Performing Joins in MySQL
We'll explore the concept of performing joins in MySQL queries using Python. Joins are used to combine rows from two or more tables based on a related column between them. We'll cover the basics of joins, including different types of joins such as inner join, left join, right join, and outer join.
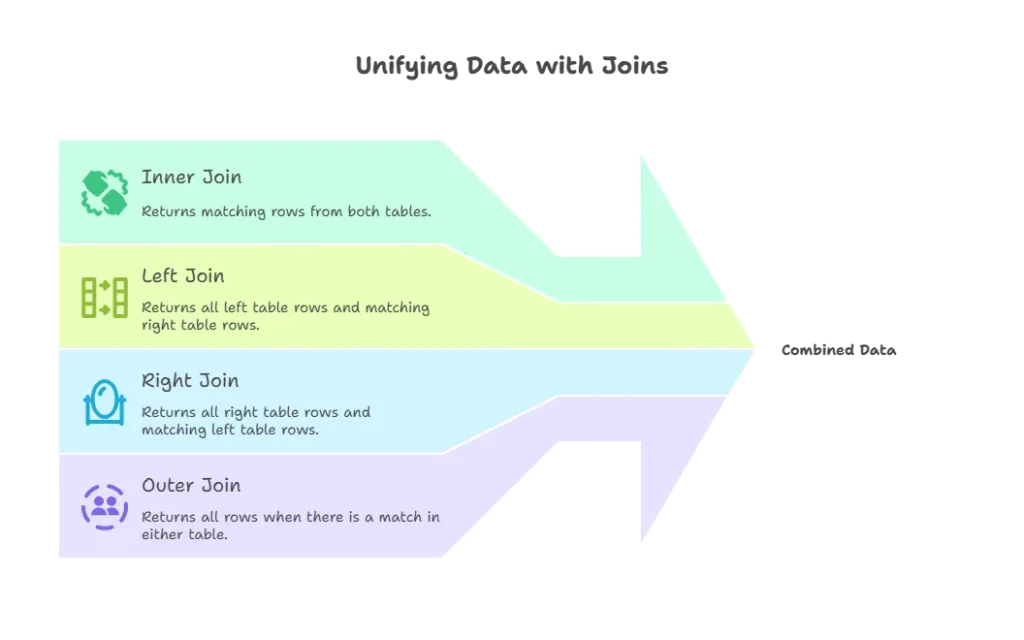
Introduction to Joins
Understanding Joins
Joins are used to retrieve data from multiple tables based on a related column between them. They allow you to combine data from different tables into a single result set.
Types of Joins
- Inner Join: Returns only the rows where there is a match in both tables.
- Left Join: Returns all rows from the left table and matching rows from the right table.
- Right Join: Returns all rows from the right table and matching rows from the left table.
- Outer Join: Returns all rows when there is a match in either table.
Inner Join
Syntax of Inner Join
SELECT columns
FROM table1
INNER JOIN table2 ON table1.column = table2.column;
Example: Inner Join
Let’s retrieve data from two tables, “students” and “grades”, where there is a match in the “student_id” column.
import mysql.connector
# Connect to MySQL database
conn = mysql.connector.connect(
host="localhost",
user="username",
password="password",
database="mydatabase"
)
# Create a cursor
cursor = conn.cursor()
# Execute INNER JOIN query
cursor.execute("SELECT students.name, grades.grade FROM students INNER JOIN grades ON students.id = grades.student_id")
# Fetch and print the results
results = cursor.fetchall()
for row in results:
print(row)
# Close cursor and connection
cursor.close()
conn.close()
Explanation:
- We establish a connection to the MySQL database where the “students” and “grades” tables are located.
- We use an INNER JOIN query to retrieve data from both tables where there is a match in the “student_id” column.
- We fetch and print the results obtained from the query.
Left Join
Syntax of Left Join
SELECT columns
FROM table1
LEFT JOIN table2 ON table1.column = table2.column;
Example: Left Join
Let’s retrieve data from the “students” table and matching grades (if available) from the “grades” table.
# Execute LEFT JOIN query
cursor.execute("SELECT students.name, grades.grade FROM students LEFT JOIN grades ON students.id = grades.student_id")
# Fetch and print the results
results = cursor.fetchall()
for row in results:
print(row)
Explanation:
- We use a LEFT JOIN query to retrieve all rows from the “students” table and matching grades (if available) from the “grades” table.
- This ensures that all rows from the left table (“students”) are included in the result set, regardless of whether there is a matching row in the right table (“grades”).
Right Join
Syntax of Right Join
SELECT columns
FROM table1
RIGHT JOIN table2 ON table1.column = table2.column;
Example: Right Join
Let’s retrieve data from the “grades” table and matching students (if available) from the “students” table.
# Execute RIGHT JOIN query
cursor.execute("SELECT students.name, grades.grade FROM students RIGHT JOIN grades ON students.id = grades.student_id")
# Fetch and print the results
results = cursor.fetchall()
for row in results:
print(row)
Explanation:
- We use a RIGHT JOIN query to retrieve all rows from the “grades” table and matching students (if available) from the “students” table.
- This ensures that all rows from the right table (“grades”) are included in the result set, regardless of whether there is a matching row in the left table (“students”).
Outer Join
Syntax of Outer Join
SELECT columns
FROM table1
FULL OUTER JOIN table2 ON table1.column = table2.column;
Example: Outer Join
Let’s retrieve data from both the “students” and “grades” tables, including unmatched rows from both tables.
# Execute OUTER JOIN query
cursor.execute("SELECT students.name, grades.grade FROM students FULL OUTER JOIN grades ON students.id = grades.student_id")
# Fetch and print the results
results = cursor.fetchall()
for row in results:
print(row)
Explanation:
- We use a FULL OUTER JOIN query to retrieve all rows from both the “students” and “grades” tables, including unmatched rows from both tables.
- This ensures that all rows from both tables are included in the result set, regardless of whether there is a matching row in the other table.
Advanced Joins
Introduction to Advanced Joins
While basic joins like inner, left, right, and outer joins cover most scenarios, there are advanced join techniques that can be useful in specific situations.
Cross Join
A cross join returns the Cartesian product of two tables, meaning it combines each row from the first table with every row from the second table.
Syntax of Cross Join
SELECT columns
FROM table1
CROSS JOIN table2;
Example: Cross Join
Let’s retrieve the Cartesian product of the “students” and “courses” tables.
# Execute CROSS JOIN query
cursor.execute("SELECT students.name, courses.course_name FROM students CROSS JOIN courses")
# Fetch and print the results
results = cursor.fetchall()
for row in results:
print(row)
Explanation:
- We use a CROSS JOIN query to retrieve the Cartesian product of the “students” and “courses” tables.
- This results in a combination of every student with every course, regardless of any matching criteria.
Self Join
A self join is a join that occurs when a table is joined with itself. It can be useful for comparing rows within the same table.
Syntax of Self Join
SELECT columns
FROM table1 alias1
INNER JOIN table1 alias2 ON alias1.column = alias2.column;
Example: Self Join
Let’s retrieve pairs of students who have the same grade.
# Execute SELF JOIN query
cursor.execute("SELECT s1.name, s2.name FROM students s1 INNER JOIN students s2 ON s1.grade = s2.grade AND s1.id != s2.id")
# Fetch and print the results
results = cursor.fetchall()
for row in results:
print(row)
Explanation:
- We use a SELF JOIN query to retrieve pairs of students (s1 and s2) who have the same grade but different student IDs.
- This allows us to compare rows within the same table based on a specific criterion.
We've explored the concept of performing joins in MySQL queries using Python. We covered the basics of joins, including inner join, left join, right join, and outer join, along with their syntax and examples. Joins are powerful tools for combining data from multiple tables in a relational database system. Happy Coding!❤️
