CI/CD Pipeline Orchestration with Node.js
CI/CD (Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment) pipelines are essential for modern software development, automating the processes of building, testing, and deploying applications. In this chapter, we will explore how to set up and orchestrate a CI/CD pipeline for Node.js applications, ensuring a seamless and automated delivery process from development to production.This chapter will guide you step by step from basic concepts to advanced techniques, with practical examples and code snippets that you can follow along with.
Introduction to CI/CD
What is CI/CD?
CI/CD stands for Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (or Delivery). It is a set of automated processes that help development teams deliver code changes more frequently and reliably. Here’s a breakdown of these two concepts:
- Continuous Integration (CI): Automatically testing and merging code changes into a shared repository, ensuring that new code doesn’t break existing functionality.
- Continuous Deployment (CD): Automatically deploying changes to production or other environments after passing tests, reducing manual intervention and speeding up the release process.
Why Use CI/CD for Node.js Applications?
Node.js is widely used for web applications, microservices, and APIs, where rapid iteration and deployment are crucial. CI/CD helps:
- Ensure code quality by automatically running tests.
- Deploy applications faster by automating build and deployment processes.
- Reduce human error and manual effort.
- Enable developers to focus on writing code while the pipeline takes care of integration and deployment.
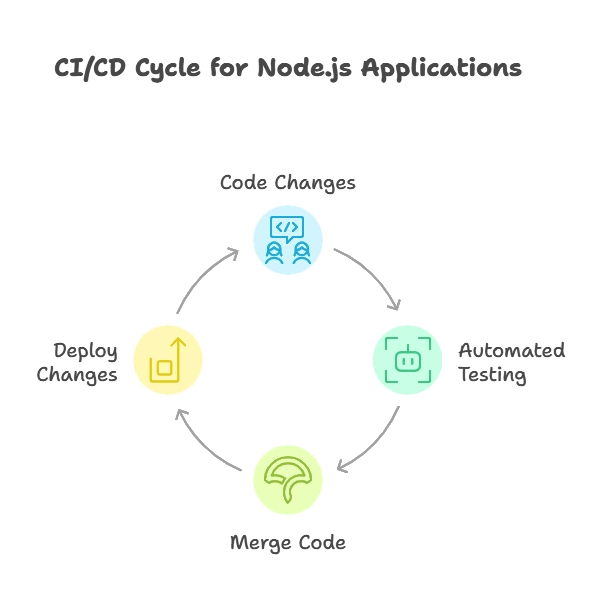
Key Components of a CI/CD Pipeline
Source Code Management (SCM)
The foundation of a CI/CD pipeline is source code management. Commonly used platforms include:
- GitHub
- GitLab
- Bitbucket
The pipeline is triggered when new code is pushed to the repository or when a pull request is opened for review.
Build Automation
Build automation compiles the source code and installs dependencies. For Node.js, this often involves tools like:
- npm or yarn for dependency management.
- webpack or Gulp for bundling and task automation.
Example command in Node.js to install dependencies:
npm install
Automated Testing
Testing is a critical part of the CI/CD pipeline. For Node.js applications, common testing frameworks include:
- Jest or Mocha for unit testing.
- Supertest for API testing.
- Cypress for end-to-end testing.
You can integrate test commands like:
npm test
This will automatically run all the test cases every time the CI pipeline is triggered, ensuring code integrity.
Deployment Automation
Deployment automation involves moving code from the testing environment to production. Tools like Docker, Kubernetes, or AWS Elastic Beanstalk are often used to automate the deployment process. CI/CD platforms integrate well with cloud providers like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud.
Setting Up a Simple CI/CD Pipeline for Node.js
Example Using GitHub Actions
GitHub Actions is a powerful tool that allows you to define custom workflows directly in your Node.js repository. Let’s walk through a simple CI/CD pipeline that automatically runs tests and deploys the application to a server.
Create a
.github/workflows/ci-cd.ymlfile in your repository.Add the following configuration to define the CI/CD pipeline:
name: Node.js CI/CD Pipeline
on:
push:
branches:
- main
pull_request:
branches:
- main
jobs:
build:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout code
uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name: Set up Node.js
uses: actions/setup-node@v2
with:
node-version: '16'
- name: Install dependencies
run: npm install
- name: Run tests
run: npm test
deploy:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
needs: build
steps:
- name: Deploy to server
run: |
ssh user@server 'cd /path/to/project && git pull origin main && npm install && pm2 restart app'
Explanation:
- on: push triggers the workflow whenever code is pushed to the
mainbranch. - The build job checks out the code, sets up Node.js, installs dependencies, and runs tests.
- The deploy job is triggered after the build job is successful, and it deploys the code to a remote server using SSH.
Example Using Jenkins
Jenkins is another popular CI/CD tool. Let’s create a simple Jenkins pipeline for a Node.js application.
- Create a
Jenkinsfilein your repository with the following content:
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('Checkout') {
steps {
git 'https://github.com/your-repo-url.git'
}
}
stage('Install Dependencies') {
steps {
sh 'npm install'
}
}
stage('Run Tests') {
steps {
sh 'npm test'
}
}
stage('Build') {
steps {
sh 'npm run build'
}
}
stage('Deploy') {
steps {
sshagent(['server-ssh-credentials']) {
sh 'ssh user@server "cd /path/to/app && git pull origin main && npm install && pm2 restart app"'
}
}
}
}
post {
always {
archiveArtifacts artifacts: '**/build/**'
}
}
}
Explanation:
- stages define the different steps of the pipeline, from checking out the code to deployment.
- The Deploy stage uses the sshagent plugin to connect to a remote server and deploy the application.
Advanced CI/CD Features
Parallel Jobs
CI/CD pipelines can run multiple jobs in parallel, which speeds up the process, especially for tasks like testing on different Node.js versions or browsers.
Example (GitHub Actions):
jobs:
test:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
strategy:
matrix:
node-version: [14, 16, 18]
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name: Setup Node.js
uses: actions/setup-node@v2
with:
node-version: ${{ matrix.node-version }}
- run: npm install
- run: npm test
In this example, tests will be run on Node.js versions 14, 16, and 18 in parallel.
Caching Dependencies
To improve the speed of the CI pipeline, you can cache dependencies so they don’t need to be reinstalled on every run.
Example (GitHub Actions):
- name: Cache npm dependencies
uses: actions/cache@v2
with:
path: ~/.npm
key: ${{ runner.os }}-node-${{ hashFiles('package-lock.json') }}
restore-keys: |
${{ runner.os }}-node-
Integration with Docker
You can integrate Docker into your CI/CD pipeline to containerize your Node.js application.
Example (GitHub Actions):
jobs:
build:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout code
uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name: Build Docker image
run: docker build -t your-app:latest .
- name: Push Docker image to DockerHub
run: docker push your-dockerhub-username/your-app:latest
env:
DOCKER_USER: ${{ secrets.DOCKER_USER }}
DOCKER_PASSWORD: ${{ secrets.DOCKER_PASSWORD }}
Monitoring and Feedback in CI/CD
Monitoring Pipeline Execution
CI/CD platforms like GitHub Actions, Jenkins, and GitLab CI provide built-in dashboards to monitor the status of each pipeline run. You can view logs, track success and failure rates, and identify issues in your workflow.
Notifications and Alerts
You can integrate notifications into your CI/CD pipeline to alert the team if a build or deployment fails. Common integrations include:
- Slack
- SMS
- name: Notify Slack
uses: slackapi/slack-github-action@v1.14.0
with:
channel-id: 'your-channel-id'
text: 'Deployment completed successfully!'
slack-token: ${{ secrets.SLACK_TOKEN }}
Orchestrating a CI/CD pipeline for Node.js applications is essential for modern software development. It ensures that code is tested, built, and deployed in a consistent and automated manner. In this chapter, we covered the basics of CI/CD, walked through setting up simple pipelines using GitHub Actions and Jenkins, and explored advanced features like parallel jobs, caching, and Docker integration.With a well-configured CI/CD pipeline, your development and deployment processes will become more efficient, reliable, and scalable, allowing your team to focus on delivering high-quality Node.js applications faster and with fewer errors.Happy coding !❤️
