Introduction to Cyber Security
Cyber Security refers to the practice of protecting computer systems, networks, programs, and data from unauthorized access, attacks, or damage. As our dependence on digital platforms grows—be it in banking, healthcare, education, or governance—the need to protect sensitive data and digital infrastructure has become more critical than ever.Cyber Security is not just about installing antivirus software; it's a multi-layered defense strategy involving people, processes, and technologies.
Why is Cyber Security Important?
With the increase in digital transformation, the frequency and complexity of cyberattacks have also grown. Key reasons for the importance of cyber security include:
Data Protection: Preventing unauthorized access to sensitive personal and organizational data.
Financial Safety: Reducing financial losses due to cyber fraud, ransomware, and data breaches.
National Security: Protecting critical infrastructure such as power grids, military systems, and communication networks.
Business Continuity: Ensuring systems and networks remain operational without disruption.
Reputation Management: Preventing damage to brand and trust due to data leaks or system breaches.
Exploring the Dimension of Cyber Security

- Protecting Computer Systems
Focuses on securing hardware, software, and operating systems from vulnerabilities, malware, and unauthorized access.
- Securing Networks
Involves safeguarding network infrastructure (e.g., firewalls, intrusion detection systems) to prevent breaches and ensure secure data transmission.
- Safeguarding Data
Emphasizes protecting sensitive information (e.g., personal, financial, or corporate data) through encryption, access controls, and backups.
- Mitigating Cyber Threats
Addresses identifying, preventing, and responding to threats like phishing, ransomware, and DDoS attacks.
- Ensuring Digital Safety
A broader goal encompassing user awareness, secure practices, and compliance with regulations to maintain trust in digital environments.
Common Types of Cyber Threats
Phishing: Fraudulent attempts to obtain sensitive information by disguising as a trustworthy entity.
Ransomware: Malware that locks users out of their systems or files until a ransom is paid.
Denial of Service (DoS): Attacks that overwhelm a system, making it unavailable to users.
Man-in-the-Middle (MitM): Interception of communication between two systems.
SQL Injection: Insertion of malicious SQL queries to manipulate databases.
Zero-Day Exploit: Attack that occurs on the same day a vulnerability is discovered.
Core Principles of Cyber Security
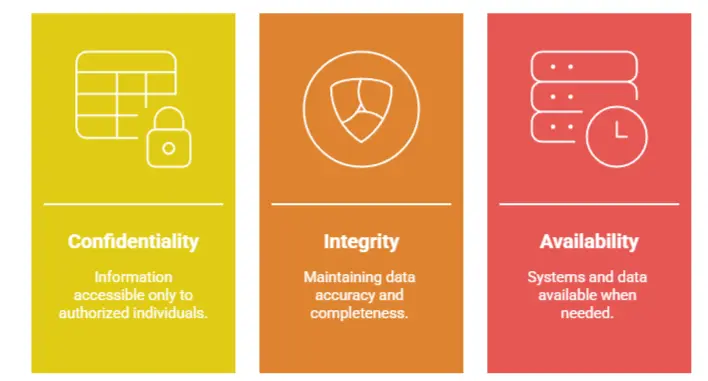
Cyber security rests on three fundamental principles, known as the CIA Triad:
Confidentiality: Ensuring that information is accessible only to authorized individuals.
Integrity: Maintaining the accuracy and completeness of data.
Availability: Ensuring systems and data are available when needed.
Key Components of a Cyber Security Strategy
Network Security: Protecting the integrity of internal networks.
Application Security: Securing software applications from threats during development and after deployment.
Information Security: Protecting data in transit and at rest.
Endpoint Security: Protecting end-user devices like laptops, desktops, and mobile phones.
Cloud Security: Protecting cloud-based infrastructure, data, and services.
Identity and Access Management (IAM): Ensuring the right individuals access the right resources.
Security Operations: Monitoring systems for signs of malicious activity and responding accordingly.
Who Needs Cyber Security?
Cyber security is not limited to tech companies or governments. It is essential for:
Individuals: Protecting personal data, identity, and finances.
Businesses: Securing proprietary data, customer information, and assets.
Educational Institutions: Protecting student records and intellectual property.
Healthcare Providers: Securing patient data and medical systems.
Governments: Protecting national infrastructure and public data.
Cyber Security Careers and Roles
The rise in threats has created a high demand for cyber security professionals. Common roles include:
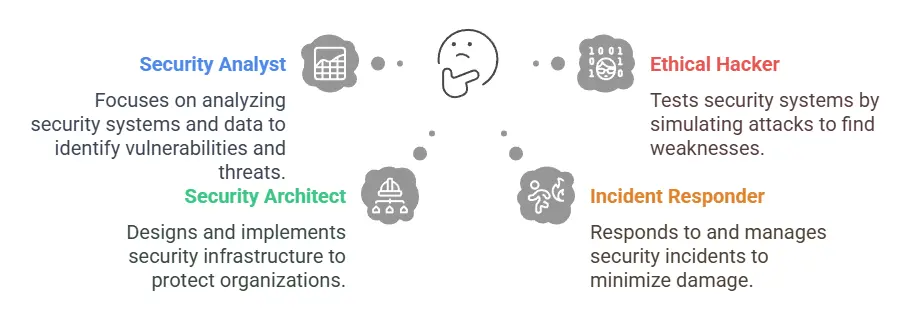
Security Analyst
Ethical Hacker (Penetration Tester)
Security Architect
Incident Responder
Which cybersecurity career path should I pursue?
Choosing a cybersecurity career path depends on your interests, skills, and long-term goals.
Cyber security is the digital armor that protects the modern world. From our smartphones to national defense systems, cyber security ensures confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data and services. As technology advances, so do the methods of cyber attackers, making it critical for everyone—from individuals to global corporations—to invest in strong cyber security practices.
