RESTful APIs
RESTful APIs (Representational State Transfer APIs) are a powerful and flexible way to expose the functionality of your application over the web. They follow a set of architectural principles that make web services more scalable and easier to maintain. This chapter will guide you through the basics to advanced concepts of building RESTful APIs with Node.js and Express.js. By the end of this chapter, you'll have a thorough understanding of how to create, manage, and secure RESTful APIs.
Bonus💡: Practical example at the end of article
RESTful APIs
REST (Representational State Transfer) is an architectural style that uses a stateless, client-server, cacheable communication protocol — the HTTP protocol. RESTful APIs are web services that conform to the REST architecture, allowing different systems to communicate over the web using standard HTTP methods.
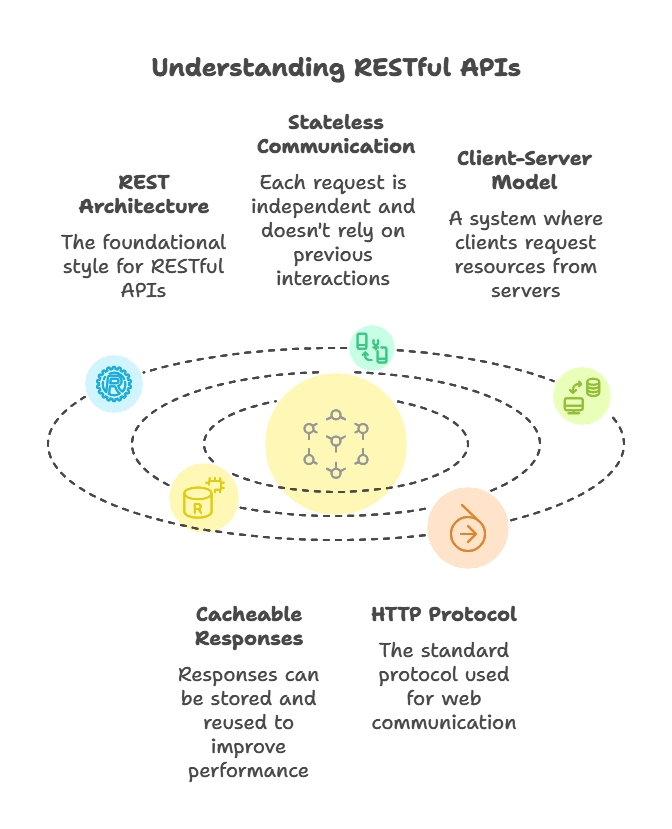
Key Principles of REST:
- Stateless: Each request from a client to the server must contain all the information needed to understand and process the request. The server does not store any state about the client session.
- Client-Server Architecture: Separation of concerns allows the client and server to evolve independently.
- Cacheable: Responses must define themselves as cacheable or non-cacheable to prevent clients from reusing stale data.
- Uniform Interface: Simplifies and decouples the architecture, which enables each part to evolve independently.
- Layered System: Enables the architecture to be composed of hierarchical layers by constraining component behavior.
Setting Up the Environment
Before we start creating a RESTful API, we need to set up our development environment.
1.Initialize the Project:
mkdir restful-api-example
cd restful-api-example
npm init -y
npm install express body-parser mongoose
2.Project Structure:
restful-api-example/
├── models/
│ └── item.js
├── routes/
│ └── items.js
├── app.js
├── index.js
├── package.json
Creating a Basic RESTful API
Setting Up Express
Create an index.js file to set up the server:
const express = require('express');
const bodyParser = require('body-parser');
const app = express();
const port = 3000;
// Middleware to parse JSON requests
app.use(bodyParser.json());
// Basic route
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.send('Welcome to the RESTful API!');
});
// Start the server
app.listen(port, () => {
console.log(`Server is running on http://localhost:${port}`);
});
Running the Server
Run the server using:
node index.js
Visit http://localhost:3000 in your browser, and you should see “Welcome to the RESTful API!”.
HTTP Methods and RESTful Routes
RESTful APIs use standard HTTP methods to perform operations on resources:
- GET: Retrieve a resource
- POST: Create a new resource
- PUT: Update an existing resource
- DELETE: Delete a resource
Example Routes
- GET /items – Retrieve a list of items
- POST /items – Create a new item
- GET /items/ – Retrieve a specific item
- PUT /items/ – Update a specific item
- DELETE /items/ – Delete a specific item
Handling Data with CRUD Operations
Setting Up Mongoose
We’ll use MongoDB as our database and Mongoose to interact with it.
Install MongoDB and Mongoose:
npm install mongoose
Create the Item Model:
// models/item.js
const mongoose = require('mongoose');
const itemSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
name: {
type: String,
required: true
},
description: String,
price: {
type: Number,
required: true
}
});
module.exports = mongoose.model('Item', itemSchema);
Create Routes for CRUD Operations
Create the items.js file:
// routes/items.js
const express = require('express');
const router = express.Router();
const Item = require('../models/item');
// Get all items
router.get('/', async (req, res) => {
try {
const items = await Item.find();
res.json(items);
} catch (err) {
res.status(500).json({ message: err.message });
}
});
// Get one item
router.get('/:id', getItem, (req, res) => {
res.json(res.item);
});
// Create an item
router.post('/', async (req, res) => {
const item = new Item({
name: req.body.name,
description: req.body.description,
price: req.body.price
});
try {
const newItem = await item.save();
res.status(201).json(newItem);
} catch (err) {
res.status(400).json({ message: err.message });
}
});
// Update an item
router.put('/:id', getItem, async (req, res) => {
if (req.body.name != null) {
res.item.name = req.body.name;
}
if (req.body.description != null) {
res.item.description = req.body.description;
}
if (req.body.price != null) {
res.item.price = req.body.price;
}
try {
const updatedItem = await res.item.save();
res.json(updatedItem);
} catch (err) {
res.status(400).json({ message: err.message });
}
});
// Delete an item
router.delete('/:id', getItem, async (req, res) => {
try {
await res.item.remove();
res.json({ message: 'Deleted Item' });
} catch (err) {
res.status(500).json({ message: err.message });
}
});
// Middleware to get item by ID
async function getItem(req, res, next) {
let item;
try {
item = await Item.findById(req.params.id);
if (item == null) {
return res.status(404).json({ message: 'Cannot find item' });
}
} catch (err) {
return res.status(500).json({ message: err.message });
}
res.item = item;
next();
}
module.exports = router;
Update app.js to Use Routes:
const express = require('express');
const mongoose = require('mongoose');
const app = express();
const itemsRouter = require('./routes/items');
const port = 3000;
// Connect to MongoDB
mongoose.connect('mongodb://localhost/restful-api', { useNewUrlParser: true, useUnifiedTopology: true });
// Middleware to parse JSON requests
app.use(express.json());
// Routes
app.use('/items', itemsRouter);
app.listen(port, () => {
console.log(`Server is running on http://localhost:${port}`);
});
Using Middleware in RESTful APIs
Middleware functions are functions that execute during the lifecycle of a request to the Express server. These functions have access to the request object (req), the response object (res), and the next middleware function in the application’s request-response cycle.
Example Middleware to Log Requests:
app.use((req, res, next) => {
console.log(`${req.method} request for '${req.url}'`);
next();
});
Error Handling in RESTful APIs
Proper error handling ensures that your API responds appropriately when things go wrong.
Example of Error Handling Middleware:
app.use((err, req, res, next) => {
console.error(err.stack);
res.status(500).send('Something broke!');
});
Validation and Sanitization
Input validation and sanitization are crucial for preventing security vulnerabilities.
Using express-validator:
npm install express-validator
Example Validation Middleware:
const { body, validationResult } = require('express-validator');
router.post('/', [
body('name').isString().notEmpty(),
body('price').isNumeric().notEmpty()
], (req, res, next) => {
const errors = validationResult(req);
if (!errors.isEmpty()) {
return res.status(400).json({ errors: errors.array() });
}
next();
}, async (req, res) => {
// Handle valid request
});
Authentication and Authorization
Authentication and authorization are critical for securing your API.
Using JSON Web Tokens (JWT) for Authentication:
npm install jsonwebtoken
Example JWT Authentication Middleware:
const jwt = require('jsonwebtoken');
function authenticateToken(req, res, next) {
const token = req.header('Authorization') && req.header('Authorization').split(' ')[1];
if (!token) return res.status(401).json({ message: 'Access Denied' });
jwt.verify(token, 'SECRET_KEY', (err, user) => {
if (err) return res.status(403).json({ message: 'Invalid Token' });
req.user = user;
next();
});
}
router.get('/protected', authenticateToken, (req, res) => {
res.json({ message: 'This is a protected route' });
});
Advanced Topics
Pagination
To handle large datasets, implement pagination.
Example Pagination Middleware:
router.get('/', async (req, res) => {
const { page = 1, limit = 10 } = req.query;
try {
const items = await Item.find()
.limit(limit * 1)
.skip((page - 1) * limit)
.exec();
const count = await Item.countDocuments();
res.json({
items,
totalPages: Math.ceil(count / limit),
currentPage: page
});
} catch (err) {
res.status(500).json({ message: err.message });
}
});
Rate Limiting
To prevent abuse, implement rate limiting.
Using express-rate-limit:
npm install express-rate-limit
Example Rate Limiting Middleware:
const rateLimit = require('express-rate-limit');
const limiter = rateLimit({
windowMs: 15 * 60 * 1000, // 15 minutes
max: 100 // limit each IP to 100 requests per windowMs
});
app.use(limiter);
Practical example
Let’s create a practical example of a RESTful API for managing a collection of books. This example will demonstrate setting up the API, handling CRUD operations, and implementing error handling, validation, and authentication.
Project Structure
book-api/
├── models/
│ └── book.js
├── routes/
│ └── books.js
├── middlewares/
│ └── auth.js
├── app.js
├── index.js
├── package.json
Setting Up the Project
1.Initialize the project:
mkdir book-api
cd book-api
npm init -y
npm install express mongoose body-parser express-validator jsonwebtoken bcryptjs
2.Create index.js:
const express = require('express');
const mongoose = require('mongoose');
const bodyParser = require('body-parser');
const booksRouter = require('./routes/books');
const app = express();
const port = 3000;
// Connect to MongoDB
mongoose.connect('mongodb://localhost/book-api', { useNewUrlParser: true, useUnifiedTopology: true });
// Middleware
app.use(bodyParser.json());
// Routes
app.use('/books', booksRouter);
app.listen(port, () => {
console.log(`Server is running on http://localhost:${port}`);
});
3.Create the Book Model:
// models/book.js
const mongoose = require('mongoose');
const bookSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
title: {
type: String,
required: true
},
author: {
type: String,
required: true
},
publishedDate: {
type: Date,
required: true
},
pages: {
type: Number,
required: true
},
genre: String
});
module.exports = mongoose.model('Book', bookSchema);
4.Create the Books Route:
// routes/books.js
const express = require('express');
const router = express.Router();
const Book = require('../models/book');
const { body, validationResult } = require('express-validator');
const authenticateToken = require('../middlewares/auth');
// Get all books
router.get('/', async (req, res) => {
try {
const books = await Book.find();
res.json(books);
} catch (err) {
res.status(500).json({ message: err.message });
}
});
// Get one book
router.get('/:id', getBook, (req, res) => {
res.json(res.book);
});
// Create a book
router.post('/', authenticateToken, [
body('title').isString().notEmpty(),
body('author').isString().notEmpty(),
body('publishedDate').isDate(),
body('pages').isInt({ min: 1 })
], async (req, res) => {
const errors = validationResult(req);
if (!errors.isEmpty()) {
return res.status(400).json({ errors: errors.array() });
}
const book = new Book({
title: req.body.title,
author: req.body.author,
publishedDate: req.body.publishedDate,
pages: req.body.pages,
genre: req.body.genre
});
try {
const newBook = await book.save();
res.status(201).json(newBook);
} catch (err) {
res.status(400).json({ message: err.message });
}
});
// Update a book
router.put('/:id', authenticateToken, getBook, [
body('title').optional().isString(),
body('author').optional().isString(),
body('publishedDate').optional().isDate(),
body('pages').optional().isInt({ min: 1 })
], async (req, res) => {
const errors = validationResult(req);
if (!errors.isEmpty()) {
return res.status(400).json({ errors: errors.array() });
}
if (req.body.title != null) {
res.book.title = req.body.title;
}
if (req.body.author != null) {
res.book.author = req.body.author;
}
if (req.body.publishedDate != null) {
res.book.publishedDate = req.body.publishedDate;
}
if (req.body.pages != null) {
res.book.pages = req.body.pages;
}
if (req.body.genre != null) {
res.book.genre = req.body.genre;
}
try {
const updatedBook = await res.book.save();
res.json(updatedBook);
} catch (err) {
res.status(400).json({ message: err.message });
}
});
// Delete a book
router.delete('/:id', authenticateToken, getBook, async (req, res) => {
try {
await res.book.remove();
res.json({ message: 'Deleted Book' });
} catch (err) {
res.status(500).json({ message: err.message });
}
});
// Middleware to get book by ID
async function getBook(req, res, next) {
let book;
try {
book = await Book.findById(req.params.id);
if (book == null) {
return res.status(404).json({ message: 'Cannot find book' });
}
} catch (err) {
return res.status(500).json({ message: err.message });
}
res.book = book;
next();
}
module.exports = router;
5.Create Authentication Middleware:
// middlewares/auth.js
const jwt = require('jsonwebtoken');
function authenticateToken(req, res, next) {
const authHeader = req.headers['authorization'];
const token = authHeader && authHeader.split(' ')[1];
if (token == null) return res.status(401).json({ message: 'Access Denied' });
jwt.verify(token, 'SECRET_KEY', (err, user) => {
if (err) return res.status(403).json({ message: 'Invalid Token' });
req.user = user;
next();
});
}
module.exports = authenticateToken;
Running the Server
node index.js
Testing the API
You can use a tool like Postman or curl to test the API endpoints.
Example Requests:
Create a Book (POST /books)
curl -X POST http://localhost:3000/books \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer <YOUR_JWT_TOKEN>" \
-d '{
"title": "The Great Gatsby",
"author": "F. Scott Fitzgerald",
"publishedDate": "1925-04-10",
"pages": 218,
"genre": "Fiction"
}'
2. Get All Books (GET /books)
curl http://localhost:3000/books
3. Get a Single Book (GET /books/)
curl http://localhost:3000/books/<BOOK_ID>
4.Update a Book (PUT /books/)
curl -X PUT http://localhost:3000/books/<BOOK_ID> \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer <YOUR_JWT_TOKEN>" \
-d '{
"title": "The Great Gatsby Updated",
"pages": 220
}'
5.Delete a Book (DELETE /books/)
curl -X DELETE http://localhost:3000/books/<BOOK_ID> \
-H "Authorization: Bearer <YOUR_JWT_TOKEN>"
Example Outputs
1.Create a Book (POST /books)
{
"_id": "60b725f10c9ebf77f8a9",
"title": "The Great Gatsby",
"author": "F. Scott Fitzgerald",
"publishedDate": "1925-04-10T00:00:00.000Z",
"pages": 218,
"genre": "Fiction",
"__v": 0
}
2.Get All Books (GET /books)
[
{
"_id": "60b725f10c9ebf77f8a9",
"title": "The Great Gatsby",
"author": "F. Scott Fitzgerald",
"publishedDate": "1925-04-10T00:00:00.000Z",
"pages": 218,
"genre": "Fiction",
"__v": 0
}
]
3.Get a Single Book (GET /books/)
{
"_id": "60b725f10c9ebf77f8a9",
"title": "The Great Gatsby",
"author": "F. Scott Fitzgerald",
"publishedDate": "1925-04-10T00:00:00.000Z",
"pages": 218,
"genre": "Fiction",
"__v": 0
}
4.Update a Book (PUT /books/)
{
"_id": "60b725f10c9ebf77f8a9",
"title": "The Great Gatsby Updated",
"author": "F. Scott Fitzgerald",
"publishedDate": "1925-04-10T00:00:00.000Z",
"pages": 220,
"genre": "Fiction",
"__v": 0
}
5.Delete a Book (DELETE /books/)
{
"message": "Deleted Book"
}
In this chapter, we've covered the fundamentals and advanced concepts of building RESTful APIs with Node.js and Express.js. We've seen how to set up an Express server, define routes, handle CRUD operations, use middleware, handle errors, validate input, and implement authentication and authorization. By following these principles and best practices, you can create robust, scalable, and secure RESTful APIs. This comprehensive guide should serve as a solid foundation for building RESTful APIs in your Node.js applications.Happy coding !❤️
