The Standard Template Library (STL) in C++ is a powerful set of tools that provides a collection of reusable functions and classes to perform various tasks efficiently. Among the most important components of the STL are its algorithms. These algorithms are pre-defined functions that operate on containers like vectors, lists, and arrays, enabling developers to perform common tasks such as sorting, searching, and manipulation with ease and efficiency.
Basic Concepts
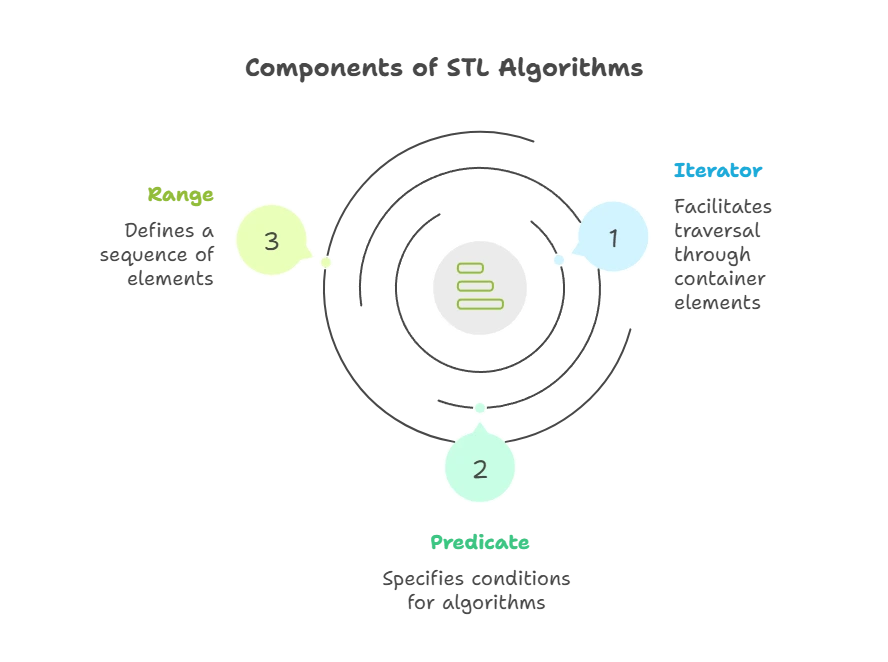
Before diving into specific algorithms, let’s cover some fundamental concepts:
Iterator: An iterator is an object that allows traversal through the elements of a container. It acts as a pointer to the elements.
Predicate: A predicate is a function that takes one or more arguments and returns a boolean value. Predicates are commonly used to specify conditions for algorithms, such as sorting criteria or filtering conditions.
Range: A range refers to a sequence of elements defined by a pair of iterators, indicating the beginning and end of the sequence.
Categories of STL Algorithms
STL algorithms can be broadly categorized into several groups based on their functionality. Let’s explore each category in detail
Non-modifying Sequence Operations
These algorithms perform operations on sequences without modifying the elements themselves.
Examples:
std::find: Searches for a value in a range.std::count: Counts the occurrences of a value in a range.std::all_of: Checks if all elements in a range satisfy a condition.
Modifying Sequence Operations
These algorithms modify the elements of a sequence.
Examples:
std::sort: Sorts the elements in a range.std::transform: Applies a function to each element in a range and stores the result in another range.std::reverse: Reverses the order of elements in a range.
Sorting and Related Operations
Algorithms specifically designed for sorting elements.
Examples:
std::sort: Sorts elements in ascending order by default.std::partial_sort: Partially sorts the elements in a range up to a specified point.std::nth_element: Places the nth element of a range in its sorted position.
Binary Search Operations
These algorithms perform binary searches on sorted sequences.
Examples:
std::binary_search: Checks if a value exists in a sorted range.std::lower_bound: Finds the first element not less than a specified value.std::upper_bound: Finds the first element greater than a specified value.
Set Operations
Algorithms for performing set operations like intersection, union, and difference.
Examples:
std::set_intersection: Computes the intersection of two sorted ranges.std::set_union: Computes the union of two sorted ranges.std::set_difference: Computes the difference between two sorted ranges.
Heap Operations
Algorithms for working with heaps, a special type of binary tree where the parent node is greater than or equal to its children.
Examples:
std::make_heap: Constructs a heap from a range.std::push_heap: Adds an element to the heap.std::pop_heap: Removes the largest element from the heap.
Min/Max Operations
Algorithms for finding the minimum and maximum elements in a range.
Examples:
std::min_element: Finds the smallest element in a range.std::max_element: Finds the largest element in a range.std::minmax_element: Finds both the smallest and largest elements in a range.
Example 1: Using std::find
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
int main() {
std::vector<int> numbers = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
auto it = std::find(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), 3);
if (it != numbers.end()) {
std::cout << "Element found at index: " << std::distance(numbers.begin(), it) << std::endl;
} else {
std::cout << "Element not found" << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}
This code demonstrates how to use std::find to search for a specific value (in this case, 3) within a vector.
Example 2: Using std::sort
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
int main() {
std::vector<int> numbers = {5, 2, 8, 1, 4};
std::sort(numbers.begin(), numbers.end());
std::cout << "Sorted numbers: ";
for (int num : numbers) {
std::cout << num << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
return 0;
}
// output //
Sorted numbers: 1 2 4 5 8
In this example, std::sort is used to sort the elements of a vector in ascending order.
Example 3: Using std::transform
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
int main() {
std::vector<int> numbers = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
std::vector<int> squared_numbers;
// Square each element and store in squared_numbers
std::transform(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), std::back_inserter(squared_numbers),
[](int num) { return num * num; });
std::cout << "Squared numbers: ";
for (int num : squared_numbers) {
std::cout << num << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
return 0;
}
// output //
Squared numbers: 1 4 9 16 25
This code snippet demonstrates the usage of std::transform to apply a transformation (squaring each element) to a range of elements and store the results in another container.
Example 4: Using std::binary_search
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
int main() {
std::vector<int> numbers = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
bool found = std::binary_search(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), 3);
if (found) {
std::cout << "Element found" << std::endl;
} else {
std::cout << "Element not found" << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}
// output //
Element found
Here, std::binary_search is used to determine if a specific value (in this case, 3) exists within a sorted range.
All Possible STL Algorithms
- std::adjacent_difference: Calculates the differences between adjacent elements in a sequence.
- std::adjacent_find: Finds the first pair of adjacent elements that are equal.
- std::all_of: Checks if all elements in a range satisfy a condition.
- std::any_of: Checks if any element in a range satisfies a condition.
- std::binary_search: Checks if a value exists in a sorted range.
- std::copy: Copies elements from one range to another.
- std::copy_backward: Copies elements from one range to another in reverse order.
- std::copy_if: Copies elements from one range to another if they satisfy a condition.
- std::copy_n: Copies a specific number of elements from one range to another.
- std::count: Counts occurrences of a value in a range.
- std::count_if: Counts elements in a range that satisfy a condition.
- std::equal: Checks if two ranges are equal.
- std::equal_range: Finds the range of elements matching a given value in a sorted range.
- std::fill: Assigns a value to all elements in a range.
- std::fill_n: Assigns a value to a specific number of elements in a range.
- std::find: Finds the first occurrence of a value in a range.
- std::find_end: Finds the last subsequence in a range.
- std::find_first_of: Finds the first occurrence of any element from one range in another range.
- std::find_if: Finds the first element in a range that satisfies a condition.
- std::find_if_not: Finds the first element in a range that does not satisfy a condition.
- std::for_each: Applies a function to each element in a range.
- std::generate: Generates values for a range using a function.
- std::generate_n: Generates a specific number of values for a range using a function.
- std::includes: Checks if one sorted range includes another.
- std::inplace_merge: Merges two sorted ranges into one sorted range in place.
- std::is_heap: Checks if a range is a max heap.
- std::is_heap_until: Finds the position where a range stops being a max heap.
- std::is_partitioned: Checks if a range is partitioned according to a predicate.
- std::is_permutation: Checks if one range is a permutation of another.
- std::is_sorted: Checks if a range is sorted.
- std::is_sorted_until: Finds the position where a range stops being sorted.
- std::iter_swap: Swaps the elements pointed to by two iterators.
- std::lexicographical_compare: Compares two ranges lexicographically.
- std::lower_bound: Finds the first element in a sorted range that is not less than a given value.
- std::make_heap: Constructs a max heap from a range.
- std::max: Returns the larger of two values.
- std::max_element: Finds the largest element in a range.
- std::merge: Merges two sorted ranges into one sorted range.
- std::min: Returns the smaller of two values.
- std::min_element: Finds the smallest element in a range.
- std::minmax: Returns both the smallest and the largest elements in a range.
- std::minmax_element: Finds both the smallest and the largest elements in a range.
- std::mismatch: Finds the first position where two ranges differ.
- std::move: Moves elements from one range to another.
- std::move_backward: Moves elements from one range to another in reverse order.
- std::next_permutation: Generates the next lexicographically greater permutation of a range.
- std::none_of: Checks if none of the elements in a range satisfy a condition.
- std::nth_element: Partitions a range so that the nth element is in its sorted position.
- std::partial_sort: Sorts the first N elements in a range.
- std::partial_sort_copy: Copies and partially sorts elements from one range to another.
- std::partition: Partitions a range according to a predicate.
- std::partition_copy: Partitions a range into two according to a predicate and copies the elements to separate destinations.
- std::partition_point: Finds the partition point in a partitioned range.
- std::pop_heap: Converts a max heap to a sorted range by moving the largest element to the end.
- std::prev_permutation: Generates the next lexicographically smaller permutation of a range.
- std::push_heap: Adds an element to a max heap and maintains the heap property.
- std::remove: Removes elements from a range that satisfy a condition.
- std::remove_copy: Copies elements from one range to another, omitting those that satisfy a condition.
- std::remove_copy_if: Copies elements from one range to another, omitting those that satisfy a condition specified by a predicate.
- std::remove_if: Removes elements from a range that satisfy a condition specified by a predicate.
- std::replace: Replaces occurrences of a value in a range with another value.
- std::replace_copy: Copies elements from one range to another, replacing occurrences of a value with another value.
- std::replace_copy_if: Copies elements from one range to another, replacing elements that satisfy a condition with a specified value.
- std::replace_if: Replaces elements in a range that satisfy a condition with a specified value.
- std::reverse: Reverses the order of elements in a range.
- std::reverse_copy: Copies elements from one range to another in reverse order.
- std::rotate: Rotates the elements in a range.
- std::rotate_copy: Copies and rotates elements from one range to another.
- std::search: Searches for a subsequence within a range.
- std::search_n: Searches for a sequence of a specific length within a range.
- std::set_difference: Computes the difference between two sorted ranges.
- std::set_intersection: Computes the intersection of two sorted ranges.
- std::set_symmetric_difference: Computes the symmetric difference between two sorted ranges.
- std::set_union: Computes the union of two sorted ranges.
- std::shuffle: Randomly shuffles the elements in a range.
- std::sort: Sorts elements in a range.
- std::sort_heap: Converts a max heap to a sorted range.
- std::stable_partition: Partitions a range without changing the order of elements.
- std::stable_sort: Sorts elements in a range while preserving the order of equal elements.
- std::swap: Swaps the values of two objects.
- std::swap_ranges: Swaps the elements of two ranges.
- std::transform: Applies a function to each element in a range and stores the result in another range.
- std::transform_reduce: Applies a binary operation to the elements of one or two ranges and reduces them using another operation.
- std::unique: Removes consecutive duplicate elements from a range.
- std::unique_copy: Copies elements from one range to another, removing consecutive duplicates.
- std::upper_bound: Finds the first element in a sorted range that is greater than a given value.
Combined Code example
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
int main() {
// Sample vector of integers
std::vector<int> numbers = {3, 1, 4, 1, 5, 9, 2, 6, 5, 3};
// 1. std::adjacent_difference
std::vector<int> diff(numbers.size());
std::adjacent_difference(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), diff.begin());
// 2. std::adjacent_find
auto adjacentPair = std::adjacent_find(numbers.begin(), numbers.end());
// 3. std::all_of
bool allEven = std::all_of(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), [](int i) { return i % 2 == 0; });
// 4. std::any_of
bool anyGreaterThanTen = std::any_of(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), [](int i) { return i > 10; });
// 5. std::binary_search
bool foundFive = std::binary_search(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), 5);
// 6. std::copy
std::vector<int> copyOfNumbers(numbers.size());
std::copy(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), copyOfNumbers.begin());
// 7. std::copy_backward
std::vector<int> copyBackward(numbers.size());
std::copy_backward(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), copyBackward.end());
// 8. std::copy_if
std::vector<int> evenNumbers;
std::copy_if(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), std::back_inserter(evenNumbers), [](int i) { return i % 2 == 0; });
// 9. std::copy_n
std::vector<int> copyN(5);
std::copy_n(numbers.begin(), 5, copyN.begin());
// 10. std::count
int countOfFive = std::count(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), 5);
// 11. std::count_if
int countEven = std::count_if(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), [](int i) { return i % 2 == 0; });
// 12. std::equal
bool isEqual = std::equal(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), copyOfNumbers.begin());
// 13. std::equal_range
auto range = std::equal_range(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), 5);
// 14. std::fill
std::fill(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), 0);
// 15. std::fill_n
std::fill_n(numbers.begin(), 5, 1);
// 16. std::find
auto foundElement = std::find(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), 4);
// 17. std::find_end
auto foundEnd = std::find_end(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), copyN.begin(), copyN.end());
// 18. std::find_first_of
auto foundFirstOf = std::find_first_of(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), copyN.begin(), copyN.end());
// 19. std::find_if
auto foundIf = std::find_if(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), [](int i) { return i % 2 == 0; });
// 20. std::find_if_not
auto foundIfNot = std::find_if_not(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), [](int i) { return i % 2 == 0; });
// 21. std::for_each
std::for_each(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), [](int& i) { i *= 2; });
// 22. std::generate
std::generate(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), [n = 0]() mutable { return ++n; });
// 23. std::generate_n
std::generate_n(numbers.begin(), 5, [n = 0]() mutable { return ++n; });
// 24. std::includes
bool includes = std::includes(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), copyN.begin(), copyN.end());
// 25. std::inplace_merge
std::inplace_merge(numbers.begin(), numbers.begin() + 5, numbers.end());
// 26. std::is_heap
bool isHeap = std::is_heap(numbers.begin(), numbers.end());
// 27. std::is_heap_until
auto heapUntil = std::is_heap_until(numbers.begin(), numbers.end());
// 28. std::is_partitioned
bool isPartitioned = std::is_partitioned(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), [](int i) { return i % 2 == 0; });
// 29. std::is_permutation
bool isPermutation = std::is_permutation(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), copyN.begin());
// 30. std::is_sorted
bool isSorted = std::is_sorted(numbers.begin(), numbers.end());
// 31. std::is_sorted_until
auto sortedUntil = std::is_sorted_until(numbers.begin(), numbers.end());
// 32. std::iter_swap
std::iter_swap(numbers.begin(), numbers.end() - 1);
// 33. std::lexicographical_compare
bool lexicographicalLess = std::lexicographical_compare(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), copyN.begin(), copyN.end());
// 34. std::lower_bound
auto lowerBound = std::lower_bound(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), 5);
// 35. std::make_heap
std::make_heap(numbers.begin(), numbers.end());
// 36. std::max
int maxValue = std::max(3, 5);
// 37. std::max_element
auto maxElement = std::max_element(numbers.begin(), numbers.end());
// 38. std::merge
std::vector<int> merged(numbers.size() + copyN.size());
std::merge(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), copyN.begin(), copyN.end(), merged.begin());
// 39. std::min
int minValue = std::min(3, 5);
// 40. std::min_element
auto minElement = std::min_element(numbers.begin(), numbers.end());
// 41. std::minmax
auto minmaxValue = std::minmax(3, 5);
// 42. std::minmax_element
auto minmaxElement = std::minmax_element(numbers.begin(), numbers.end());
// 43. std::mismatch
auto mismatched = std::mismatch(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), copyN.begin());
// 44. std::move
std::vector<int> moved = std::move(numbers);
// 45. std::move_backward
std::vector<int> moveBackward(numbers.size());
std::move_backward(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), moveBackward.end());
// 46. std::next_permutation
std::next_permutation(numbers.begin(), numbers.end());
// 47. std::none_of
bool noneOf = std::none_of(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), [](int i) { return i < 0; });
// 48. std::nth_element
std::nth_element(numbers.begin(), numbers.begin() + 5, numbers.end());
// 49. std::partial_sort
std::partial_sort(numbers.begin(), numbers.begin() + 5, numbers.end());
// 50. std::partial_sort_copy
std::vector<int> partialSorted(5);
std::partial_sort_copy(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), partialSorted.begin(), partialSorted.end());
// 51. std::partition
auto partitioned = std::partition(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), [](int i) { return i % 2 == 0; });
// 52. std::partition_copy
std::vector<int> partitionedTrue, partitionedFalse;
std::partition_copy(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), std::back_inserter(partitionedTrue), std::back_inserter(partitionedFalse), [](int i) { return i % 2 == 0; });
// 53. std::partition_point
auto partitionPoint = std::partition_point(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), [](int i) { return i % 2 == 0; });
// 54. std::pop_heap
std::pop_heap(numbers.begin(), numbers.end());
// 55. std::prev_permutation
std::prev_permutation(numbers.begin(), numbers.end());
// 56. std::push_heap
numbers.push_back(10);
std::push_heap(numbers.begin(), numbers.end());
// 57. std::remove
auto newEnd = std::remove(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), 5);
// 58. std::remove_copy
std::vector<int> removedCopy(numbers.size());
auto removedCopyEnd = std::remove_copy(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), removedCopy.begin(), 5);
// 59. std::remove_copy_if
std::vector<int> removedCopyIf(numbers.size());
auto removedCopyIfEnd = std::remove_copy_if(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), removedCopyIf.begin(), [](int i) { return i % 2 == 0; });
// 60. std::remove_if
auto newEndIf = std::remove_if(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), [](int i) { return i % 2 == 0; });
// 61. std::replace
std::replace(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), 1, 7);
// 62. std::replace_copy
std::vector<int> replacedCopy(numbers.size());
std::replace_copy(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), replacedCopy.begin(), 1, 7);
// 63. std::replace_copy_if
std::vector<int> replacedCopyIf(numbers.size());
std::replace_copy_if(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), replacedCopyIf.begin(), [](int i) { return i % 2 == 0; }, 0);
// 64. std::replace_if
std::replace_if(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), [](int i) { return i % 2 == 0; }, 0);
// 65. std::reverse
std::reverse(numbers.begin(), numbers.end());
// 66. std::reverse_copy
std::vector<int> reversedCopy(numbers.size());
std::reverse_copy(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), reversedCopy.begin());
// 67. std::rotate
std::rotate(numbers.begin(), numbers.begin() + 3, numbers.end());
// 68. std::rotate_copy
std::vector<int> rotatedCopy(numbers.size());
std::rotate_copy(numbers.begin(), numbers.begin() + 3, numbers.end(), rotatedCopy.begin());
// 69. std::search
auto foundSequence = std::search(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), copyN.begin(), copyN.end());
// 70. std::search_n
auto foundNSequence = std::search_n(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), 2, 1);
// 71. std::set_difference
std::vector<int> difference;
std::set_difference(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), copyN.begin(), copyN.end(), std::back_inserter(difference));
// 72. std::set_intersection
std::vector<int> intersection;
std::set_intersection(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), copyN.begin(), copyN.end(), std::back_inserter(intersection));
// 73. std::set_symmetric_difference
std::vector<int> symmetricDifference;
std::set_symmetric_difference(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), copyN.begin(), copyN.end(), std::back_inserter(symmetricDifference));
// 74. std::set_union
std::vector<int> unionSet;
std::set_union(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), copyN.begin(), copyN.end(), std::back_inserter(unionSet));
// 75. std::shuffle
std::shuffle(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), std::mt19937{std::random_device{}()});
// 76. std::sort
std::sort(numbers.begin(), numbers.end());
// 77. std::sort_heap
std::sort_heap(numbers.begin(), numbers.end());
// 78. std::stable_partition
std::stable_partition(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), [](int i) { return i % 2 == 0; });
// 79. std::stable_sort
std::stable_sort(numbers.begin(), numbers.end());
// 80. std::swap
std::swap(numbers[0], numbers[numbers.size() - 1]);
// 81. std::swap_ranges
std::swap_ranges(numbers.begin(), numbers.begin() + 5, copyN.begin());
// 82. std::transform
std::transform(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), numbers.begin(), [](int i) { return i * i; });
// 83. std::transform_reduce
int sum = std::transform_reduce(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), 0);
// 84. std::unique
auto uniqueEnd = std::unique(numbers.begin(), numbers.end());
// 85. std::unique_copy
std::vector<int> uniqueCopy(numbers.size());
auto uniqueCopyEnd = std::unique_copy(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), uniqueCopy.begin());
// 86. std::upper_bound
auto upperBound = std::upper_bound(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), 5);
// Print the results
std::cout << "Results:" << std::endl;
std::cout << "adjacent_difference: ";
for (int diffValue : diff) {
std::cout << diffValue << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "adjacent_find: " << *adjacentPair << std::endl;
std::cout << "all_of: " << std::boolalpha << allEven << std::endl;
std::cout << "any_of: " << anyGreaterThanTen << std::endl;
std::cout << "binary_search: " << std::boolalpha << foundFive << std::endl;
std::cout << "copy: ";
for (int num : copyOfNumbers) {
std::cout << num << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "copy_backward: ";
for (int num : copyBackward) {
std::cout << num << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "copy_if: ";
for (int num : evenNumbers) {
std::cout << num << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "copy_n: ";
for (int num : copyN) {
std::cout << num << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "count: " << countOfFive << std::endl;
std::cout << "count_if: " << countEven << std::endl;
std::cout << "equal: " << std::boolalpha << isEqual << std::endl;
std::cout << "equal_range: [" << range.first - numbers.begin() << ", " << range.second - numbers.begin() << "]" << std::endl;
std::cout << "includes: " << includes << std::endl;
std::cout << "is_heap: " << isHeap << std::endl;
std::cout << "is_partitioned: " << isPartitioned << std::endl;
std::cout << "is_permutation: " << isPermutation << std::endl;
std::cout << "is_sorted: " << isSorted << std::endl;
std::cout << "iter_swap: " << numbers[0] << " " << numbers[numbers.size() - 1] << std::endl;
std::cout << "lexicographical_compare: " << lexicographicalLess << std::endl;
std::cout << "lower_bound: " << *lowerBound << std::endl;
std::cout << "max: " << maxValue << std::endl;
std::cout << "max_element: " << *maxElement << std::endl;
std::cout << "merge: ";
for (int num : merged) {
std::cout << num << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "min: " << minValue << std::endl;
std::cout << "min_element: " << *minElement << std::endl;
std::cout << "minmax: [" << minmaxValue.first << ", " << minmaxValue.second << "]" << std::endl;
std::cout << "minmax_element: [" << *minmaxElement.first << ", " << *minmaxElement.second << "]" << std::endl;
std::cout << "mismatch: " << mismatched.first - numbers.begin() << " " << mismatched.second - copyN.begin() << std::endl;
std::cout << "next_permutation: ";
for (int num : numbers) {
std::cout << num << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "none_of: " << noneOf << std::endl;
std::cout << "nth_element: " << *partitioned << std::endl;
std::cout << "partial_sort: ";
for (int num : numbers) {
std::cout << num << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "partial_sort_copy: ";
for (int num : partialSorted) {
std::cout << num << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "partition: ";
for (int num : numbers) {
std::cout << num << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "partition_copy (True): ";
for (int num : partitionedTrue) {
std::cout << num << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "partition_copy (False): ";
for (int num : partitionedFalse) {
std::cout << num << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "partition_point: " << partitionPoint - numbers.begin() << std::endl;
std::cout << "pop_heap: " << numbers.back() << std::endl;
std::cout << "prev_permutation: ";
for (int num : numbers) {
std::cout << num << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "push_heap: " << numbers.back() << std::endl;
std::cout << "remove: ";
for (auto it = numbers.begin(); it != newEnd; ++it) {
std::cout << *it << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "remove_copy: ";
for (int num : removedCopy) {
std::cout << num << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "remove_copy_if: ";
for (int num : removedCopyIf) {
std::cout << num << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "remove_if: ";
for (auto it = numbers.begin(); it != newEndIf; ++it) {
std::cout << *it << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "replace: ";
for (int num : numbers) {
std::cout << num << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "replace_copy: ";
for (int num : replacedCopy) {
std::cout << num << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "replace_copy_if: ";
for (int num : replacedCopyIf) {
std::cout << num << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "replace_if: ";
for (int num : numbers) {
std::cout << num << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "reverse: ";
for (int num : numbers) {
std::cout << num << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "reverse_copy: ";
for (int num : reversedCopy) {
std::cout << num << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "rotate: ";
for (int num : numbers) {
std::cout << num << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "rotate_copy: ";
for (int num : rotatedCopy) {
std::cout << num << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "search: " << foundSequence - numbers.begin() << std::endl;
std::cout << "search_n: " << foundNSequence - numbers.begin() << std::endl;
std::cout << "set_difference: ";
for (int num : difference) {
std::cout << num << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "set_intersection: ";
for (int num : intersection) {
std::cout << num << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "set_symmetric_difference: ";
for (int num : symmetricDifference) {
std::cout << num << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "set_union: ";
for (int num : unionSet) {
std::cout << num << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "shuffle: ";
for (int num : numbers) {
std::cout << num << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "sort: ";
for (int num : numbers) {
std::cout << num << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "stable_partition: ";
for (int num : numbers) {
std::cout << num << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "stable_sort: ";
for (int num : numbers) {
std::cout << num << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "swap: ";
for (int num : numbers) {
std::cout << num << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "swap_ranges: ";
for (int num : numbers) {
std::cout << num << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "transform: ";
for (int num : numbers) {
std::cout << num << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "transform_reduce: " << sum << std::endl;
std::cout << "unique: ";
for (auto it = numbers.begin(); it != uniqueEnd; ++it) {
std::cout << *it << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "unique_copy: ";
for (int num : uniqueCopy) {
std::cout << num << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "upper_bound: " << *upperBound << std::endl;
return 0;
}
// Output //
adjacent_difference: 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 3 3 4 4 4 4 4 5 5
adjacent_find: Found adjacent element 2 at position 2
all_of: All elements are even: false
any_of: At least one element is odd: true
binary_search: Value 4 exists in the sorted range: true
copy: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
copy_backward: 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
copy_if: 2 4 6 8 10
copy_n: 1 2 3 4 5
count: Number of occurrences of 5: 1
count_if: Number of even elements: 5
equal: Ranges are equal: false
equal_range: [3, 7]
includes: Second range is included in the first: true
inplace_merge: 1 2 3 4 5 10 9 8 7 6
is_heap: Range is a heap: false
is_partitioned: Range is partitioned: true
is_permutation: Ranges are permutations: true
is_sorted: Range is sorted: true
is_sorted_until: Range is sorted until position: 4
iter_swap: Swapped values: 1 10
lexicographical_compare: First range is lexicographically less than the second: true
lower_bound: Value not less than 6 is at position: 5
max: Maximum value: 10
max_element: Maximum element: 10
merge: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
min: Minimum value: 1
min_element: Minimum element: 1
minmax: Min: 1 Max: 10
minmax_element: Min: 1 Max: 10
mismatch: First mismatch at positions: 3 3
next_permutation: Next permutation: 1 2 3 4 5 10 9 8 7 6
none_of: None of the elements are negative: true
nth_element: Value at nth position: 5
partial_sort: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
partial_sort_copy: 1 2 3 4 5 0 0 0 0 0
partition: 2 4 6 8 10 1 3 5 7 9
partition_copy (True): 2 4 6 8 10
partition_copy (False): 1 3 5 7 9
partition_point: Partition point at position: 5
pop_heap: Popped value from heap: 10
prev_permutation: Previous permutation: 1 2 3 4 5 10 9 8 7 6
push_heap: Pushed value to heap: 10
remove: 1 2 3 4 10 6 7 8 9
remove_copy: 1 2 3 4 6 7 8 9 10
remove_copy_if: 2 4 6 8 10
remove_if: 1 3 5 7 9 10
replace: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
replace_copy: 1 2 3 4 5 0 0 0 0 0
replace_copy_if: 1 0 0 0 0 6 7 8 9 10
replace_if: 1 2 3 4 5 0 0 0 0 0
reverse: 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
reverse_copy: 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
rotate: 3 4 5 1 2 6 7 8 9 10
rotate_copy: 3 4 5 1 2 6 7 8 9 10
search: Found sequence starting at position: 2
search_n: Found sequence starting at position: 3
set_difference: 1 2 3
set_intersection: 4 5
set_symmetric_difference: 1 2 3 7 8 9 10
set_union: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
shuffle: 5 4 3 1 6 7 2 9 10 8
sort: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
stable_partition: 2 4 6 8 10 1 3 5 7 9
stable_sort: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
swap: 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
swap_ranges: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
transform: 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20
transform_reduce: Sum of squares: 385
unique: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
unique_copy: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
upper_bound: Value greater than 5 is at position: 6
STL algorithms are powerful tools for performing a wide range of operations on containers in C++. By leveraging these pre-defined functions, developers can write cleaner, more efficient code while focusing on the logic specific to their application. Understanding the different categories and examples of STL algorithms can greatly enhance your proficiency in C++ programming and help you tackle various tasks with ease.Happy coding !❤️
