Blockchain Development with Node.js Smart Contract Apps
Blockchain technology has revolutionized how we think about data, transactions, and security. By offering a decentralized, immutable ledger, it has become a cornerstone for industries like finance, healthcare, and supply chain management. In this chapter, we’ll explore how Node.js can be used to develop blockchain applications, specifically focusing on smart contracts. We’ll cover everything from basic concepts to advanced topics, with practical code examples to guide you through building smart contract apps with Node.js.
What is Blockchain?
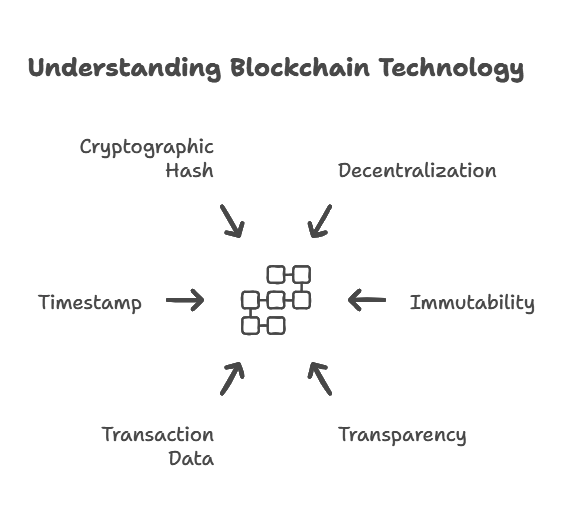
Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology (DLT) that allows data to be stored across multiple systems in a decentralized manner. A blockchain is composed of blocks, which are linked (chained) together. Each block contains transaction data, a timestamp, and a cryptographic hash of the previous block.
Key Features:
- Decentralization: No single entity controls the data.
- Immutability: Data, once written to the blockchain, cannot be altered.
- Transparency: All transactions are visible to participants in the network.
Example:
If you imagine a book where every page is a “block,” each page contains a record of transactions, and the pages are linked together. Changing the content of one page affects all subsequent pages, making fraud extremely difficult.
What are Smart Contracts?
A smart contract is a self-executing contract where the terms are written directly into code. It runs on the blockchain, ensuring automatic, secure, and transparent execution of agreements between parties.
Example:
Imagine a vending machine. You insert money, press a button, and get a snack. The machine automatically verifies your payment and delivers the product without needing a middleman. Smart contracts work in a similar fashion.
Benefits of Smart Contracts:
- Automation: Contracts execute automatically when conditions are met.
- Security: Immutable and resistant to tampering.
- Efficiency: Faster and less costly than traditional methods.
Why Use Node.js for Blockchain Development?
Node.js is a powerful, event-driven JavaScript runtime that excels at handling asynchronous operations, making it ideal for blockchain development.
Benefits of Node.js:
- Asynchronous Nature: Efficient for handling multiple tasks concurrently (transactions, network requests).
- Rich Ecosystem: Numerous libraries and tools for blockchain development.
- Cross-Platform: Runs on multiple platforms, ensuring that blockchain applications can be deployed easily.
Setting Up a Node.js Environment
Before we start coding, we need to set up the environment for developing blockchain applications with Node.js.
Steps:
- Install Node.js:
- Download and install Node.js from Node.js official website.
- Initialize a Project:
mkdir blockchain-nodejs
cd blockchain-nodejs
npm init -y
Install Required Libraries:
- Web3.js: A JavaScript library for interacting with Ethereum blockchain.
- Solc: Solidity compiler to compile smart contracts.
npm install web3 solc
Building a Blockchain with Node.js
Now, let’s build a basic blockchain using Node.js. We’ll create a Blockchain class that represents a chain of blocks.
Code Example:
class Block {
constructor(index, timestamp, data, previousHash = '') {
this.index = index;
this.timestamp = timestamp;
this.data = data;
this.previousHash = previousHash;
this.hash = this.calculateHash();
}
calculateHash() {
return require('crypto').createHash('sha256').update(
this.index + this.previousHash + this.timestamp + JSON.stringify(this.data)
).digest('hex');
}
}
class Blockchain {
constructor() {
this.chain = [this.createGenesisBlock()];
}
createGenesisBlock() {
return new Block(0, '01/01/2024', 'Genesis Block', '0');
}
getLatestBlock() {
return this.chain[this.chain.length - 1];
}
addBlock(newBlock) {
newBlock.previousHash = this.getLatestBlock().hash;
newBlock.hash = newBlock.calculateHash();
this.chain.push(newBlock);
}
isChainValid() {
for (let i = 1; i < this.chain.length; i++) {
const currentBlock = this.chain[i];
const previousBlock = this.chain[i - 1];
if (currentBlock.hash !== currentBlock.calculateHash()) {
return false;
}
if (currentBlock.previousHash !== previousBlock.hash) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
Code Explanation:
- Block Class: Represents a block with an index, timestamp, data, and the hash of the previous block.
- Blockchain Class: Manages the chain of blocks, starting with the genesis block (the first block).
- Hashing: Uses the SHA-256 algorithm to create unique hashes for each block.
- Chain Validation: Ensures that the blockchain is not tampered with by checking the hashes.
Interacting with Ethereum Blockchain Using Node.js
To build decentralized applications (dApps), you’ll need to interact with an actual blockchain like Ethereum.
Web3.js Library:
Web3.js allows you to interact with an Ethereum node, perform transactions, and deploy smart contracts.
Connecting to Ethereum:
const Web3 = require('web3');
const web3 = new Web3('http://localhost:8545'); // Connect to local Ethereum node
2 Deploying a Smart Contract
You can use Solidity to write a smart contract, then compile and deploy it.
Example Solidity contract (SimpleStorage.sol):
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
contract SimpleStorage {
uint256 storedData;
function set(uint256 x) public {
storedData = x;
}
function get() public view returns (uint256) {
return storedData;
}
}
3 Compiling and Deploying with Node.js:
const fs = require('fs');
const solc = require('solc');
const source = fs.readFileSync('SimpleStorage.sol', 'utf8');
const input = {
language: 'Solidity',
sources: {
'SimpleStorage.sol': {
content: source,
},
},
settings: {
outputSelection: {
'*': {
'*': ['abi', 'evm.bytecode'],
},
},
},
};
const output = JSON.parse(solc.compile(JSON.stringify(input)));
const abi = output.contracts['SimpleStorage.sol'].SimpleStorage.abi;
const bytecode = output.contracts['SimpleStorage.sol'].SimpleStorage.evm.bytecode.object;
const deploy = async () => {
const contract = new web3.eth.Contract(abi);
const deployTx = contract.deploy({ data: bytecode });
const accounts = await web3.eth.getAccounts();
const result = await deployTx.send({ from: accounts[0], gas: '1000000' });
console.log('Contract deployed at:', result.options.address);
};
deploy();
Explanation:
- Solidity Contract: A simple storage contract with
setandgetfunctions. - Deployment: The contract is compiled with Solc and deployed using Web3.js to an Ethereum node.
Working with Smart Contracts
After deploying the smart contract, you can interact with it using Node.js and Web3.js.
Example:
const contractAddress = '0x...'; // Deployed contract address
const simpleStorage = new web3.eth.Contract(abi, contractAddress);
// Setting a value
await simpleStorage.methods.set(42).send({ from: accounts[0] });
// Getting the value
const value = await simpleStorage.methods.get().call();
console.log('Stored Value:', value);
Integrating Node.js with Decentralized Applications (dApps)
A decentralized application (dApp) interacts with the blockchain through smart contracts. Node.js can serve as the backend to manage interactions with the blockchain, handling user requests and storing data.
Example dApp Architecture:
- Frontend: Built with React or Vue.js.
- Backend: Node.js communicates with the Ethereum network via Web3.js.
- Smart Contracts: Deployed on the blockchain to handle business logic.
Advanced Blockchain Concepts with Node.js
- InterPlanetary File System (IPFS): Decentralized file storage.
- Consensus Mechanisms: Proof of Work (PoW), Proof of Stake (PoS).
- Layer 2 Scaling Solutions: Optimizing blockchain performance.
Node.js is a powerful tool for building blockchain applications. With its asynchronous nature and wide array of libraries like Web3.js, developing decentralized applications with smart contracts becomes a smooth experience. By understanding the fundamentals of blockchain, smart contracts, and how Node.js fits into the ecosystem, you're well-equipped to build sophisticated dApps and contribute to the rapidly evolving world of blockchain. Happy coding !❤️
