Inserting Data in MongoDB
Inserting data into MongoDB is a fundamental operation when working with databases. In this topic, we'll explore various methods to insert data into MongoDB using Python. From basic single document inserts to advanced bulk inserts, we'll cover everything you need to know to effectively add data to your MongoDB collections.
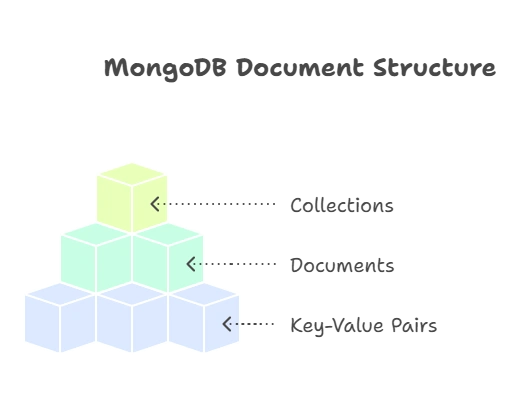
Understanding Document Structure
Before we dive into inserting data, let’s understand the structure of documents in MongoDB. Documents are JSON-like objects that store data in key-value pairs. Each document is stored in a collection and can have a unique _id field.
Inserting a Single Document
The simplest way to insert data into MongoDB is by inserting a single document. Let’s see how to do this:
import pymongo
# Connect to MongoDB
client = pymongo.MongoClient("mongodb://localhost:27017/")
# Access database
db = client["mydatabase"]
# Access collection
col = db["mycollection"]
# Create a document
document = {"name": "John", "age": 30, "city": "New York"}
# Insert document
result = col.insert_one(document)
# Print the inserted document ID
print("Inserted ID:", result.inserted_id)
Explaination:
In this example, we connected to MongoDB, accessed a database and collection, created a document, inserted it into the collection, and printed the inserted document’s ID.
# Output
Inserted ID: ObjectId('6065c7c4f097a4854f5169a8')
Inserting Multiple Documents
Inserting multiple documents at once is more efficient than inserting them one by one. Let’s insert multiple documents into our collection:
# Create multiple documents
documents = [
{"name": "Alice", "age": 25, "city": "London"},
{"name": "Bob", "age": 35, "city": "Paris"},
{"name": "Charlie", "age": 40, "city": "Tokyo"}
]
# Insert multiple documents
result = col.insert_many(documents)
# Print the inserted documents' IDs
print("Inserted IDs:", result.inserted_ids)
Explaination:
Here, we created multiple documents as a list of dictionaries and inserted them into the collection using insert_many().
# Output
Inserted IDs: [ObjectId('6065c7c4f097a4854f5169a9'), ObjectId('6065c7c4f097a4854f5169aa'), ObjectId('6065c7c4f097a4854f5169ab')]
Inserting Data with Custom IDs
By default, MongoDB generates unique _id values for inserted documents. However, you can specify your own _id values if needed:
# Create a document with a custom ID
document_with_custom_id = {"_id": 1001, "name": "David", "age": 45, "city": "Berlin"}
# Insert document with custom ID
result = col.insert_one(document_with_custom_id)
# Print the inserted document ID
print("Inserted ID:", result.inserted_id)
# Output
Inserted ID: 1001
Handling Insertion Errors
Sometimes, insertions may fail due to various reasons such as network issues or duplicate _id values. It’s essential to handle such errors gracefully. Here’s how you can handle insertion errors using error handling in Python:
try:
# Attempt to insert a document with a duplicate _id
result = col.insert_one({"_id": 1001, "name": "Eva", "age": 50, "city": "Madrid"})
print("Inserted ID:", result.inserted_id)
except pymongo.errors.DuplicateKeyError:
print("Error: Document with the same _id already exists.")
except Exception as e:
print("An error occurred:", e)
Explanation:
- We attempt to insert a document with the same custom
_id(1001) as the one inserted earlier. - We use a
try-exceptblock to catch specific errors. If aDuplicateKeyErroroccurs (indicating that a document with the same_idalready exists), we handle it gracefully by printing an error message. - We also catch any other unexpected exceptions and print an error message.
We covered the basics of inserting data into MongoDB using Python. We learned how to insert single and multiple documents into collections, as well as how to specify custom IDs for documents.
Inserting data is the first step in building a database-driven application. By mastering these techniques, you'll be well-equipped to handle data insertion tasks in your MongoDB projects. Experiment with different data structures and insertion methods to effectively store and manage your data in MongoDB. Happy coding!❤️
