Network Security Principles
Cyber Security refers to the practice of protecting computer systems, networks, programs, and data from unauthorized access, attacks, or damage. As our dependence on digital platforms grows—be it in banking, healthcare, education, or governance—the need to protect sensitive data and digital infrastructure has become more critical than ever.Cyber Security is not just about installing antivirus software; it's a multi-layered defense strategy involving people, processes, and technologies.
Understanding Network Security
What is Network Security?
Network Security refers to the policies, practices, and technologies designed to prevent unauthorized access, misuse, modification, or denial of a computer network and its resources.
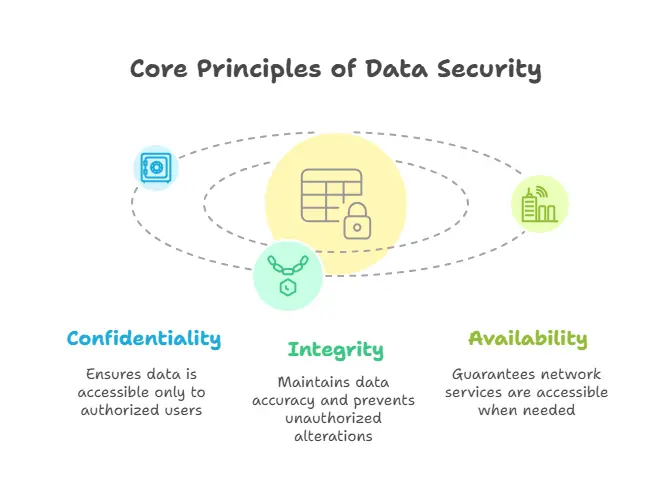
It ensures:
Confidentiality – Data is accessible only to authorized users.
Integrity – Data remains accurate and unaltered.
Availability – Network services remain accessible when needed.
The CIA Triad
The CIA Triad is the foundation of all information security models:
| Principle | Description |
|---|---|
| Confidentiality | Prevents unauthorized access to information. |
| Integrity | Protects data from being altered without permission. |
| Availability | Ensures reliable access to resources when needed. |
Each security measure should align with one or more of these principles.
Common Network Threats
Understanding the threats is essential before planning a defense.
A. Malware
Malicious software such as viruses, worms, trojans, and ransomware.
B. Phishing
Fraudulent attempts to acquire sensitive data via deceptive emails or messages.
C. Denial of Service (DoS/DDoS)
Attacks that flood a network with traffic to make it unavailable.
D. Man-in-the-Middle (MitM)
Intercepting communication between two parties without their knowledge.
E. Zero-Day Exploits
Attacks that occur before the vendor knows and fixes a vulnerability.
F. Insider Threats
Employees or contractors who misuse access privileges.
Key Principles of Network Security
A. Defense in Depth
Implementing multiple layers of security across the network.
B. Least Privilege
Users and systems get only the access they need—nothing more.
C. Segmentation
Dividing networks into zones to contain breaches.
D. Access Control
Authentication (who you are) and Authorization (what you’re allowed to do).
E. Auditing and Logging
Track access and changes to quickly detect malicious behavior.
F. Regular Updates and Patch Management
Keep software and firmware up to date to close security holes.
G. Encryption
Secure communication and storage using algorithms like AES, RSA, TLS.
H. Incident Response Plan
A documented strategy for detecting, responding to, and recovering from security breaches.
Security Technologies and Tools
| Tool/Technology | Use Case |
|---|---|
| Firewall | Blocks unauthorized inbound/outbound traffic. |
| Antivirus/Antimalware | Detects and removes malicious software. |
| Intrusion Detection System (IDS) | Monitors network traffic for suspicious activity. |
| Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) | Blocks suspicious activity in real-time. |
| VPN (Virtual Private Network) | Creates encrypted tunnels for secure remote access. |
| Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) | Adds extra layers to verify identity. |
| SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) | Aggregates logs for analysis and alerts. |
Best Practices for Network Security
Implement strong passwords and change them regularly.
Disable unused ports/services on routers and switches.
Educate users through security awareness training.
Regularly scan and audit network configurations.
Use network segmentation for better control and isolation.
Ensure physical security of networking hardware.
Set up automated backups and test recovery procedures
Compliance and Legal Considerations
Security is also a legal obligation under many regulations:
GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation)
HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act)
ISO/IEC 27001 (Information Security Management)
PCI-DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard)
These frameworks define the baseline requirements for network security in regulated industries.
Future Trends in Network Security
AI-Powered Threat Detection
Zero Trust Network Architecture (ZTNA)
Behavioral Biometrics
Quantum-Resistant Cryptography
Secure Access Service Edge (SASE)
These evolving approaches aim to respond faster to modern threats and adapt to dynamic IT environments like cloud and edge computing.
Network security is a dynamic and multi-layered discipline that requires continuous improvement and vigilance. From the core principles like the CIA triad to advanced technologies such as AI and zero trust models, securing a network is essential to protect information and infrastructure from both internal and external threats.Understanding these principles helps organizations build resilient networks capable of withstanding cyber threats in an increasingly digital world.
