Middleware in Go
Middleware in Go is a powerful concept used to enhance the functionality of HTTP servers by allowing developers to intercept and manipulate incoming requests and outgoing responses. This chapter delves into the intricacies of middleware, covering everything from basic principles to advanced techniques, enabling developers to leverage middleware effectively in their Go applications.
Understanding Middleware Basics
Basic Concepts
Middleware acts as a bridge between the incoming HTTP request and the final HTTP response. It allows developers to perform tasks such as logging, authentication, rate limiting, and more, in a modular and reusable manner.
Middleware Chain
Middleware functions are chained together, with each function executing in sequence before passing control to the next middleware or the final handler. This sequential execution model enables developers to compose complex behaviors by combining multiple middleware functions.
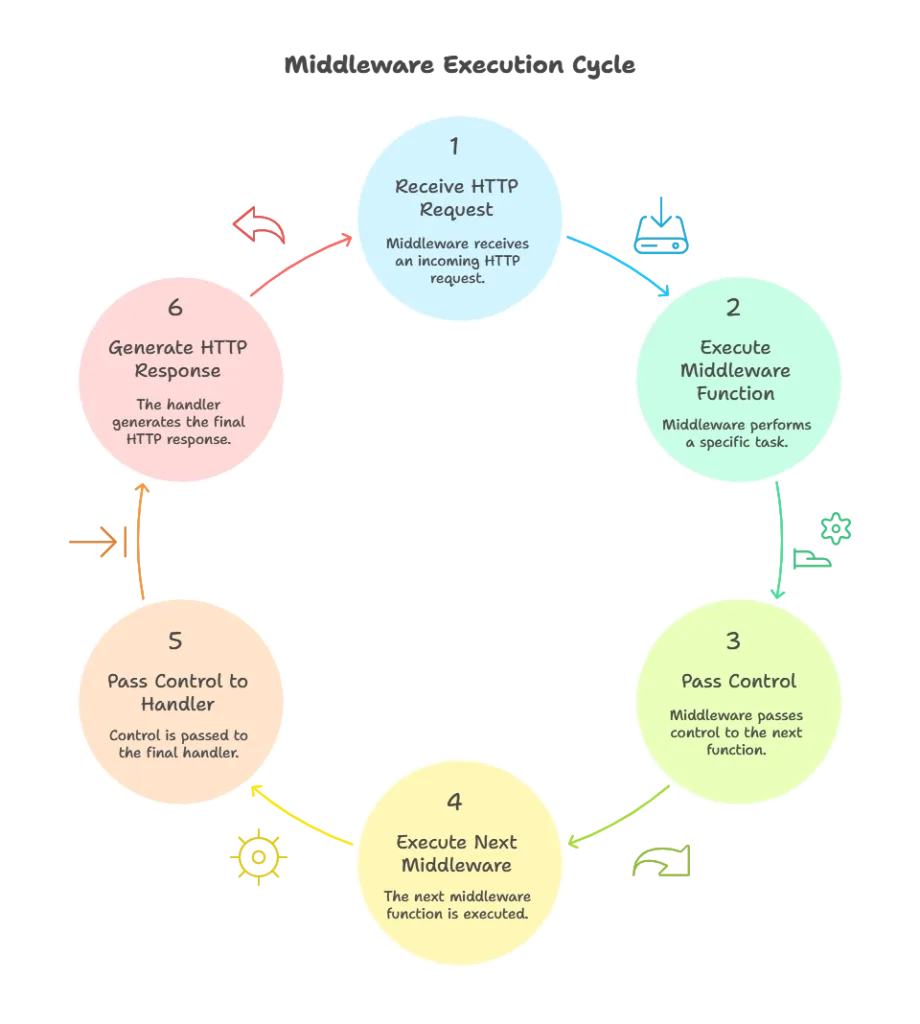
HTTP Handlers: Before delving into middleware, it’s important to understand HTTP handlers in Go. Handlers are functions that process incoming HTTP requests and generate responses.
package main
import (
"fmt"
"net/http"
)
func helloHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
fmt.Fprintf(w, "Hello, World!")
}
func main() {
http.HandleFunc("/", helloHandler)
http.ListenAndServe(":8080", nil)
}
In this example,
helloHandleris an HTTP handler that responds with “Hello, World!” when the root URL is accessed.Middleware Functions: Middleware functions wrap HTTP handlers, allowing you to perform pre-processing and post-processing tasks on requests and responses.
Implementing Middleware in Go
Writing Middleware Functions: Let’s create a middleware function that logs information about incoming requests.
package main
import (
"fmt"
"net/http"
)
func loggerMiddleware(next http.Handler) http.Handler {
return http.HandlerFunc(func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
fmt.Printf("Request URL: %s\n", r.URL.Path)
next.ServeHTTP(w, r)
})
}
func helloHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
fmt.Fprintf(w, "Hello, World!")
}
func main() {
http.Handle("/", loggerMiddleware(http.HandlerFunc(helloHandler)))
http.ListenAndServe(":8080", nil)
}
Here,
loggerMiddlewareis a middleware function that logs the request URL before passing it to the next handler.Chaining Middleware: You can chain multiple middleware functions together to create a pipeline of processing tasks.
package main
import (
"fmt"
"net/http"
)
func loggerMiddleware(next http.Handler) http.Handler {
return http.HandlerFunc(func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
fmt.Printf("Request URL: %s\n", r.URL.Path)
next.ServeHTTP(w, r)
})
}
func authMiddleware(next http.Handler) http.Handler {
return http.HandlerFunc(func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
// Authentication logic goes here
next.ServeHTTP(w, r)
})
}
func helloHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
fmt.Fprintf(w, "Hello, World!")
}
func main() {
http.Handle("/", loggerMiddleware(authMiddleware(http.HandlerFunc(helloHandler))))
http.ListenAndServe(":8080", nil)
}
In this example, authMiddleware is added to perform authentication before handling the request.
Advanced Topics in Middleware
Context Passing: Middleware can pass contextual information between each other and to the request handlers using the
contextpackage.Error Handling: Middleware can intercept errors and handle them gracefully, providing meaningful responses to clients.
Request Modification: Middleware can modify incoming requests or outgoing responses to add headers, manipulate data, or perform other operations.
Middleware is a powerful concept in Go web development, allowing developers to modularize request processing logic and enhance the functionality and maintainability of their applications. By understanding the basics of middleware, implementing custom middleware functions, and exploring advanced topics, you can effectively leverage middleware to build robust and scalable web applications in Go. Happy coding !❤️
