Understanding XProc
As XML usage has grown, so has the need for efficient ways to process and manage XML documents. Often, working with XML involves multiple steps: validating the document, transforming it, filtering, merging with other documents, and more. To handle this complexity, XProc (XML Pipeline Language) was introduced. XProc provides a standard way to define and execute pipelines, enabling developers to automate and manage complex XML workflows in a structured manner.
What is XProc?
XProc is a W3C standard XML Pipeline Language that defines a way to describe sequences of operations to process XML documents. It enables you to build pipelines that orchestrate the processing of XML data in a modular and reusable way. A pipeline in XProc defines a series of steps, where each step performs a specific task like transforming XML, validating against a schema, or filtering content.
Why Use XProc?
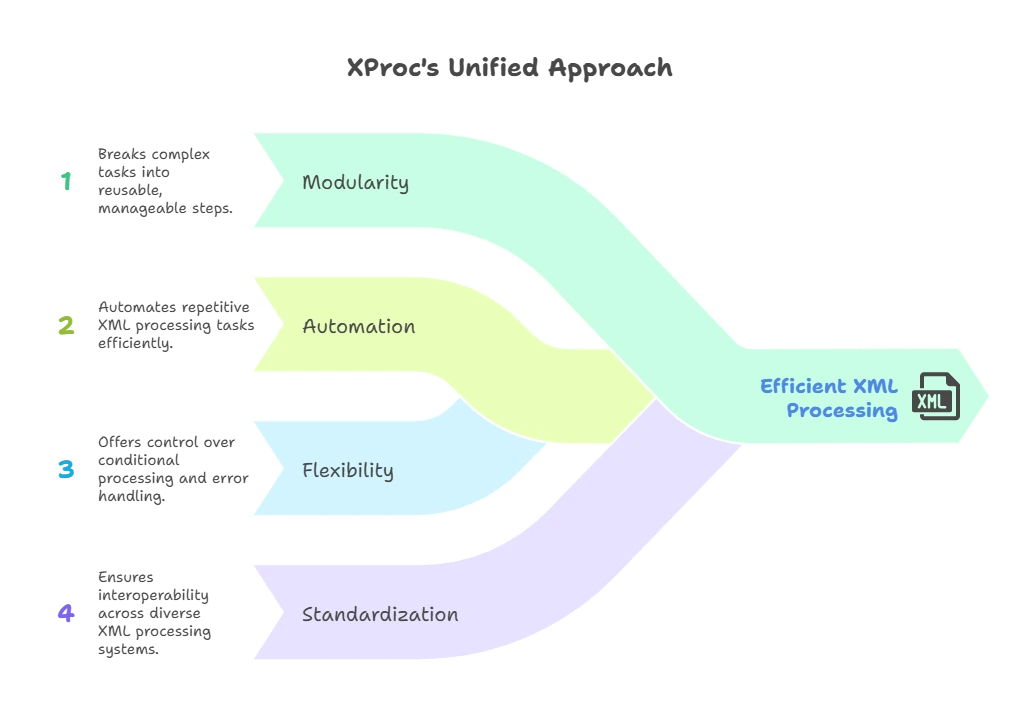
- Modularity: XProc allows breaking complex workflows into smaller, reusable steps.
- Automation: Repeated XML processing tasks can be automated using XProc pipelines.
- Flexibility: It provides control over conditional processing, error handling, and parallel task execution.
- Standardization: Since XProc is a W3C standard, it ensures interoperability across different systems.
Key Concepts and Terminology in XProc
To fully understand XProc, it’s essential to familiarize yourself with some key concepts and components:
Steps
Steps are the core building blocks of an XProc pipeline. Each step represents a specific action, such as transforming an XML document, validating it, or combining multiple XML files.
Types of steps:
- Atomic Steps: Perform specific actions like XSLT transformations or validation.
- Compound Steps: A combination of multiple steps, forming a sub-pipeline.
Pipelines
A pipeline is a collection of steps executed in a particular sequence. Pipelines can be nested within one another, allowing for complex workflows.
Ports
Ports define how data flows into and out of each step in a pipeline. Every step has at least one input port (for receiving data) and one output port (for sending data to the next step).
Bindings
Bindings specify where the data comes from for each step and where it should go after the step is executed. This allows the connection of input and output data between steps.
Variables and Parameters
Variables and parameters are used to pass values between steps. They provide a way to make pipelines dynamic and reusable by changing values without modifying the pipeline itself.
Basic XProc Structure
An XProc pipeline typically follows a specific structure, starting with a p:declare-step element that defines the pipeline and its steps. Each step performs a specific task, such as loading an XML document, transforming it using XSLT, or validating it.
Basic Example of an XProc Pipeline
Let’s look at a simple pipeline that loads an XML document, applies an XSLT transformation to it, and outputs the result.
Input XML (books.xml)
<library>
<book>
<title>Learning XML</title>
<author>John Doe</author>
</book>
<book>
<title>Mastering XSLT</title>
<author>Jane Smith</author>
</book>
</library>
XSLT (transform.xsl)
<xsl:stylesheet xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform" version="1.0">
<xsl:template match="/">
<html>
<body>
<h1>Library Books</h1>
<ul>
<xsl:for-each select="library/book">
<li><xsl:value-of select="title"/> by <xsl:value-of select="author"/></li>
</xsl:for-each>
</ul> <script data-no-optimize="1">window.lazyLoadOptions=Object.assign({},{threshold:300},window.lazyLoadOptions||{});!function(t,e){"object"==typeof exports&&"undefined"!=typeof module?module.exports=e():"function"==typeof define&&define.amd?define(e):(t="undefined"!=typeof globalThis?globalThis:t||self).LazyLoad=e()}(this,function(){"use strict";function e(){return(e=Object.assign||function(t){for(var e=1;e<arguments.length;e++){var n,a=arguments[e];for(n in a)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(a,n)&&(t[n]=a[n])}return t}).apply(this,arguments)}function o(t){return e({},at,t)}function l(t,e){return t.getAttribute(gt+e)}function c(t){return l(t,vt)}function s(t,e){return function(t,e,n){e=gt+e;null!==n?t.setAttribute(e,n):t.removeAttribute(e)}(t,vt,e)}function i(t){return s(t,null),0}function r(t){return null===c(t)}function u(t){return c(t)===_t}function d(t,e,n,a){t&&(void 0===a?void 0===n?t(e):t(e,n):t(e,n,a))}function f(t,e){et?t.classList.add(e):t.className+=(t.className?" ":"")+e}function _(t,e){et?t.classList.remove(e):t.className=t.className.replace(new RegExp("(^|\\s+)"+e+"(\\s+|$)")," ").replace(/^\s+/,"").replace(/\s+$/,"")}function g(t){return t.llTempImage}function v(t,e){!e||(e=e._observer)&&e.unobserve(t)}function b(t,e){t&&(t.loadingCount+=e)}function p(t,e){t&&(t.toLoadCount=e)}function n(t){for(var e,n=[],a=0;e=t.children[a];a+=1)"SOURCE"===e.tagName&&n.push(e);return n}function h(t,e){(t=t.parentNode)&&"PICTURE"===t.tagName&&n(t).forEach(e)}function a(t,e){n(t).forEach(e)}function m(t){return!!t[lt]}function E(t){return t[lt]}function I(t){return delete t[lt]}function y(e,t){var n;m(e)||(n={},t.forEach(function(t){n[t]=e.getAttribute(t)}),e[lt]=n)}function L(a,t){var o;m(a)&&(o=E(a),t.forEach(function(t){var e,n;e=a,(t=o[n=t])?e.setAttribute(n,t):e.removeAttribute(n)}))}function k(t,e,n){f(t,e.class_loading),s(t,st),n&&(b(n,1),d(e.callback_loading,t,n))}function A(t,e,n){n&&t.setAttribute(e,n)}function O(t,e){A(t,rt,l(t,e.data_sizes)),A(t,it,l(t,e.data_srcset)),A(t,ot,l(t,e.data_src))}function w(t,e,n){var a=l(t,e.data_bg_multi),o=l(t,e.data_bg_multi_hidpi);(a=nt&&o?o:a)&&(t.style.backgroundImage=a,n=n,f(t=t,(e=e).class_applied),s(t,dt),n&&(e.unobserve_completed&&v(t,e),d(e.callback_applied,t,n)))}function x(t,e){!e||0<e.loadingCount||0<e.toLoadCount||d(t.callback_finish,e)}function M(t,e,n){t.addEventListener(e,n),t.llEvLisnrs[e]=n}function N(t){return!!t.llEvLisnrs}function z(t){if(N(t)){var e,n,a=t.llEvLisnrs;for(e in a){var o=a[e];n=e,o=o,t.removeEventListener(n,o)}delete t.llEvLisnrs}}function C(t,e,n){var a;delete t.llTempImage,b(n,-1),(a=n)&&--a.toLoadCount,_(t,e.class_loading),e.unobserve_completed&&v(t,n)}function R(i,r,c){var l=g(i)||i;N(l)||function(t,e,n){N(t)||(t.llEvLisnrs={});var a="VIDEO"===t.tagName?"loadeddata":"load";M(t,a,e),M(t,"error",n)}(l,function(t){var e,n,a,o;n=r,a=c,o=u(e=i),C(e,n,a),f(e,n.class_loaded),s(e,ut),d(n.callback_loaded,e,a),o||x(n,a),z(l)},function(t){var e,n,a,o;n=r,a=c,o=u(e=i),C(e,n,a),f(e,n.class_error),s(e,ft),d(n.callback_error,e,a),o||x(n,a),z(l)})}function T(t,e,n){var a,o,i,r,c;t.llTempImage=document.createElement("IMG"),R(t,e,n),m(c=t)||(c[lt]={backgroundImage:c.style.backgroundImage}),i=n,r=l(a=t,(o=e).data_bg),c=l(a,o.data_bg_hidpi),(r=nt&&c?c:r)&&(a.style.backgroundImage='url("'.concat(r,'")'),g(a).setAttribute(ot,r),k(a,o,i)),w(t,e,n)}function G(t,e,n){var a;R(t,e,n),a=e,e=n,(t=Et[(n=t).tagName])&&(t(n,a),k(n,a,e))}function D(t,e,n){var a;a=t,(-1<It.indexOf(a.tagName)?G:T)(t,e,n)}function S(t,e,n){var a;t.setAttribute("loading","lazy"),R(t,e,n),a=e,(e=Et[(n=t).tagName])&&e(n,a),s(t,_t)}function V(t){t.removeAttribute(ot),t.removeAttribute(it),t.removeAttribute(rt)}function j(t){h(t,function(t){L(t,mt)}),L(t,mt)}function F(t){var e;(e=yt[t.tagName])?e(t):m(e=t)&&(t=E(e),e.style.backgroundImage=t.backgroundImage)}function P(t,e){var n;F(t),n=e,r(e=t)||u(e)||(_(e,n.class_entered),_(e,n.class_exited),_(e,n.class_applied),_(e,n.class_loading),_(e,n.class_loaded),_(e,n.class_error)),i(t),I(t)}function U(t,e,n,a){var o;n.cancel_on_exit&&(c(t)!==st||"IMG"===t.tagName&&(z(t),h(o=t,function(t){V(t)}),V(o),j(t),_(t,n.class_loading),b(a,-1),i(t),d(n.callback_cancel,t,e,a)))}function $(t,e,n,a){var o,i,r=(i=t,0<=bt.indexOf(c(i)));s(t,"entered"),f(t,n.class_entered),_(t,n.class_exited),o=t,i=a,n.unobserve_entered&&v(o,i),d(n.callback_enter,t,e,a),r||D(t,n,a)}function q(t){return t.use_native&&"loading"in HTMLImageElement.prototype}function H(t,o,i){t.forEach(function(t){return(a=t).isIntersecting||0<a.intersectionRatio?$(t.target,t,o,i):(e=t.target,n=t,a=o,t=i,void(r(e)||(f(e,a.class_exited),U(e,n,a,t),d(a.callback_exit,e,n,t))));var e,n,a})}function B(e,n){var t;tt&&!q(e)&&(n._observer=new IntersectionObserver(function(t){H(t,e,n)},{root:(t=e).container===document?null:t.container,rootMargin:t.thresholds||t.threshold+"px"}))}function J(t){return Array.prototype.slice.call(t)}function K(t){return t.container.querySelectorAll(t.elements_selector)}function Q(t){return c(t)===ft}function W(t,e){return e=t||K(e),J(e).filter(r)}function X(e,t){var n;(n=K(e),J(n).filter(Q)).forEach(function(t){_(t,e.class_error),i(t)}),t.update()}function t(t,e){var n,a,t=o(t);this._settings=t,this.loadingCount=0,B(t,this),n=t,a=this,Y&&window.addEventListener("online",function(){X(n,a)}),this.update(e)}var Y="undefined"!=typeof window,Z=Y&&!("onscroll"in window)||"undefined"!=typeof navigator&&/(gle|ing|ro)bot|crawl|spider/i.test(navigator.userAgent),tt=Y&&"IntersectionObserver"in window,et=Y&&"classList"in document.createElement("p"),nt=Y&&1<window.devicePixelRatio,at={elements_selector:".lazy",container:Z||Y?document:null,threshold:300,thresholds:null,data_src:"src",data_srcset:"srcset",data_sizes:"sizes",data_bg:"bg",data_bg_hidpi:"bg-hidpi",data_bg_multi:"bg-multi",data_bg_multi_hidpi:"bg-multi-hidpi",data_poster:"poster",class_applied:"applied",class_loading:"litespeed-loading",class_loaded:"litespeed-loaded",class_error:"error",class_entered:"entered",class_exited:"exited",unobserve_completed:!0,unobserve_entered:!1,cancel_on_exit:!0,callback_enter:null,callback_exit:null,callback_applied:null,callback_loading:null,callback_loaded:null,callback_error:null,callback_finish:null,callback_cancel:null,use_native:!1},ot="src",it="srcset",rt="sizes",ct="poster",lt="llOriginalAttrs",st="loading",ut="loaded",dt="applied",ft="error",_t="native",gt="data-",vt="ll-status",bt=[st,ut,dt,ft],pt=[ot],ht=[ot,ct],mt=[ot,it,rt],Et={IMG:function(t,e){h(t,function(t){y(t,mt),O(t,e)}),y(t,mt),O(t,e)},IFRAME:function(t,e){y(t,pt),A(t,ot,l(t,e.data_src))},VIDEO:function(t,e){a(t,function(t){y(t,pt),A(t,ot,l(t,e.data_src))}),y(t,ht),A(t,ct,l(t,e.data_poster)),A(t,ot,l(t,e.data_src)),t.load()}},It=["IMG","IFRAME","VIDEO"],yt={IMG:j,IFRAME:function(t){L(t,pt)},VIDEO:function(t){a(t,function(t){L(t,pt)}),L(t,ht),t.load()}},Lt=["IMG","IFRAME","VIDEO"];return t.prototype={update:function(t){var e,n,a,o=this._settings,i=W(t,o);{if(p(this,i.length),!Z&&tt)return q(o)?(e=o,n=this,i.forEach(function(t){-1!==Lt.indexOf(t.tagName)&&S(t,e,n)}),void p(n,0)):(t=this._observer,o=i,t.disconnect(),a=t,void o.forEach(function(t){a.observe(t)}));this.loadAll(i)}},destroy:function(){this._observer&&this._observer.disconnect(),K(this._settings).forEach(function(t){I(t)}),delete this._observer,delete this._settings,delete this.loadingCount,delete this.toLoadCount},loadAll:function(t){var e=this,n=this._settings;W(t,n).forEach(function(t){v(t,e),D(t,n,e)})},restoreAll:function(){var e=this._settings;K(e).forEach(function(t){P(t,e)})}},t.load=function(t,e){e=o(e);D(t,e)},t.resetStatus=function(t){i(t)},t}),function(t,e){"use strict";function n(){e.body.classList.add("litespeed_lazyloaded")}function a(){console.log("[LiteSpeed] Start Lazy Load"),o=new LazyLoad(Object.assign({},t.lazyLoadOptions||{},{elements_selector:"[data-lazyloaded]",callback_finish:n})),i=function(){o.update()},t.MutationObserver&&new MutationObserver(i).observe(e.documentElement,{childList:!0,subtree:!0,attributes:!0})}var o,i;t.addEventListener?t.addEventListener("load",a,!1):t.attachEvent("onload",a)}(window,document);</script><script data-no-optimize="1">window.litespeed_ui_events=window.litespeed_ui_events||["mouseover","click","keydown","wheel","touchmove","touchstart"];var urlCreator=window.URL||window.webkitURL;function litespeed_load_delayed_js_force(){console.log("[LiteSpeed] Start Load JS Delayed"),litespeed_ui_events.forEach(e=>{window.removeEventListener(e,litespeed_load_delayed_js_force,{passive:!0})}),document.querySelectorAll("iframe[data-litespeed-src]").forEach(e=>{e.setAttribute("src",e.getAttribute("data-litespeed-src"))}),"loading"==document.readyState?window.addEventListener("DOMContentLoaded",litespeed_load_delayed_js):litespeed_load_delayed_js()}litespeed_ui_events.forEach(e=>{window.addEventListener(e,litespeed_load_delayed_js_force,{passive:!0})});async function litespeed_load_delayed_js(){let t=[];for(var d in document.querySelectorAll('script[type="litespeed/javascript"]').forEach(e=>{t.push(e)}),t)await new Promise(e=>litespeed_load_one(t[d],e));document.dispatchEvent(new Event("DOMContentLiteSpeedLoaded")),window.dispatchEvent(new Event("DOMContentLiteSpeedLoaded"))}function litespeed_load_one(t,e){console.log("[LiteSpeed] Load ",t);var d=document.createElement("script");d.addEventListener("load",e),d.addEventListener("error",e),t.getAttributeNames().forEach(e=>{"type"!=e&&d.setAttribute("data-src"==e?"src":e,t.getAttribute(e))});let a=!(d.type="text/javascript");!d.src&&t.textContent&&(d.src=litespeed_inline2src(t.textContent),a=!0),t.after(d),t.remove(),a&&e()}function litespeed_inline2src(t){try{var d=urlCreator.createObjectURL(new Blob([t.replace(/^(?:<!--)?(.*?)(?:-->)?$/gm,"$1")],{type:"text/javascript"}))}catch(e){d="data:text/javascript;base64,"+btoa(t.replace(/^(?:<!--)?(.*?)(?:-->)?$/gm,"$1"))}return d}</script><script data-no-optimize="1">var litespeed_vary=document.cookie.replace(/(?:(?:^|.*;\s*)_lscache_vary\s*\=\s*([^;]*).*$)|^.*$/,"");litespeed_vary||fetch("/wp-content/plugins/litespeed-cache/guest.vary.php",{method:"POST",cache:"no-cache",redirect:"follow"}).then(e=>e.json()).then(e=>{console.log(e),e.hasOwnProperty("reload")&&"yes"==e.reload&&(sessionStorage.setItem("litespeed_docref",document.referrer),window.location.reload(!0))});</script><script data-optimized="1" type="litespeed/javascript" data-src="https://diginode.in/wp-content/litespeed/js/5ad5da7e80e1ecf64f3d75c5dab7ddb4.js?ver=da7aa"></script></body>
</html>
</xsl:template>
</xsl:stylesheet>
XProc Pipeline (pipeline.xpl)
<p:declare-step xmlns:p="http://www.w3.org/ns/xproc">
<p:input port="source"/>
<p:input port="stylesheet"/>
<p:output port="result"/>
<p:xslt name="transform">
<p:with-input port="source" href="books.xml"/>
<p:with-input port="stylesheet" href="transform.xsl"/>
<p:output port="result"/>
</p:xslt>
</p:declare-step>
Explanation of the Code
p:declare-step: Declares the pipeline and its steps.p:input: Defines the input ports where the XML document and XSLT are loaded.p:xslt: Executes an XSLT transformation.p:output: Specifies where the output of the transformation will be sent.
Output:
This XProc pipeline processes the books.xml file, applies the XSLT transformation, and outputs an HTML file listing the book titles and authors.
<html>
<body>
<h1>Library Books</h1>
<ul>
<li>Learning XML by John Doe</li>
<li>Mastering XSLT by Jane Smith</li>
</ul> <script data-no-optimize="1">window.lazyLoadOptions=Object.assign({},{threshold:300},window.lazyLoadOptions||{});!function(t,e){"object"==typeof exports&&"undefined"!=typeof module?module.exports=e():"function"==typeof define&&define.amd?define(e):(t="undefined"!=typeof globalThis?globalThis:t||self).LazyLoad=e()}(this,function(){"use strict";function e(){return(e=Object.assign||function(t){for(var e=1;e<arguments.length;e++){var n,a=arguments[e];for(n in a)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(a,n)&&(t[n]=a[n])}return t}).apply(this,arguments)}function o(t){return e({},at,t)}function l(t,e){return t.getAttribute(gt+e)}function c(t){return l(t,vt)}function s(t,e){return function(t,e,n){e=gt+e;null!==n?t.setAttribute(e,n):t.removeAttribute(e)}(t,vt,e)}function i(t){return s(t,null),0}function r(t){return null===c(t)}function u(t){return c(t)===_t}function d(t,e,n,a){t&&(void 0===a?void 0===n?t(e):t(e,n):t(e,n,a))}function f(t,e){et?t.classList.add(e):t.className+=(t.className?" ":"")+e}function _(t,e){et?t.classList.remove(e):t.className=t.className.replace(new RegExp("(^|\\s+)"+e+"(\\s+|$)")," ").replace(/^\s+/,"").replace(/\s+$/,"")}function g(t){return t.llTempImage}function v(t,e){!e||(e=e._observer)&&e.unobserve(t)}function b(t,e){t&&(t.loadingCount+=e)}function p(t,e){t&&(t.toLoadCount=e)}function n(t){for(var e,n=[],a=0;e=t.children[a];a+=1)"SOURCE"===e.tagName&&n.push(e);return n}function h(t,e){(t=t.parentNode)&&"PICTURE"===t.tagName&&n(t).forEach(e)}function a(t,e){n(t).forEach(e)}function m(t){return!!t[lt]}function E(t){return t[lt]}function I(t){return delete t[lt]}function y(e,t){var n;m(e)||(n={},t.forEach(function(t){n[t]=e.getAttribute(t)}),e[lt]=n)}function L(a,t){var o;m(a)&&(o=E(a),t.forEach(function(t){var e,n;e=a,(t=o[n=t])?e.setAttribute(n,t):e.removeAttribute(n)}))}function k(t,e,n){f(t,e.class_loading),s(t,st),n&&(b(n,1),d(e.callback_loading,t,n))}function A(t,e,n){n&&t.setAttribute(e,n)}function O(t,e){A(t,rt,l(t,e.data_sizes)),A(t,it,l(t,e.data_srcset)),A(t,ot,l(t,e.data_src))}function w(t,e,n){var a=l(t,e.data_bg_multi),o=l(t,e.data_bg_multi_hidpi);(a=nt&&o?o:a)&&(t.style.backgroundImage=a,n=n,f(t=t,(e=e).class_applied),s(t,dt),n&&(e.unobserve_completed&&v(t,e),d(e.callback_applied,t,n)))}function x(t,e){!e||0<e.loadingCount||0<e.toLoadCount||d(t.callback_finish,e)}function M(t,e,n){t.addEventListener(e,n),t.llEvLisnrs[e]=n}function N(t){return!!t.llEvLisnrs}function z(t){if(N(t)){var e,n,a=t.llEvLisnrs;for(e in a){var o=a[e];n=e,o=o,t.removeEventListener(n,o)}delete t.llEvLisnrs}}function C(t,e,n){var a;delete t.llTempImage,b(n,-1),(a=n)&&--a.toLoadCount,_(t,e.class_loading),e.unobserve_completed&&v(t,n)}function R(i,r,c){var l=g(i)||i;N(l)||function(t,e,n){N(t)||(t.llEvLisnrs={});var a="VIDEO"===t.tagName?"loadeddata":"load";M(t,a,e),M(t,"error",n)}(l,function(t){var e,n,a,o;n=r,a=c,o=u(e=i),C(e,n,a),f(e,n.class_loaded),s(e,ut),d(n.callback_loaded,e,a),o||x(n,a),z(l)},function(t){var e,n,a,o;n=r,a=c,o=u(e=i),C(e,n,a),f(e,n.class_error),s(e,ft),d(n.callback_error,e,a),o||x(n,a),z(l)})}function T(t,e,n){var a,o,i,r,c;t.llTempImage=document.createElement("IMG"),R(t,e,n),m(c=t)||(c[lt]={backgroundImage:c.style.backgroundImage}),i=n,r=l(a=t,(o=e).data_bg),c=l(a,o.data_bg_hidpi),(r=nt&&c?c:r)&&(a.style.backgroundImage='url("'.concat(r,'")'),g(a).setAttribute(ot,r),k(a,o,i)),w(t,e,n)}function G(t,e,n){var a;R(t,e,n),a=e,e=n,(t=Et[(n=t).tagName])&&(t(n,a),k(n,a,e))}function D(t,e,n){var a;a=t,(-1<It.indexOf(a.tagName)?G:T)(t,e,n)}function S(t,e,n){var a;t.setAttribute("loading","lazy"),R(t,e,n),a=e,(e=Et[(n=t).tagName])&&e(n,a),s(t,_t)}function V(t){t.removeAttribute(ot),t.removeAttribute(it),t.removeAttribute(rt)}function j(t){h(t,function(t){L(t,mt)}),L(t,mt)}function F(t){var e;(e=yt[t.tagName])?e(t):m(e=t)&&(t=E(e),e.style.backgroundImage=t.backgroundImage)}function P(t,e){var n;F(t),n=e,r(e=t)||u(e)||(_(e,n.class_entered),_(e,n.class_exited),_(e,n.class_applied),_(e,n.class_loading),_(e,n.class_loaded),_(e,n.class_error)),i(t),I(t)}function U(t,e,n,a){var o;n.cancel_on_exit&&(c(t)!==st||"IMG"===t.tagName&&(z(t),h(o=t,function(t){V(t)}),V(o),j(t),_(t,n.class_loading),b(a,-1),i(t),d(n.callback_cancel,t,e,a)))}function $(t,e,n,a){var o,i,r=(i=t,0<=bt.indexOf(c(i)));s(t,"entered"),f(t,n.class_entered),_(t,n.class_exited),o=t,i=a,n.unobserve_entered&&v(o,i),d(n.callback_enter,t,e,a),r||D(t,n,a)}function q(t){return t.use_native&&"loading"in HTMLImageElement.prototype}function H(t,o,i){t.forEach(function(t){return(a=t).isIntersecting||0<a.intersectionRatio?$(t.target,t,o,i):(e=t.target,n=t,a=o,t=i,void(r(e)||(f(e,a.class_exited),U(e,n,a,t),d(a.callback_exit,e,n,t))));var e,n,a})}function B(e,n){var t;tt&&!q(e)&&(n._observer=new IntersectionObserver(function(t){H(t,e,n)},{root:(t=e).container===document?null:t.container,rootMargin:t.thresholds||t.threshold+"px"}))}function J(t){return Array.prototype.slice.call(t)}function K(t){return t.container.querySelectorAll(t.elements_selector)}function Q(t){return c(t)===ft}function W(t,e){return e=t||K(e),J(e).filter(r)}function X(e,t){var n;(n=K(e),J(n).filter(Q)).forEach(function(t){_(t,e.class_error),i(t)}),t.update()}function t(t,e){var n,a,t=o(t);this._settings=t,this.loadingCount=0,B(t,this),n=t,a=this,Y&&window.addEventListener("online",function(){X(n,a)}),this.update(e)}var Y="undefined"!=typeof window,Z=Y&&!("onscroll"in window)||"undefined"!=typeof navigator&&/(gle|ing|ro)bot|crawl|spider/i.test(navigator.userAgent),tt=Y&&"IntersectionObserver"in window,et=Y&&"classList"in document.createElement("p"),nt=Y&&1<window.devicePixelRatio,at={elements_selector:".lazy",container:Z||Y?document:null,threshold:300,thresholds:null,data_src:"src",data_srcset:"srcset",data_sizes:"sizes",data_bg:"bg",data_bg_hidpi:"bg-hidpi",data_bg_multi:"bg-multi",data_bg_multi_hidpi:"bg-multi-hidpi",data_poster:"poster",class_applied:"applied",class_loading:"litespeed-loading",class_loaded:"litespeed-loaded",class_error:"error",class_entered:"entered",class_exited:"exited",unobserve_completed:!0,unobserve_entered:!1,cancel_on_exit:!0,callback_enter:null,callback_exit:null,callback_applied:null,callback_loading:null,callback_loaded:null,callback_error:null,callback_finish:null,callback_cancel:null,use_native:!1},ot="src",it="srcset",rt="sizes",ct="poster",lt="llOriginalAttrs",st="loading",ut="loaded",dt="applied",ft="error",_t="native",gt="data-",vt="ll-status",bt=[st,ut,dt,ft],pt=[ot],ht=[ot,ct],mt=[ot,it,rt],Et={IMG:function(t,e){h(t,function(t){y(t,mt),O(t,e)}),y(t,mt),O(t,e)},IFRAME:function(t,e){y(t,pt),A(t,ot,l(t,e.data_src))},VIDEO:function(t,e){a(t,function(t){y(t,pt),A(t,ot,l(t,e.data_src))}),y(t,ht),A(t,ct,l(t,e.data_poster)),A(t,ot,l(t,e.data_src)),t.load()}},It=["IMG","IFRAME","VIDEO"],yt={IMG:j,IFRAME:function(t){L(t,pt)},VIDEO:function(t){a(t,function(t){L(t,pt)}),L(t,ht),t.load()}},Lt=["IMG","IFRAME","VIDEO"];return t.prototype={update:function(t){var e,n,a,o=this._settings,i=W(t,o);{if(p(this,i.length),!Z&&tt)return q(o)?(e=o,n=this,i.forEach(function(t){-1!==Lt.indexOf(t.tagName)&&S(t,e,n)}),void p(n,0)):(t=this._observer,o=i,t.disconnect(),a=t,void o.forEach(function(t){a.observe(t)}));this.loadAll(i)}},destroy:function(){this._observer&&this._observer.disconnect(),K(this._settings).forEach(function(t){I(t)}),delete this._observer,delete this._settings,delete this.loadingCount,delete this.toLoadCount},loadAll:function(t){var e=this,n=this._settings;W(t,n).forEach(function(t){v(t,e),D(t,n,e)})},restoreAll:function(){var e=this._settings;K(e).forEach(function(t){P(t,e)})}},t.load=function(t,e){e=o(e);D(t,e)},t.resetStatus=function(t){i(t)},t}),function(t,e){"use strict";function n(){e.body.classList.add("litespeed_lazyloaded")}function a(){console.log("[LiteSpeed] Start Lazy Load"),o=new LazyLoad(Object.assign({},t.lazyLoadOptions||{},{elements_selector:"[data-lazyloaded]",callback_finish:n})),i=function(){o.update()},t.MutationObserver&&new MutationObserver(i).observe(e.documentElement,{childList:!0,subtree:!0,attributes:!0})}var o,i;t.addEventListener?t.addEventListener("load",a,!1):t.attachEvent("onload",a)}(window,document);</script><script data-no-optimize="1">window.litespeed_ui_events=window.litespeed_ui_events||["mouseover","click","keydown","wheel","touchmove","touchstart"];var urlCreator=window.URL||window.webkitURL;function litespeed_load_delayed_js_force(){console.log("[LiteSpeed] Start Load JS Delayed"),litespeed_ui_events.forEach(e=>{window.removeEventListener(e,litespeed_load_delayed_js_force,{passive:!0})}),document.querySelectorAll("iframe[data-litespeed-src]").forEach(e=>{e.setAttribute("src",e.getAttribute("data-litespeed-src"))}),"loading"==document.readyState?window.addEventListener("DOMContentLoaded",litespeed_load_delayed_js):litespeed_load_delayed_js()}litespeed_ui_events.forEach(e=>{window.addEventListener(e,litespeed_load_delayed_js_force,{passive:!0})});async function litespeed_load_delayed_js(){let t=[];for(var d in document.querySelectorAll('script[type="litespeed/javascript"]').forEach(e=>{t.push(e)}),t)await new Promise(e=>litespeed_load_one(t[d],e));document.dispatchEvent(new Event("DOMContentLiteSpeedLoaded")),window.dispatchEvent(new Event("DOMContentLiteSpeedLoaded"))}function litespeed_load_one(t,e){console.log("[LiteSpeed] Load ",t);var d=document.createElement("script");d.addEventListener("load",e),d.addEventListener("error",e),t.getAttributeNames().forEach(e=>{"type"!=e&&d.setAttribute("data-src"==e?"src":e,t.getAttribute(e))});let a=!(d.type="text/javascript");!d.src&&t.textContent&&(d.src=litespeed_inline2src(t.textContent),a=!0),t.after(d),t.remove(),a&&e()}function litespeed_inline2src(t){try{var d=urlCreator.createObjectURL(new Blob([t.replace(/^(?:<!--)?(.*?)(?:-->)?$/gm,"$1")],{type:"text/javascript"}))}catch(e){d="data:text/javascript;base64,"+btoa(t.replace(/^(?:<!--)?(.*?)(?:-->)?$/gm,"$1"))}return d}</script><script data-optimized="1" type="litespeed/javascript" data-src="https://diginode.in/wp-content/litespeed/js/5ad5da7e80e1ecf64f3d75c5dab7ddb4.js?ver=da7aa"></script></body>
</html>
Types of XProc Steps
XProc offers various types of steps, each designed to perform a specific function in an XML processing pipeline.
Atomic Steps
Atomic steps are the building blocks of XProc pipelines. Each atomic step performs a simple, well-defined operation. Examples include:
p:load: Loads an XML document.p:xslt: Applies an XSLT stylesheet to transform an XML document.p:validate-with-xml-schema: Validates an XML document against an XML Schema.
Example: Loading and Validating XML
<p:declare-step xmlns:p="http://www.w3.org/ns/xproc">
<p:load href="document.xml" name="load-doc"/>
<p:validate-with-xml-schema schema="schema.xsd">
<p:with-input port="source" href="document.xml"/>
</p:validate-with-xml-schema>
</p:declare-step>
Compound Steps
Compound steps combine multiple atomic steps to form a more complex pipeline. This allows you to create sub-pipelines within the main pipeline.
Example: Combining Steps
<p:declare-step xmlns:p="http://www.w3.org/ns/xproc">
<p:input port="source"/>
<p:group>
<p:xslt>
<p:with-input port="source" href="input.xml"/>
<p:with-input port="stylesheet" href="style.xsl"/>
</p:xslt>
<p:validate-with-xml-schema schema="schema.xsd"/>
</p:group>
</p:declare-step>
Advanced XProc Features
Conditional Execution
XProc supports conditional processing, allowing steps to be executed only when certain conditions are met. This can be achieved using the p:choose element.
Example: Conditional Pipeline Execution
<p:declare-step xmlns:p="http://www.w3.org/ns/xproc">
<p:choose>
<p:when test="count(//book) > 10">
<p:xslt name="transform">
<p:with-input port="source" href="books.xml"/>
<p:with-input port="stylesheet" href="transform.xsl"/>
</p:xslt>
</p:when>
<p:otherwise>
<p:log message="Fewer than 10 books, skipping transformation"/>
</p:otherwise>
</p:choose>
</p:declare-step>
Error Handling in XProc
XProc includes error-handling mechanisms that allow you to manage and log errors gracefully using the p:catch element.
Example: Error Handling
<p:declare-step xmlns:p="http://www.w3.org/ns/xproc">
<p:try>
<p:xslt name="transform">
<p:with-input port="source" href="books.xml"/>
<p:with-input port="stylesheet" href="transform.xsl"/>
</p:xslt>
</p:try>
<p:catch>
<p:log message="Transformation failed."/>
</p:catch>
</p:declare-step>
Parallel Execution
XProc allows steps to be executed in parallel, which can be useful for tasks like generating multiple outputs from a single input document (e.g., HTML, PDF, and JSON).
Example: Parallel Pipeline
<p:declare-step xmlns:p="http://www.w3.org/ns/xproc">
<p:for-each>
<p:xslt>
<p:with-input port="source" href="books.xml"/>
<p:with-input port="stylesheet" href="transform.xsl"/>
</p:xslt>
</p:for-each>
</p:declare-step>
Common Use Cases for XProc
Batch XML Processing
XProc is widely used for batch processing XML files. For example, you can create a pipeline that processes multiple XML documents, applies transformations, and validates them before sending the output to various destinations (like a database or a web service).
Automated Publishing Systems
XProc is also used in publishing systems where XML documents, such as technical manuals or books, need to be transformed into multiple formats like HTML, PDF, or ePub.
XProc provides a powerful, flexible, and modular approach to processing XML documents. With the ability to define pipelines, automate workflows, and handle complex tasks like transformations, validation, and error handling, XProc is an essential tool for XML developers. Happy Coding!❤️
