresholds:null,data_src:"src",data_srcset:"srcset",data_sizes:"sizes",data_bg:"bg",data_bg_hidpi:"bg-hidpi",data_bg_multi:"bg-multi",data_bg_multi_hidpi:"bg-multi-hidpi",data_poster:"poster",class_applied:"applied",class_loading:"litespeed-loading",class_loaded:"litespeed-loaded",class_error:"error",class_entered:"entered",class_exited:"exited",unobserve_completed:!0,unobserve_entered:!1,cancel_on_exit:!0,callback_enter:null,callback_exit:null,callback_applied:null,callback_loading:null,callback_loaded:null,callback_error:null,callback_finish:null,callback_cancel:null,use_native:!1},ot="src",it="srcset",rt="sizes",ct="poster",lt="llOriginalAttrs",st="loading",ut="loaded",dt="applied",ft="error",_t="native",gt="data-",vt="ll-status",bt=[st,ut,dt,ft],pt=[ot],ht=[ot,ct],mt=[ot,it,rt],Et={IMG:function(t,e){h(t,function(t){y(t,mt),O(t,e)}),y(t,mt),O(t,e)},IFRAME:function(t,e){y(t,pt),A(t,ot,l(t,e.data_src))},VIDEO:function(t,e){a(t,function(t){y(t,pt),A(t,ot,l(t,e.data_src))}),y(t,ht),A(t,ct,l(t,e.data_poster)),A(t,ot,l(t,e.data_src)),t.load()}},It=["IMG","IFRAME","VIDEO"],yt={IMG:j,IFRAME:function(t){L(t,pt)},VIDEO:function(t){a(t,function(t){L(t,pt)}),L(t,ht),t.load()}},Lt=["IMG","IFRAME","VIDEO"];return t.prototype={update:function(t){var e,n,a,o=this._settings,i=W(t,o);{if(p(this,i.length),!Z&&tt)return q(o)?(e=o,n=this,i.forEach(function(t){-1!==Lt.indexOf(t.tagName)&&S(t,e,n)}),void p(n,0)):(t=this._observer,o=i,t.disconnect(),a=t,void o.forEach(function(t){a.observe(t)}));this.loadAll(i)}},destroy:function(){this._observer&&this._observer.disconnect(),K(this._settings).forEach(function(t){I(t)}),delete this._observer,delete this._settings,delete this.loadingCount,delete this.toLoadCount},loadAll:function(t){var e=this,n=this._settings;W(t,n).forEach(function(t){v(t,e),D(t,n,e)})},restoreAll:function(){var e=this._settings;K(e).forEach(function(t){P(t,e)})}},t.load=function(t,e){e=o(e);D(t,e)},t.resetStatus=function(t){i(t)},t}),function(t,e){"use strict";function n(){e.body.classList.add("litespeed_lazyloaded")}function a(){console.log("[LiteSpeed] Start Lazy Load"),o=new LazyLoad(Object.assign({},t.lazyLoadOptions||{},{elements_selector:"[data-lazyloaded]",callback_finish:n})),i=function(){o.update()},t.MutationObserver&&new MutationObserver(i).observe(e.documentElement,{childList:!0,subtree:!0,attributes:!0})}var o,i;t.addEventListener?t.addEventListener("load",a,!1):t.attachEvent("onload",a)}(window,document);</script><script data-no-optimize="1">window.litespeed_ui_events=window.litespeed_ui_events||["mouseover","click","keydown","wheel","touchmove","touchstart"];var urlCreator=window.URL||window.webkitURL;function litespeed_load_delayed_js_force(){console.log("[LiteSpeed] Start Load JS Delayed"),litespeed_ui_events.forEach(e=>{window.removeEventListener(e,litespeed_load_delayed_js_force,{passive:!0})}),document.querySelectorAll("iframe[data-litespeed-src]").forEach(e=>{e.setAttribute("src",e.getAttribute("data-litespeed-src"))}),"loading"==document.readyState?window.addEventListener("DOMContentLoaded",litespeed_load_delayed_js):litespeed_load_delayed_js()}litespeed_ui_events.forEach(e=>{window.addEventListener(e,litespeed_load_delayed_js_force,{passive:!0})});async function litespeed_load_delayed_js(){let t=[];for(var d in document.querySelectorAll('script[type="litespeed/javascript"]').forEach(e=>{t.push(e)}),t)await new Promise(e=>litespeed_load_one(t[d],e));document.dispatchEvent(new Event("DOMContentLiteSpeedLoaded")),window.dispatchEvent(new Event("DOMContentLiteSpeedLoaded"))}function litespeed_load_one(t,e){console.log("[LiteSpeed] Load ",t);var d=document.createElement("script");d.addEventListener("load",e),d.addEventListener("error",e),t.getAttributeNames().forEach(e=>{"type"!=e&&d.setAttribute("data-src"==e?"src":e,t.getAttribute(e))});let a=!(d.type="text/javascript");!d.src&&t.textContent&&(d.src=litespeed_inline2src(t.textContent),a=!0),t.after(d),t.remove(),a&&e()}function litespeed_inline2src(t){try{var d=urlCreator.createObjectURL(new Blob([t.replace(/^(?:<!--)?(.*?)(?:-->)?$/gm,"$1")],{type:"text/javascript"}))}catch(e){d="data:text/javascript;base64,"+btoa(t.replace(/^(?:<!--)?(.*?)(?:-->)?$/gm,"$1"))}return d}</script><script data-optimized="1" type="litespeed/javascript" data-src="https://diginode.in/wp-content/litespeed/js/5ad5da7e80e1ecf64f3d75c5dab7ddb4.js?ver=da7aa"></script></body>
</html>
Explanation:
- This script loads the content of
data.xmlinto the#xml-contentdiv. The callback function processes the XML data and appends each<item>‘s text to the#xml-contentdiv.
Output:
- The content of each
<item>element indata.xmlis appended as a paragraph to the#xml-contentdiv.
Sending Data with Load
You can send data to the server using the .load() method by passing data as key-value pairs.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Sending Data with Load</title> <script type="litespeed/javascript" data-src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.6.0.min.js"></script> </head>
<body>
<form id="data-form">
<input type="text" name="name" placeholder="Name">
<input type="email" name="email" placeholder="Email">
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
</form>
<div id="response">Waiting for response...</div> <script type="litespeed/javascript">$(document).ready(function(){$('#data-form').submit(function(event){event.preventDefault();var formData=$(this).serialize();$('#response').load('submit.php',formData)})})</script> <script data-no-optimize="1">window.lazyLoadOptions=Object.assign({},{threshold:300},window.lazyLoadOptions||{});!function(t,e){"object"==typeof exports&&"undefined"!=typeof module?module.exports=e():"function"==typeof define&&define.amd?define(e):(t="undefined"!=typeof globalThis?globalThis:t||self).LazyLoad=e()}(this,function(){"use strict";function e(){return(e=Object.assign||function(t){for(var e=1;e<arguments.length;e++){var n,a=arguments[e];for(n in a)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(a,n)&&(t[n]=a[n])}return t}).apply(this,arguments)}function o(t){return e({},at,t)}function l(t,e){return t.getAttribute(gt+e)}function c(t){return l(t,vt)}function s(t,e){return function(t,e,n){e=gt+e;null!==n?t.setAttribute(e,n):t.removeAttribute(e)}(t,vt,e)}function i(t){return s(t,null),0}function r(t){return null===c(t)}function u(t){return c(t)===_t}function d(t,e,n,a){t&&(void 0===a?void 0===n?t(e):t(e,n):t(e,n,a))}function f(t,e){et?t.classList.add(e):t.className+=(t.className?" ":"")+e}function _(t,e){et?t.classList.remove(e):t.className=t.className.replace(new RegExp("(^|\\s+)"+e+"(\\s+|$)")," ").replace(/^\s+/,"").replace(/\s+$/,"")}function g(t){return t.llTempImage}function v(t,e){!e||(e=e._observer)&&e.unobserve(t)}function b(t,e){t&&(t.loadingCount+=e)}function p(t,e){t&&(t.toLoadCount=e)}function n(t){for(var e,n=[],a=0;e=t.children[a];a+=1)"SOURCE"===e.tagName&&n.push(e);return n}function h(t,e){(t=t.parentNode)&&"PICTURE"===t.tagName&&n(t).forEach(e)}function a(t,e){n(t).forEach(e)}function m(t){return!!t[lt]}function E(t){return t[lt]}function I(t){return delete t[lt]}function y(e,t){var n;m(e)||(n={},t.forEach(function(t){n[t]=e.getAttribute(t)}),e[lt]=n)}function L(a,t){var o;m(a)&&(o=E(a),t.forEach(function(t){var e,n;e=a,(t=o[n=t])?e.setAttribute(n,t):e.removeAttribute(n)}))}function k(t,e,n){f(t,e.class_loading),s(t,st),n&&(b(n,1),d(e.callback_loading,t,n))}function A(t,e,n){n&&t.setAttribute(e,n)}function O(t,e){A(t,rt,l(t,e.data_sizes)),A(t,it,l(t,e.data_srcset)),A(t,ot,l(t,e.data_src))}function w(t,e,n){var a=l(t,e.data_bg_multi),o=l(t,e.data_bg_multi_hidpi);(a=nt&&o?o:a)&&(t.style.backgroundImage=a,n=n,f(t=t,(e=e).class_applied),s(t,dt),n&&(e.unobserve_completed&&v(t,e),d(e.callback_applied,t,n)))}function x(t,e){!e||0<e.loadingCount||0<e.toLoadCount||d(t.callback_finish,e)}function M(t,e,n){t.addEventListener(e,n),t.llEvLisnrs[e]=n}function N(t){return!!t.llEvLisnrs}function z(t){if(N(t)){var e,n,a=t.llEvLisnrs;for(e in a){var o=a[e];n=e,o=o,t.removeEventListener(n,o)}delete t.llEvLisnrs}}function C(t,e,n){var a;delete t.llTempImage,b(n,-1),(a=n)&&--a.toLoadCount,_(t,e.class_loading),e.unobserve_completed&&v(t,n)}function R(i,r,c){var l=g(i)||i;N(l)||function(t,e,n){N(t)||(t.llEvLisnrs={});var a="VIDEO"===t.tagName?"loadeddata":"load";M(t,a,e),M(t,"error",n)}(l,function(t){var e,n,a,o;n=r,a=c,o=u(e=i),C(e,n,a),f(e,n.class_loaded),s(e,ut),d(n.callback_loaded,e,a),o||x(n,a),z(l)},function(t){var e,n,a,o;n=r,a=c,o=u(e=i),C(e,n,a),f(e,n.class_error),s(e,ft),d(n.callback_error,e,a),o||x(n,a),z(l)})}function T(t,e,n){var a,o,i,r,c;t.llTempImage=document.createElement("IMG"),R(t,e,n),m(c=t)||(c[lt]={backgroundImage:c.style.backgroundImage}),i=n,r=l(a=t,(o=e).data_bg),c=l(a,o.data_bg_hidpi),(r=nt&&c?c:r)&&(a.style.backgroundImage='url("'.concat(r,'")'),g(a).setAttribute(ot,r),k(a,o,i)),w(t,e,n)}function G(t,e,n){var a;R(t,e,n),a=e,e=n,(t=Et[(n=t).tagName])&&(t(n,a),k(n,a,e))}function D(t,e,n){var a;a=t,(-1<It.indexOf(a.tagName)?G:T)(t,e,n)}function S(t,e,n){var a;t.setAttribute("loading","lazy"),R(t,e,n),a=e,(e=Et[(n=t).tagName])&&e(n,a),s(t,_t)}function V(t){t.removeAttribute(ot),t.removeAttribute(it),t.removeAttribute(rt)}function j(t){h(t,function(t){L(t,mt)}),L(t,mt)}function F(t){var e;(e=yt[t.tagName])?e(t):m(e=t)&&(t=E(e),e.style.backgroundImage=t.backgroundImage)}function P(t,e){var n;F(t),n=e,r(e=t)||u(e)||(_(e,n.class_entered),_(e,n.class_exited),_(e,n.class_applied),_(e,n.class_loading),_(e,n.class_loaded),_(e,n.class_error)),i(t),I(t)}function U(t,e,n,a){var o;n.cancel_on_exit&&(c(t)!==st||"IMG"===t.tagName&&(z(t),h(o=t,function(t){V(t)}),V(o),j(t),_(t,n.class_loading),b(a,-1),i(t),d(n.callback_cancel,t,e,a)))}function $(t,e,n,a){var o,i,r=(i=t,0<=bt.indexOf(c(i)));s(t,"entered"),f(t,n.class_entered),_(t,n.class_exited),o=t,i=a,n.unobserve_entered&&v(o,i),d(n.callback_enter,t,e,a),r||D(t,n,a)}function q(t){return t.use_native&&"loading"in HTMLImageElement.prototype}function H(t,o,i){t.forEach(function(t){return(a=t).isIntersecting||0<a.intersectionRatio?$(t.target,t,o,i):(e=t.target,n=t,a=o,t=i,void(r(e)||(f(e,a.class_exited),U(e,n,a,t),d(a.callback_exit,e,n,t))));var e,n,a})}function B(e,n){var t;tt&&!q(e)&&(n._observer=new IntersectionObserver(function(t){H(t,e,n)},{root:(t=e).container===document?null:t.container,rootMargin:t.thresholds||t.threshold+"px"}))}function J(t){return Array.prototype.slice.call(t)}function K(t){return t.container.querySelectorAll(t.elements_selector)}function Q(t){return c(t)===ft}function W(t,e){return e=t||K(e),J(e).filter(r)}function X(e,t){var n;(n=K(e),J(n).filter(Q)).forEach(function(t){_(t,e.class_error),i(t)}),t.update()}function t(t,e){var n,a,t=o(t);this._settings=t,this.loadingCount=0,B(t,this),n=t,a=this,Y&&window.addEventListener("online",function(){X(n,a)}),this.update(e)}var Y="undefined"!=typeof window,Z=Y&&!("onscroll"in window)||"undefined"!=typeof navigator&&/(gle|ing|ro)bot|crawl|spider/i.test(navigator.userAgent),tt=Y&&"IntersectionObserver"in window,et=Y&&"classList"in document.createElement("p"),nt=Y&&1<window.devicePixelRatio,at={elements_selector:".lazy",container:Z||Y?document:null,threshold:300,thresholds:null,data_src:"src",data_srcset:"srcset",data_sizes:"sizes",data_bg:"bg",data_bg_hidpi:"bg-hidpi",data_bg_multi:"bg-multi",data_bg_multi_hidpi:"bg-multi-hidpi",data_poster:"poster",class_applied:"applied",class_loading:"litespeed-loading",class_loaded:"litespeed-loaded",class_error:"error",class_entered:"entered",class_exited:"exited",unobserve_completed:!0,unobserve_entered:!1,cancel_on_exit:!0,callback_enter:null,callback_exit:null,callback_applied:null,callback_loading:null,callback_loaded:null,callback_error:null,callback_finish:null,callback_cancel:null,use_native:!1},ot="src",it="srcset",rt="sizes",ct="poster",lt="llOriginalAttrs",st="loading",ut="loaded",dt="applied",ft="error",_t="native",gt="data-",vt="ll-status",bt=[st,ut,dt,ft],pt=[ot],ht=[ot,ct],mt=[ot,it,rt],Et={IMG:function(t,e){h(t,function(t){y(t,mt),O(t,e)}),y(t,mt),O(t,e)},IFRAME:function(t,e){y(t,pt),A(t,ot,l(t,e.data_src))},VIDEO:function(t,e){a(t,function(t){y(t,pt),A(t,ot,l(t,e.data_src))}),y(t,ht),A(t,ct,l(t,e.data_poster)),A(t,ot,l(t,e.data_src)),t.load()}},It=["IMG","IFRAME","VIDEO"],yt={IMG:j,IFRAME:function(t){L(t,pt)},VIDEO:function(t){a(t,function(t){L(t,pt)}),L(t,ht),t.load()}},Lt=["IMG","IFRAME","VIDEO"];return t.prototype={update:function(t){var e,n,a,o=this._settings,i=W(t,o);{if(p(this,i.length),!Z&&tt)return q(o)?(e=o,n=this,i.forEach(function(t){-1!==Lt.indexOf(t.tagName)&&S(t,e,n)}),void p(n,0)):(t=this._observer,o=i,t.disconnect(),a=t,void o.forEach(function(t){a.observe(t)}));this.loadAll(i)}},destroy:function(){this._observer&&this._observer.disconnect(),K(this._settings).forEach(function(t){I(t)}),delete this._observer,delete this._settings,delete this.loadingCount,delete this.toLoadCount},loadAll:function(t){var e=this,n=this._settings;W(t,n).forEach(function(t){v(t,e),D(t,n,e)})},restoreAll:function(){var e=this._settings;K(e).forEach(function(t){P(t,e)})}},t.load=function(t,e){e=o(e);D(t,e)},t.resetStatus=function(t){i(t)},t}),function(t,e){"use strict";function n(){e.body.classList.add("litespeed_lazyloaded")}function a(){console.log("[LiteSpeed] Start Lazy Load"),o=new LazyLoad(Object.assign({},t.lazyLoadOptions||{},{elements_selector:"[data-lazyloaded]",callback_finish:n})),i=function(){o.update()},t.MutationObserver&&new MutationObserver(i).observe(e.documentElement,{childList:!0,subtree:!0,attributes:!0})}var o,i;t.addEventListener?t.addEventListener("load",a,!1):t.attachEvent("onload",a)}(window,document);</script><script data-no-optimize="1">window.litespeed_ui_events=window.litespeed_ui_events||["mouseover","click","keydown","wheel","touchmove","touchstart"];var urlCreator=window.URL||window.webkitURL;function litespeed_load_delayed_js_force(){console.log("[LiteSpeed] Start Load JS Delayed"),litespeed_ui_events.forEach(e=>{window.removeEventListener(e,litespeed_load_delayed_js_force,{passive:!0})}),document.querySelectorAll("iframe[data-litespeed-src]").forEach(e=>{e.setAttribute("src",e.getAttribute("data-litespeed-src"))}),"loading"==document.readyState?window.addEventListener("DOMContentLoaded",litespeed_load_delayed_js):litespeed_load_delayed_js()}litespeed_ui_events.forEach(e=>{window.addEventListener(e,litespeed_load_delayed_js_force,{passive:!0})});async function litespeed_load_delayed_js(){let t=[];for(var d in document.querySelectorAll('script[type="litespeed/javascript"]').forEach(e=>{t.push(e)}),t)await new Promise(e=>litespeed_load_one(t[d],e));document.dispatchEvent(new Event("DOMContentLiteSpeedLoaded")),window.dispatchEvent(new Event("DOMContentLiteSpeedLoaded"))}function litespeed_load_one(t,e){console.log("[LiteSpeed] Load ",t);var d=document.createElement("script");d.addEventListener("load",e),d.addEventListener("error",e),t.getAttributeNames().forEach(e=>{"type"!=e&&d.setAttribute("data-src"==e?"src":e,t.getAttribute(e))});let a=!(d.type="text/javascript");!d.src&&t.textContent&&(d.src=litespeed_inline2src(t.textContent),a=!0),t.after(d),t.remove(),a&&e()}function litespeed_inline2src(t){try{var d=urlCreator.createObjectURL(new Blob([t.replace(/^(?:<!--)?(.*?)(?:-->)?$/gm,"$1")],{type:"text/javascript"}))}catch(e){d="data:text/javascript;base64,"+btoa(t.replace(/^(?:<!--)?(.*?)(?:-->)?$/gm,"$1"))}return d}</script><script data-optimized="1" type="litespeed/javascript" data-src="https://diginode.in/wp-content/litespeed/js/5ad5da7e80e1ecf64f3d75c5dab7ddb4.js?ver=da7aa"></script></body>
</html>
Explanation:
- The form data is serialized and sent to
submit.phpwhen the form is submitted. The response fromsubmit.phpis loaded into the#responsediv.
Output:
- The server’s response is displayed in the
#responsediv.
Chaining Load Requests
You can chain multiple .load() requests to load different parts of a page or to perform sequential operations.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Chaining Load Requests</title> <script type="litespeed/javascript" data-src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.6.0.min.js"></script> </head>
<body>
<div id="header">Loading header...</div>
<div id="main-content">Loading main content...</div>
<div id="footer">Loading footer...</div> <script type="litespeed/javascript">$(document).ready(function(){$('#header').load('header.html',function(){$('#main-content').load('main.html',function(){$('#footer').load('footer.html')})})})</script> <script data-no-optimize="1">window.lazyLoadOptions=Object.assign({},{threshold:300},window.lazyLoadOptions||{});!function(t,e){"object"==typeof exports&&"undefined"!=typeof module?module.exports=e():"function"==typeof define&&define.amd?define(e):(t="undefined"!=typeof globalThis?globalThis:t||self).LazyLoad=e()}(this,function(){"use strict";function e(){return(e=Object.assign||function(t){for(var e=1;e<arguments.length;e++){var n,a=arguments[e];for(n in a)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(a,n)&&(t[n]=a[n])}return t}).apply(this,arguments)}function o(t){return e({},at,t)}function l(t,e){return t.getAttribute(gt+e)}function c(t){return l(t,vt)}function s(t,e){return function(t,e,n){e=gt+e;null!==n?t.setAttribute(e,n):t.removeAttribute(e)}(t,vt,e)}function i(t){return s(t,null),0}function r(t){return null===c(t)}function u(t){return c(t)===_t}function d(t,e,n,a){t&&(void 0===a?void 0===n?t(e):t(e,n):t(e,n,a))}function f(t,e){et?t.classList.add(e):t.className+=(t.className?" ":"")+e}function _(t,e){et?t.classList.remove(e):t.className=t.className.replace(new RegExp("(^|\\s+)"+e+"(\\s+|$)")," ").replace(/^\s+/,"").replace(/\s+$/,"")}function g(t){return t.llTempImage}function v(t,e){!e||(e=e._observer)&&e.unobserve(t)}function b(t,e){t&&(t.loadingCount+=e)}function p(t,e){t&&(t.toLoadCount=e)}function n(t){for(var e,n=[],a=0;e=t.children[a];a+=1)"SOURCE"===e.tagName&&n.push(e);return n}function h(t,e){(t=t.parentNode)&&"PICTURE"===t.tagName&&n(t).forEach(e)}function a(t,e){n(t).forEach(e)}function m(t){return!!t[lt]}function E(t){return t[lt]}function I(t){return delete t[lt]}function y(e,t){var n;m(e)||(n={},t.forEach(function(t){n[t]=e.getAttribute(t)}),e[lt]=n)}function L(a,t){var o;m(a)&&(o=E(a),t.forEach(function(t){var e,n;e=a,(t=o[n=t])?e.setAttribute(n,t):e.removeAttribute(n)}))}function k(t,e,n){f(t,e.class_loading),s(t,st),n&&(b(n,1),d(e.callback_loading,t,n))}function A(t,e,n){n&&t.setAttribute(e,n)}function O(t,e){A(t,rt,l(t,e.data_sizes)),A(t,it,l(t,e.data_srcset)),A(t,ot,l(t,e.data_src))}function w(t,e,n){var a=l(t,e.data_bg_multi),o=l(t,e.data_bg_multi_hidpi);(a=nt&&o?o:a)&&(t.style.backgroundImage=a,n=n,f(t=t,(e=e).class_applied),s(t,dt),n&&(e.unobserve_completed&&v(t,e),d(e.callback_applied,t,n)))}function x(t,e){!e||0<e.loadingCount||0<e.toLoadCount||d(t.callback_finish,e)}function M(t,e,n){t.addEventListener(e,n),t.llEvLisnrs[e]=n}function N(t){return!!t.llEvLisnrs}function z(t){if(N(t)){var e,n,a=t.llEvLisnrs;for(e in a){var o=a[e];n=e,o=o,t.removeEventListener(n,o)}delete t.llEvLisnrs}}function C(t,e,n){var a;delete t.llTempImage,b(n,-1),(a=n)&&--a.toLoadCount,_(t,e.class_loading),e.unobserve_completed&&v(t,n)}function R(i,r,c){var l=g(i)||i;N(l)||function(t,e,n){N(t)||(t.llEvLisnrs={});var a="VIDEO"===t.tagName?"loadeddata":"load";M(t,a,e),M(t,"error",n)}(l,function(t){var e,n,a,o;n=r,a=c,o=u(e=i),C(e,n,a),f(e,n.class_loaded),s(e,ut),d(n.callback_loaded,e,a),o||x(n,a),z(l)},function(t){var e,n,a,o;n=r,a=c,o=u(e=i),C(e,n,a),f(e,n.class_error),s(e,ft),d(n.callback_error,e,a),o||x(n,a),z(l)})}function T(t,e,n){var a,o,i,r,c;t.llTempImage=document.createElement("IMG"),R(t,e,n),m(c=t)||(c[lt]={backgroundImage:c.style.backgroundImage}),i=n,r=l(a=t,(o=e).data_bg),c=l(a,o.data_bg_hidpi),(r=nt&&c?c:r)&&(a.style.backgroundImage='url("'.concat(r,'")'),g(a).setAttribute(ot,r),k(a,o,i)),w(t,e,n)}function G(t,e,n){var a;R(t,e,n),a=e,e=n,(t=Et[(n=t).tagName])&&(t(n,a),k(n,a,e))}function D(t,e,n){var a;a=t,(-1<It.indexOf(a.tagName)?G:T)(t,e,n)}function S(t,e,n){var a;t.setAttribute("loading","lazy"),R(t,e,n),a=e,(e=Et[(n=t).tagName])&&e(n,a),s(t,_t)}function V(t){t.removeAttribute(ot),t.removeAttribute(it),t.removeAttribute(rt)}function j(t){h(t,function(t){L(t,mt)}),L(t,mt)}function F(t){var e;(e=yt[t.tagName])?e(t):m(e=t)&&(t=E(e),e.style.backgroundImage=t.backgroundImage)}function P(t,e){var n;F(t),n=e,r(e=t)||u(e)||(_(e,n.class_entered),_(e,n.class_exited),_(e,n.class_applied),_(e,n.class_loading),_(e,n.class_loaded),_(e,n.class_error)),i(t),I(t)}function U(t,e,n,a){var o;n.cancel_on_exit&&(c(t)!==st||"IMG"===t.tagName&&(z(t),h(o=t,function(t){V(t)}),V(o),j(t),_(t,n.class_loading),b(a,-1),i(t),d(n.callback_cancel,t,e,a)))}function $(t,e,n,a){var o,i,r=(i=t,0<=bt.indexOf(c(i)));s(t,"entered"),f(t,n.class_entered),_(t,n.class_exited),o=t,i=a,n.unobserve_entered&&v(o,i),d(n.callback_enter,t,e,a),r||D(t,n,a)}function q(t){return t.use_native&&"loading"in HTMLImageElement.prototype}function H(t,o,i){t.forEach(function(t){return(a=t).isIntersecting||0<a.intersectionRatio?$(t.target,t,o,i):(e=t.target,n=t,a=o,t=i,void(r(e)||(f(e,a.class_exited),U(e,n,a,t),d(a.callback_exit,e,n,t))));var e,n,a})}function B(e,n){var t;tt&&!q(e)&&(n._observer=new IntersectionObserver(function(t){H(t,e,n)},{root:(t=e).container===document?null:t.container,rootMargin:t.thresholds||t.threshold+"px"}))}function J(t){return Array.prototype.slice.call(t)}function K(t){return t.container.querySelectorAll(t.elements_selector)}function Q(t){return c(t)===ft}function W(t,e){return e=t||K(e),J(e).filter(r)}function X(e,t){var n;(n=K(e),J(n).filter(Q)).forEach(function(t){_(t,e.class_error),i(t)}),t.update()}function t(t,e){var n,a,t=o(t);this._settings=t,this.loadingCount=0,B(t,this),n=t,a=this,Y&&window.addEventListener("online",function(){X(n,a)}),this.update(e)}var Y="undefined"!=typeof window,Z=Y&&!("onscroll"in window)||"undefined"!=typeof navigator&&/(gle|ing|ro)bot|crawl|spider/i.test(navigator.userAgent),tt=Y&&"IntersectionObserver"in window,et=Y&&"classList"in document.createElement("p"),nt=Y&&1<window.devicePixelRatio,at={elements_selector:".lazy",container:Z||Y?document:null,threshold:300,thresholds:null,data_src:"src",data_srcset:"srcset",data_sizes:"sizes",data_bg:"bg",data_bg_hidpi:"bg-hidpi",data_bg_multi:"bg-multi",data_bg_multi_hidpi:"bg-multi-hidpi",data_poster:"poster",class_applied:"applied",class_loading:"litespeed-loading",class_loaded:"litespeed-loaded",class_error:"error",class_entered:"entered",class_exited:"exited",unobserve_completed:!0,unobserve_entered:!1,cancel_on_exit:!0,callback_enter:null,callback_exit:null,callback_applied:null,callback_loading:null,callback_loaded:null,callback_error:null,callback_finish:null,callback_cancel:null,use_native:!1},ot="src",it="srcset",rt="sizes",ct="poster",lt="llOriginalAttrs",st="loading",ut="loaded",dt="applied",ft="error",_t="native",gt="data-",vt="ll-status",bt=[st,ut,dt,ft],pt=[ot],ht=[ot,ct],mt=[ot,it,rt],Et={IMG:function(t,e){h(t,function(t){y(t,mt),O(t,e)}),y(t,mt),O(t,e)},IFRAME:function(t,e){y(t,pt),A(t,ot,l(t,e.data_src))},VIDEO:function(t,e){a(t,function(t){y(t,pt),A(t,ot,l(t,e.data_src))}),y(t,ht),A(t,ct,l(t,e.data_poster)),A(t,ot,l(t,e.data_src)),t.load()}},It=["IMG","IFRAME","VIDEO"],yt={IMG:j,IFRAME:function(t){L(t,pt)},VIDEO:function(t){a(t,function(t){L(t,pt)}),L(t,ht),t.load()}},Lt=["IMG","IFRAME","VIDEO"];return t.prototype={update:function(t){var e,n,a,o=this._settings,i=W(t,o);{if(p(this,i.length),!Z&&tt)return q(o)?(e=o,n=this,i.forEach(function(t){-1!==Lt.indexOf(t.tagName)&&S(t,e,n)}),void p(n,0)):(t=this._observer,o=i,t.disconnect(),a=t,void o.forEach(function(t){a.observe(t)}));this.loadAll(i)}},destroy:function(){this._observer&&this._observer.disconnect(),K(this._settings).forEach(function(t){I(t)}),delete this._observer,delete this._settings,delete this.loadingCount,delete this.toLoadCount},loadAll:function(t){var e=this,n=this._settings;W(t,n).forEach(function(t){v(t,e),D(t,n,e)})},restoreAll:function(){var e=this._settings;K(e).forEach(function(t){P(t,e)})}},t.load=function(t,e){e=o(e);D(t,e)},t.resetStatus=function(t){i(t)},t}),function(t,e){"use strict";function n(){e.body.classList.add("litespeed_lazyloaded")}function a(){console.log("[LiteSpeed] Start Lazy Load"),o=new LazyLoad(Object.assign({},t.lazyLoadOptions||{},{elements_selector:"[data-lazyloaded]",callback_finish:n})),i=function(){o.update()},t.MutationObserver&&new MutationObserver(i).observe(e.documentElement,{childList:!0,subtree:!0,attributes:!0})}var o,i;t.addEventListener?t.addEventListener("load",a,!1):t.attachEvent("onload",a)}(window,document);</script><script data-no-optimize="1">window.litespeed_ui_events=window.litespeed_ui_events||["mouseover","click","keydown","wheel","touchmove","touchstart"];var urlCreator=window.URL||window.webkitURL;function litespeed_load_delayed_js_force(){console.log("[LiteSpeed] Start Load JS Delayed"),litespeed_ui_events.forEach(e=>{window.removeEventListener(e,litespeed_load_delayed_js_force,{passive:!0})}),document.querySelectorAll("iframe[data-litespeed-src]").forEach(e=>{e.setAttribute("src",e.getAttribute("data-litespeed-src"))}),"loading"==document.readyState?window.addEventListener("DOMContentLoaded",litespeed_load_delayed_js):litespeed_load_delayed_js()}litespeed_ui_events.forEach(e=>{window.addEventListener(e,litespeed_load_delayed_js_force,{passive:!0})});async function litespeed_load_delayed_js(){let t=[];for(var d in document.querySelectorAll('script[type="litespeed/javascript"]').forEach(e=>{t.push(e)}),t)await new Promise(e=>litespeed_load_one(t[d],e));document.dispatchEvent(new Event("DOMContentLiteSpeedLoaded")),window.dispatchEvent(new Event("DOMContentLiteSpeedLoaded"))}function litespeed_load_one(t,e){console.log("[LiteSpeed] Load ",t);var d=document.createElement("script");d.addEventListener("load",e),d.addEventListener("error",e),t.getAttributeNames().forEach(e=>{"type"!=e&&d.setAttribute("data-src"==e?"src":e,t.getAttribute(e))});let a=!(d.type="text/javascript");!d.src&&t.textContent&&(d.src=litespeed_inline2src(t.textContent),a=!0),t.after(d),t.remove(),a&&e()}function litespeed_inline2src(t){try{var d=urlCreator.createObjectURL(new Blob([t.replace(/^(?:<!--)?(.*?)(?:-->)?$/gm,"$1")],{type:"text/javascript"}))}catch(e){d="data:text/javascript;base64,"+btoa(t.replace(/^(?:<!--)?(.*?)(?:-->)?$/gm,"$1"))}return d}</script><script data-optimized="1" type="litespeed/javascript" data-src="https://diginode.in/wp-content/litespeed/js/5ad5da7e80e1ecf64f3d75c5dab7ddb4.js?ver=da7aa"></script></body>
</html>
Explanation:
- The script loads
header.htmlinto the#headerdiv. Once the header is loaded, it loadsmain.htmlinto the#main-contentdiv. After the main content is loaded, it loadsfooter.htmlinto the#footerdiv.
Output:
- The header, main content, and footer are loaded sequentially into their respective divs
Performance Considerations
When using the .load() method, be mindful of performance:
- Minimize the amount of data being loaded to improve performance.
- Use caching where possible to avoid unnecessary server requests.
- Handle errors gracefully to ensure a good user experience.
The .load() method in jQuery is a versatile tool for fetching and displaying content dynamically without reloading the entire page. From basic content loading to advanced techniques like handling parameters, callbacks, and errors, the .load() method simplifies the process of integrating dynamic content into your web applications. By understanding and utilizing the features of the .load() method, you can create more interactive and responsive web experiences for your users.Happy coding !❤️
