DevSecOps Practices for Node.js Development
DevSecOps is an approach that integrates security into every phase of the software development lifecycle (SDLC). Traditionally, security was often introduced late in the process, leading to vulnerabilities in production. DevSecOps embeds security from the very beginning, ensuring that security is prioritized alongside development and operations activities.In this chapter, we will explore the principles and practices of DevSecOps in the context of Node.js development, providing a complete, end-to-end guide on how to secure a Node.js application from coding to deployment. We will cover static analysis, vulnerability scanning, secure coding practices, automated security testing, and continuous monitoring in a Node.js DevSecOps pipeline.
Introduction to DevSecOps
What is DevSecOps?
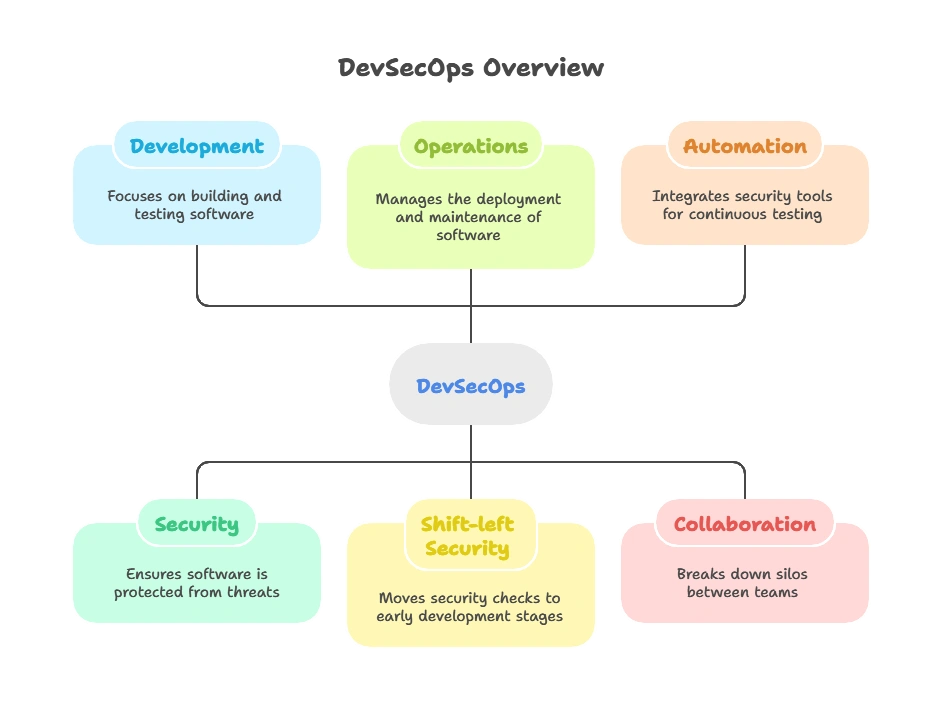
DevSecOps is a blend of development (Dev), security (Sec), and operations (Ops) that automates and embeds security practices throughout the SDLC. The goal is to address security early on and ensure that it is a shared responsibility between developers, security teams, and operations teams.
Key Principles of DevSecOps:
- Shift-left security: Moving security checks to the earliest stages of development.
- Automation: Integrating security tools in CI/CD pipelines for continuous testing.
- Collaboration: Breaking down silos between development, security, and operations teams.
Why DevSecOps is Important for Node.js
Node.js applications, like any other software, are vulnerable to security issues. DevSecOps ensures that common vulnerabilities (e.g., cross-site scripting, SQL injection, etc.) are detected and addressed early on. Given Node.js’ popularity for web and backend services, DevSecOps practices protect not only the application but also its runtime environment.
Setting Up a Secure Development Environment
Secure Version of Node.js
It’s critical to ensure that you’re using the latest stable version of Node.js, as security patches are regularly released.
- Check your current Node.js version:
node -v
- Install the latest stable version using Node Version Manager (NVM):
nvm install stable
Enforcing Secure Dependencies
Node.js heavily relies on third-party libraries, managed by npm. Outdated or compromised libraries can introduce security risks. To minimize this:
- Use npm audit to detect vulnerabilities:
npm audit
Fix vulnerabilities automatically:
npm audit fix
This command checks your package.json and package-lock.json for known vulnerabilities and applies the fixes where available.
Implementing Linting for Secure Code
Use ESLint to enforce secure coding practices. Configure ESLint to catch common issues like insecure code patterns (e.g., using eval()).
Install and set up ESLint:
npm install eslint --save-dev
npx eslint --init
In the .eslintrc.json file, add secure coding rules, such as preventing the use of potentially dangerous functions:
Static Application Security Testing (SAST)
Introduction to SAST
Static Application Security Testing (SAST) involves scanning your codebase for security vulnerabilities without executing it. This ensures that insecure coding patterns are caught early.
Integrating SAST Tools for Node.js
- ESLint Security Plugin: Extend your ESLint configuration to perform security scans.
Install the security plugin:
npm install eslint-plugin-security --save-dev
Update your .eslintrc.json file to include security checks:
{
"plugins": ["security"],
"extends": ["plugin:security/recommended"]
}
- SonarQube: A popular SAST tool that can be integrated into CI/CD pipelines for continuous security scanning. You can set up SonarQube to analyze your Node.js code and enforce security best practices.
Example: Detecting Insecure Code
Consider the following insecure usage of eval
const userInput = '2 + 2';
console.log(eval(userInput)); // Dangerous!
With the security plugin enabled, ESLint will raise a warning, encouraging developers to refactor the code to avoid using eval.
Dependency Vulnerability Management
Managing Vulnerabilities in Node.js Dependencies
Third-party libraries can have vulnerabilities that can expose your application to attacks. Managing dependencies securely is crucial in the Node.js ecosystem.
Using Dependency Scanning Tools
npm audit: As mentioned earlier, this is a built-in tool to scan dependencies for vulnerabilities.
Snyk: Snyk is a popular tool that integrates with your Node.js project to continuously monitor dependencies for vulnerabilities.
To install Snyk:
npm install snyk --global
snyk test
Snyk will provide detailed vulnerability reports and suggest patches.
Example: Fixing Vulnerabilities in Dependencies
If npm audit finds a vulnerability in a library like lodash, you can upgrade it:
npm install lodash@latest --save
Regularly check for updates and run these scans in your CI pipeline.
Security in Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD)
Securing the CI/CD Pipeline
CI/CD pipelines automate the building, testing, and deployment of applications. Ensuring the pipeline itself is secure is a key aspect of DevSecOps.
Tools for CI/CD Security
Jenkins, GitLab CI, CircleCI: Integrate security checks (e.g., SAST, dependency scanning) within these CI/CD platforms.
OWASP ZAP: A tool that performs automated vulnerability scanning during CI/CD builds to detect security issues in web applications.
Example: Adding npm Audit in a CI Pipeline
In a Jenkins pipeline, you can add an npm audit stage:
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('Security Scan') {
steps {
sh 'npm audit'
}
}
}
}
If vulnerabilities are found, the pipeline will fail, preventing insecure code from being deployed.
Runtime Security Practices for Node.js
Secure Node.js Configuration
At runtime, certain configurations help secure Node.js applications.
- Avoid running Node.js as root: Always run Node.js with a non-root user to prevent privilege escalation attacks.
# Start the Node.js app with a non-root user
sudo -u nodeuser node app.js
- Use environment variables for sensitive data: Never hard-code credentials or sensitive information in your source code.
Securing APIs
When building APIs in Node.js, ensure they are secure by:
Using HTTPS: Always encrypt communication using TLS/SSL.
Implementing proper authentication: Use JWT or OAuth2 for token-based authentication.
Example: Implementing JWT authentication in a Node.js API
const jwt = require('jsonwebtoken');
app.post('/login', (req, res) => {
const user = { id: 1, username: 'test' };
const token = jwt.sign(user, 'your-secret-key');
res.json({ token });
});
app.get('/protected', authenticateToken, (req, res) => {
res.send('This is protected');
});
function authenticateToken(req, res, next) {
const token = req.headers['authorization'];
if (!token) return res.sendStatus(403);
jwt.verify(token, 'your-secret-key', (err, user) => {
if (err) return res.sendStatus(403);
req.user = user;
next();
});
}
This code demonstrates how to protect routes using JWTs.
Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST)
What is DAST?
Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST) involves running tests on a running application to detect vulnerabilities during runtime.
DAST Tools for Node.js
- OWASP ZAP: A free and popular DAST tool that can automatically scan your Node.js web application for vulnerabilities such as XSS or SQL injection.
Example: Running OWASP ZAP in CI/CD for Node.js
Configure OWASP ZAP to scan your running application in a CI pipeline:
zap-cli quick-scan --self-contained --start-options '-config api.disablekey=true' http://localhost:3000
Infrastructure Security for Node.js Applications
Securing Containers and Kubernetes
- Docker Security: Ensure that your Docker containers running Node.js apps are secure by minimizing the image size and avoiding root access.
Use a secure base image like node:alpine:
FROM node:alpine
WORKDIR /app
COPY . .
RUN npm install
CMD ["node", "server.js"]
- Kubernetes Security: Use network policies, role-based access control (RBAC), and secure secrets management in Kubernetes clusters running Node.js applications.
Cloud Security Best Practices
When deploying Node.js applications on cloud platforms, use security best practices like:
- IAM (Identity and Access Management): Limit access to cloud resources.
- Encryption: Encrypt data at rest and in transit.
DevSecOps practices are essential for developing secure Node.js applications in today’s threat landscape. By shifting security left in the development cycle and integrating automated tools for testing, scanning, and monitoring, you can secure your Node.js application from the development phase through deployment. With tools like ESLint, npm audit, and Snyk for dependency management, as well as Jenkins or GitLab CI for CI/CD integration, security becomes an ongoing part of the Node.js development process. Adopting DevSecOps practices will make your Node.js applications not only more secure but also more resilient to emerging threats.Happy coding !❤️
