Cloud-Native Node.js Development (Kubernetes, Istio)
In this chapter, we will dive deep into Cloud-Native Node.js Development, focusing on how you can use Kubernetes and Istio to manage, scale, and secure your Node.js applications in a cloud-native environment. The cloud-native approach allows developers to build applications that are resilient, scalable, and maintainable, leveraging cloud infrastructure to handle distributed systems and microservices.This chapter will cover everything from the basics to advanced topics to help you understand and implement cloud-native Node.js development effectively.
Introduction to Cloud-Native Development
Definition
Cloud-native development refers to building and running applications that exploit the advantages of cloud computing delivery models. Cloud-native applications are designed to be scalable, resilient, and fault-tolerant, leveraging microservices, containers, continuous integration/continuous delivery (CI/CD), and orchestration technologies like Kubernetes.
Why Cloud-Native?
Traditional applications were built as monoliths, which were hard to scale and maintain. Cloud-native applications use microservices architecture, where each service runs independently. This allows for rapid development, scalability, and resilience.
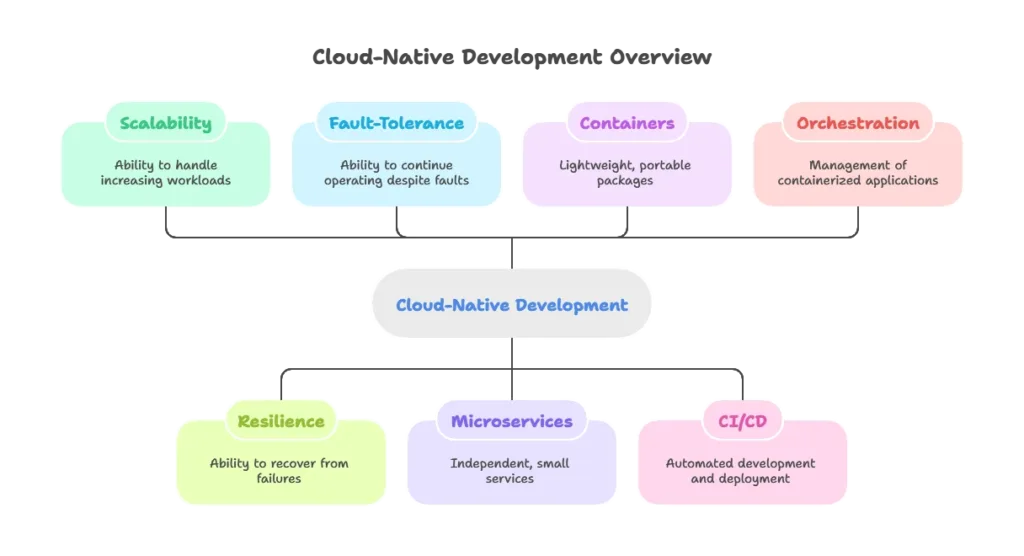
Why Node.js in Cloud-Native Development?
Node.js is an excellent choice for cloud-native development due to its lightweight, non-blocking, and event-driven architecture. It’s particularly effective for microservices because of its efficiency in handling I/O-bound tasks, making it a natural fit for distributed cloud systems.
Key Benefits of Node.js in Cloud-Native:
- Asynchronous nature: Handles multiple requests efficiently.
- Microservice-friendly: Each service can be lightweight and isolated.
- Easy to scale: Node.js can scale horizontally across multiple containers or instances.
- Rich ecosystem: NPM (Node Package Manager) provides a wealth of modules to build cloud-native solutions quickly.
Introduction to Kubernetes
Definition:
Kubernetes is an open-source platform for automating the deployment, scaling, and operation of application containers across clusters of hosts. It provides container orchestration, ensuring that your application is available, scalable, and fault-tolerant.
Why Kubernetes?
Kubernetes automates many of the manual processes involved in deploying and managing containerized applications. It helps you:
- Scale applications automatically.
- Load-balance traffic across services.
- Ensure high availability through self-healing and rollback capabilities.
Key Kubernetes Concepts:
- Pod: The smallest unit in Kubernetes, representing one or more containers.
- Node: A machine (physical or virtual) in the Kubernetes cluster.
- Service: Defines how to access pods, often as a load balancer.
- Ingress: Manages external access to services, usually HTTP.
Setting Up a Node.js Application in Kubernetes
Step 1: Containerizing a Node.js Application Using Docker Before deploying to Kubernetes, you must containerize your Node.js app using Docker.
Example: Dockerfile for Node.js App
# Use Node.js official image from Docker Hub
FROM node:14
# Create an application directory
WORKDIR /usr/src/app
# Install app dependencies
COPY package*.json ./
RUN npm install
# Bundle app source code
COPY . .
# Expose the application port
EXPOSE 3000
# Run the app
CMD ["node", "app.js"]
Explanation:
This Dockerfile creates a containerized version of your Node.js app, which can now be deployed in Kubernetes.
Step 2: Deploying a Node.js Application to Kubernetes Once your Node.js app is containerized, the next step is to deploy it to Kubernetes using a Deployment.
Example: Kubernetes Deployment YAML
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nodejs-app
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nodejs-app
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nodejs-app
spec:
containers:
- name: nodejs
image: your-dockerhub-username/nodejs-app:latest
ports:
- containerPort: 3000
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nodejs-service
spec:
selector:
app: nodejs-app
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 3000
type: LoadBalancer
Explanation:
- Deployment: Manages the Node.js app and ensures there are always 3 replicas running.
- Service: Exposes the app to the external world using a load balancer.
Scaling Node.js Applications with Kubernetes
Horizontal Pod Autoscaling (HPA):
Kubernetes allows for automatic scaling based on CPU utilization, memory usage, or custom metrics.
Example: Autoscaler YAML
apiVersion: autoscaling/v1
kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler
metadata:
name: nodejs-app-hpa
spec:
scaleTargetRef:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: nodejs-app
minReplicas: 2
maxReplicas: 10
targetCPUUtilizationPercentage: 50
Explanation:
- The HPA automatically adjusts the number of pods based on CPU usage. For example, if CPU usage exceeds 50%, Kubernetes will increase the number of pods.
Introduction to Istio for Service Mesh
Definition:
Istio is an open-source service mesh that provides a way to control how microservices communicate over a network. It offers features like traffic management, security, observability, and resilience.
Why Istio?
In a microservice architecture, managing service-to-service communication can be challenging. Istio solves this by abstracting the communication into a layer separate from the application, allowing you to:
- Control traffic routing.
- Monitor and secure microservice communication.
- Implement resilience features like retries and circuit breakers.
Implementing Traffic Management in Istio
Overview:
Istio provides fine-grained control over traffic routing between services, allowing developers to perform advanced traffic-shifting, canary releases, or blue-green deployments.
Example: Traffic Management in Istio (Routing Traffic)
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: nodejs-app
spec:
hosts:
- nodejs-service
http:
- route:
- destination:
host: nodejs-service
subset: v1
weight: 50
- destination:
host: nodejs-service
subset: v2
weight: 50
Explanation:
- This configuration splits traffic between two versions (
v1andv2) of thenodejs-service, with 50% of traffic going to each version.
Security in Istio (mTLS)
Overview:
Istio supports mutual TLS (mTLS), a way to encrypt and secure communication between services within the cluster. It ensures that all service-to-service communication is authenticated and encrypted.
Example: Enabling mTLS in Istio
apiVersion: security.istio.io/v1beta1
kind: PeerAuthentication
metadata:
name: default
namespace: default
spec:
mtls:
mode: STRICT
Explanation:
- By setting the
mtlsmode toSTRICT, all services in the namespace require mutual TLS for communication.
Monitoring and Observability with Istiolopment
Overview:
Istio provides detailed metrics and logs for all service communication. By integrating with tools like Prometheus, Grafana, and Jaeger, Istio can give you deep insight into traffic patterns, failures, and latencies.
Example: Prometheus Integration with Istio
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: prometheus
labels:
app: prometheus
spec:
ports:
- name: web
protocol: TCP
port: 9090
selector:
app: prometheus
Explanation:
- Prometheus collects metrics exposed by Istio, allowing you to visualize and analyze them in Grafana.
Cloud-native development with Node.js, Kubernetes, and Istio enables developers to build highly scalable, resilient, and efficient applications. Kubernetes manages deployment, scaling, and load balancing, while Istio adds advanced traffic management, security, and observability features to the mix.By adopting these tools, you can create robust, future-proof applications that are designed to thrive in modern cloud environments.Through containerization, automation, service mesh technology, and monitoring, cloud-native Node.js development brings agility, scalability, and security to your application development process.Happy coding !❤️
