Using React with Blockchain Technologies
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing various industries by providing a decentralized and secure way of recording transactions and data. React, a popular JavaScript library for building user interfaces, can be combined with blockchain to create powerful, decentralized applications (dApps). This chapter will guide you through integrating React with blockchain technologies, covering everything from basic concepts to advanced implementations
Basics of Blockchain
What is Blockchain?
Blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across multiple computers. These transactions are grouped into blocks, which are then linked together in a chronological chain. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data.
Key Features of Blockchain
- Decentralization: No single point of control.
- Transparency: All transactions are publicly accessible.
- Immutability: Once recorded, transactions cannot be altered.
- Security: Cryptographic techniques ensure data integrity and authenticity.
Setting Up a React Project
Before integrating blockchain technology, let’s set up a basic React project.
Create a new React project:
npx create-react-app blockchain-demo
cd blockchain-demo
Install necessary dependencies:
npm install web3
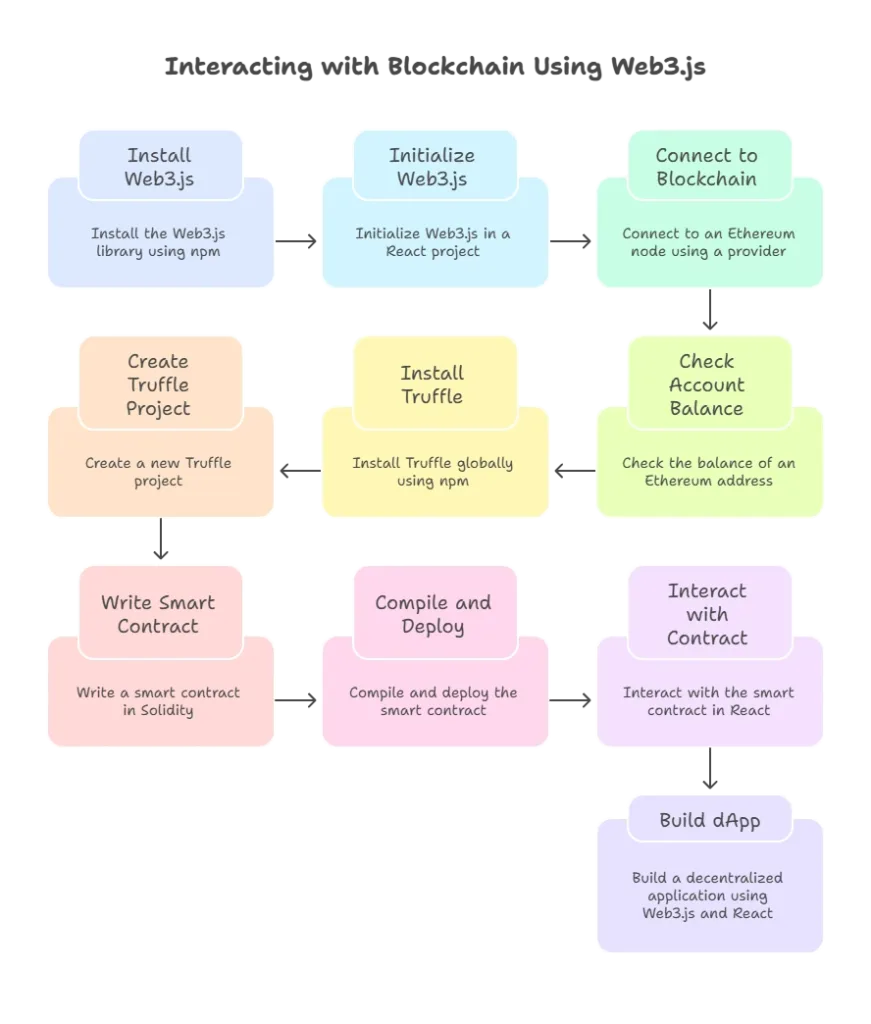
Interacting with Blockchain Using Web3.js
Web3.js is a JavaScript library that allows you to interact with the Ethereum blockchain. It provides functions to connect to an Ethereum node, send transactions, and interact with smart contracts.
Setting Up Web3.js
Install Web3.js:
npm install web3
Initialize Web3.js in your React project:
import Web3 from 'web3';
const web3 = new Web3(Web3.givenProvider || 'http://localhost:8545');
Connecting to a Blockchain Network
To interact with a blockchain network, you need to connect to an Ethereum node. This can be done using a provider like Infura or by running your own node.
Example:
import Web3 from 'web3';
const web3 = new Web3(new Web3.providers.HttpProvider('https://mainnet.infura.io/v3/YOUR_INFURA_PROJECT_ID'));
Checking Account Balance
You can use Web3.js to check the balance of an Ethereum address.
Example:
import React, { useState, useEffect } from 'react';
import Web3 from 'web3';
const App = () => {
const [balance, setBalance] = useState(0);
const address = '0xYourEthereumAddress';
useEffect(() => {
const web3 = new Web3(Web3.givenProvider || 'http://localhost:8545');
web3.eth.getBalance(address).then(bal => {
setBalance(web3.utils.fromWei(bal, 'ether'));
});
}, [address]);
return (
<div>
<h1>Balance: {balance} ETH</h1>
</div>
);
};
export default App;
Interacting with Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms directly written into code. They run on the Ethereum blockchain and can be interacted with using Web3.js.
Deploying a Smart Contract
To deploy a smart contract, you’ll need Solidity (a programming language for writing smart contracts) and an Ethereum development environment like Truffle.
Install Truffle:
npm install -g truffle
Create a new Truffle project:
truffle init
Write a simple smart contract in contracts/MyContract.sol:
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
contract MyContract {
string public message;
constructor(string memory initialMessage) {
message = initialMessage;
}
function setMessage(string memory newMessage) public {
message = newMessage;
}
}
Compile and deploy the contract:
truffle compile
truffle migrate
Interacting with a Smart Contract in React
Get the contract ABI and address from Truffle:
import MyContract from './build/contracts/MyContract.json';
const contract = new web3.eth.Contract(MyContract.abi, '0xYourContractAddress');
Call contract methods:
import React, { useState, useEffect } from 'react';
import Web3 from 'web3';
import MyContract from './build/contracts/MyContract.json';
const App = () => {
const [message, setMessage] = useState('');
const [newMessage, setNewMessage] = useState('');
useEffect(() => {
const web3 = new Web3(Web3.givenProvider || 'http://localhost:8545');
const contract = new web3.eth.Contract(MyContract.abi, '0xYourContractAddress');
contract.methods.message().call().then(setMessage);
}, []);
const updateMessage = async () => {
const web3 = new Web3(Web3.givenProvider || 'http://localhost:8545');
const accounts = await web3.eth.getAccounts();
const contract = new web3.eth.Contract(MyContract.abi, '0xYourContractAddress');
await contract.methods.setMessage(newMessage).send({ from: accounts[0] });
const updatedMessage = await contract.methods.message().call();
setMessage(updatedMessage);
};
return (
<div>
<h1>Message: {message}</h1>
<input
value={newMessage}
onChange={e => setNewMessage(e.target.value)}
/>
<button onClick={updateMessage}>Update Message</button>
</div>
);
};
export default App;
Building a Decentralized Application (dApp)
Requirements for a dApp
- Smart Contracts: Backend logic and data storage.
- Web3.js: Interaction layer between the frontend and blockchain.
- React: Frontend framework for building the user interface.
Example dApp: Simple Voting System
Smart Contract
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
contract Voting {
mapping(string => uint256) public votes;
function vote(string memory candidate) public {
votes[candidate]++;
}
function getVotes(string memory candidate) public view returns (uint256) {
return votes[candidate];
}
}
Deploying the Contract
- Compile and deploy using Truffle:
truffle compile
truffle migrate
React Frontend
Set up Web3 and the Voting contract:
import Web3 from 'web3';
import Voting from './build/contracts/Voting.json';
const web3 = new Web3(Web3.givenProvider || 'http://localhost:8545');
const contract = new web3.eth.Contract(Voting.abi, '0xYourContractAddress');
Create the Voting component:
import React, { useState, useEffect } from 'react';
import Web3 from 'web3';
import Voting from './build/contracts/Voting.json';
const App = () => {
const [candidate, setCandidate] = useState('');
const [votes, setVotes] = useState(0);
const [newCandidate, setNewCandidate] = useState('');
useEffect(() => {
const web3 = new Web3(Web3.givenProvider || 'http://localhost:8545');
const contract = new web3.eth.Contract(Voting.abi, '0xYourContractAddress');
contract.methods.getVotes(candidate).call().then(setVotes);
}, [candidate]);
const voteForCandidate = async () => {
const web3 = new Web3(Web3.givenProvider || 'http://localhost:8545');
const accounts = await web3.eth.getAccounts();
const contract = new web3.eth.Contract(Voting.abi, '0xYourContractAddress');
await contract.methods.vote(newCandidate).send({ from: accounts[0] });
const updatedVotes = await contract.methods.getVotes(newCandidate).call();
setVotes(updatedVotes);
};
return (
<div>
<h1>Votes for {candidate}: {votes}</h1>
<input
value={newCandidate}
onChange={e => setNewCandidate(e.target.value)}
/>
<button onClick={voteForCandidate}>Vote</button>
</div>
);
};
export default App;
Integrating React with blockchain technologies enables the creation of decentralized applications that leverage the security, transparency, and immutability of blockchain. This chapter covered the fundamentals of blockchain, how to set up a React project with Web3.js, interact with smart contracts, and build a simple dApp. With this knowledge, you can explore and develop more complex and innovative decentralized applications, pushing the boundaries of what web applications can achieve. Happy coding !❤️
