Cyber Security Mindset
In today's digital world, cyber threats are everywhere—from phishing emails to ransomware attacks. A Cyber Security Mindset is not about just using tools—it's about developing the right habits, behaviors, and attitudes that help you and your organization stay safe online. The diagram in this chapter outlines the six foundational pillars of cultivating this mindset.
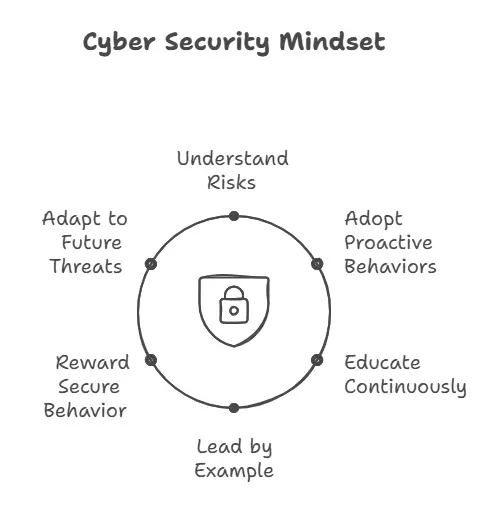
Understand Risks
The first step in building a cyber security mindset is recognizing the risks you face online. Cyber threats come in many forms—malware, phishing, social engineering, and data breaches.
Example: A user clicking on a malicious email link can lead to full system compromise.
Key Practices:
Stay updated on common attack types.
Know what data is sensitive and how it’s targeted.
Identify risky behavior (e.g., weak passwords, public Wi-Fi use).
Adopt Proactive Behaviors
Proactive behavior is about preventing issues before they arise. It means not waiting for an incident to take action, but instead anticipating vulnerabilities.
Examples of Proactive Behavior:
Using multi-factor authentication (MFA).
Regularly updating software and firmware.
Locking devices when not in use.
Auditing your digital footprint.
Proactive thinking is your shield in a digital battlefield.
Educate Continuously
Cyber threats evolve, and so must our knowledge. Continuous education ensures that you and your team stay one step ahead.
Ways to Educate:
Attend security webinars or workshops.
Encourage team-wide training sessions.
Stay subscribed to cybersecurity newsletters or threat intelligence feeds.
Tip: Even a 10-minute monthly update session can reduce incidents dramatically.
Lead by Example
If you’re in a leadership position, your attitude toward cybersecurity sets the tone for others. People replicate what they observe, not just what they are told.
Leadership Practices:
Follow password and email security best practices.
Publicly support security training and policies.
Never bypass or disable security protocols yourself.
Culture starts from the top—leaders must walk the talk.
Reward Secure Behavior
Encouraging a cyber-safe culture means celebrating and rewarding good behavior.
Ways to Reward:
Recognize employees who report phishing attempts.
Offer small incentives for completing cybersecurity training.
Highlight secure practices in team meetings or internal newsletters.
Recognition reinforces behavior better than rules.
Adapt to Future Threats
Cybersecurity is not static. As technology advances, so do threats. A true cyber security mindset is flexible and ready to evolve.
How to Stay Adaptable:
Regularly review and update security policies.
Test incident response plans through simulations.
Stay informed about emerging technologies like AI-based attacks or quantum encryption.
Being adaptive turns fear of change into a strategic advantage.
The Cyber Security Mindset is a holistic approach that combines awareness, proactive habits, and ongoing education. It isn’t just a job for IT—it’s a responsibility shared by everyone. By understanding risks, acting before threats occur, and continuously evolving, we build a resilient digital future.
