Error Types in Go
In programming, errors are inevitable. They occur when something unexpected happens during the execution of a program. In Go, errors are treated as values, making error handling a fundamental aspect of writing robust and reliable code. In this chapter, we will delve into the various aspects of error handling in Go, focusing specifically on error types.
Error Basics
In Go, errors are represented by the error interface, which is defined as:
type error interface {
Error() string
}
This interface has just one method, Error(), which returns a string describing the error. Any type that implements this method can be treated as an error in Go.
Let’s look at a simple example:
package main
import (
"errors"
"fmt"
)
func divide(a, b int) (int, error) {
if b == 0 {
return 0, errors.New("cannot divide by zero")
}
return a / b, nil
}
func main() {
result, err := divide(10, 0)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error:", err)
return
}
fmt.Println("Result:", result)
}
In this example, the divide function returns an error if the divisor is zero. The errors.New function creates a new error with the given message.
- We define a
dividefunction that takes two integers and returns the result of their division along with an error. - Inside the
dividefunction, we check if the divisor is zero. If it is, we return an error usingerrors.New. - In the
mainfunction, we calldividewith arguments10and0. If an error occurs, we print it; otherwise, we print the result.
Custom Error Types
While using errors.New is convenient for creating simple error messages, sometimes you may need more context or structured errors. In such cases, you can define your custom error types.
package main
import "fmt"
type CustomError struct {
Code int
Message string
}
func (e CustomError) Error() string {
return fmt.Sprintf("Error %d: %s", e.Code, e.Message)
}
func process() error {
// Simulating an error
return CustomError{Code: 500, Message: "Internal Server Error"}
}
func main() {
err := process()
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error:", err)
return
}
fmt.Println("Process completed successfully")
}
- We define a
CustomErrorstruct with fieldsCodeandMessage. This struct implements theErrormethod, which formats the error message. - The
processfunction simulates an error by returning an instance ofCustomError. - In the
mainfunction, we callprocessand handle the error if it occurs.
Handling Multiple Errors
Sometimes, you may encounter scenarios where multiple errors occur simultaneously. Go provides the errors package to handle multiple errors efficiently using the New and Wrap functions.
package main
import (
"errors"
"fmt"
"github.com/pkg/errors"
)
func processA() error {
return errors.New("error in process A")
}
func processB() error {
return errors.New("error in process B")
}
func main() {
errA := processA()
errB := processB()
if err := errors.Wrap(errA, "process A failed"); err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error A:", err)
}
if err := errors.Wrap(errB, "process B failed"); err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error B:", err)
}
}
- We define two functions,
processAandprocessB, which simulate errors. - In the
mainfunction, we call these functions and useerrors.Wrapto wrap each error with additional context. - The wrapped errors provide a chain of errors, making it easier to trace the origin of each error.
Error Wrapping and Unwrapping
In complex systems, errors can propagate through multiple layers of function calls. Error wrapping allows you to add context to an error without losing the original error information. Go provides the errors.Wrap function and its variants for this purpose.
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/pkg/errors"
)
func process() error {
// Simulating an error
return errors.New("error in process")
}
func main() {
err := process()
if err != nil {
wrappedErr := errors.Wrap(err, "process failed")
fmt.Println("Wrapped Error:", wrappedErr)
// Unwrapping the error to access the original error
originalErr := errors.Unwrap(wrappedErr)
fmt.Println("Original Error:", originalErr)
}
}
- We define a
processfunction that returns a simple error. - In the
mainfunction, we callprocessand wrap the returned error with additional context usingerrors.Wrap. - We then demonstrate how to unwrap the error using
errors.Unwrapto access the original error.
Error Handling in Concurrent Programs
In concurrent programs, error handling becomes more challenging due to the asynchronous nature of goroutines. It’s essential to handle errors appropriately to prevent goroutines from crashing the entire program.
package main
import (
"fmt"
"sync"
)
func worker(wg *sync.WaitGroup, errCh chan<- error) {
defer wg.Done()
// Simulating an error
errCh <- fmt.Errorf("error in worker")
}
func main() {
var wg sync.WaitGroup
errCh := make(chan error)
for i := 0; i < 3; i++ {
wg.Add(1)
go worker(&wg, errCh)
}
go func() {
wg.Wait()
close(errCh)
}()
for err := range errCh {
fmt.Println("Error:", err)
}
}
- We define a
workerfunction that simulates an error and sends it to an error channel. - In the
mainfunction, we create a wait group and an error channel. - We spawn multiple goroutines to execute the
workerfunction concurrently. - A separate goroutine waits for all workers to finish and then closes the error channel.
- Finally, we range over the error channel to handle any errors produced by the workers.
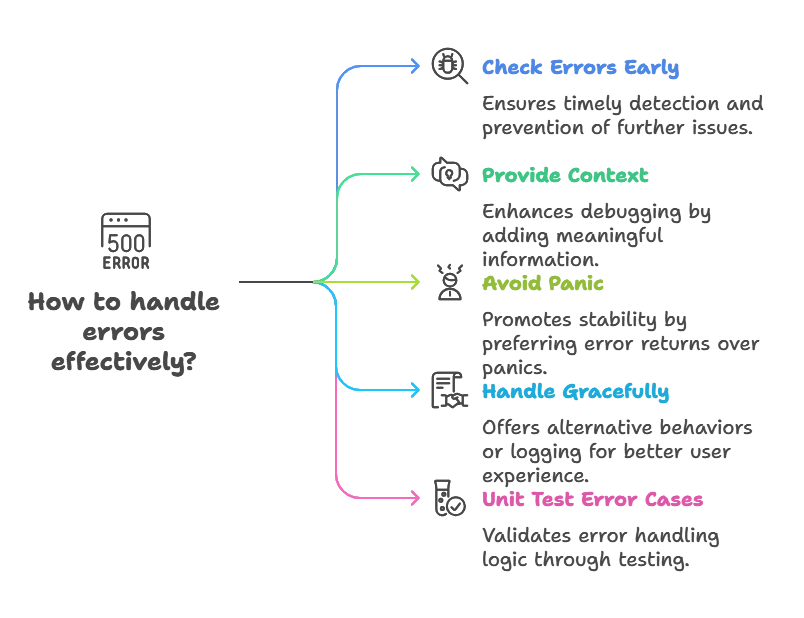
Error Handling Best Practices
- Check Errors Early: Always check errors as soon as possible after a function call that may return an error.
- Provide Context: Add meaningful context to errors using error wrapping to make debugging easier.
- Avoid Panic: Avoid using
panicfor error handling except in exceptional circumstances. Prefer returning errors to calling functions. - Handle Errors Gracefully: Gracefully handle errors by logging them, returning them to the caller, or providing alternative behavior.
- Unit Test Error Cases: Write unit tests to cover error cases and ensure your error handling logic behaves as expected.
Error handling in Go is a nuanced topic that requires careful consideration, especially in complex systems and concurrent programs. By following best practices, handling errors gracefully, and understanding error types and propagation mechanisms, you can write more robust and maintainable Go applications. Remember to test your error handling logic thoroughly and continuously refine it as your codebase evolves. Happy coding !❤️
