Introduction to Cryptography
Cryptography is the science of securing communication and data through mathematical techniques. In this chapter, we introduce the fundamental concepts of cryptography, its historical evolution, core principles, types of encryption, and real-world applications in modern cybersecurity.
What is Cryptography?
Cryptography is the practice and study of techniques for securing information and communication from unauthorized access. It ensures confidentiality, integrity, authentication, and non-repudiation of data. Cryptography converts readable data (plaintext) into an unreadable format (ciphertext) and vice versa using algorithms and keys.

History and Evolution of Cryptography
Ancient Cryptography: Caesar Cipher, Spartan Scytale
Medieval Period: Frequency analysis and manual encryption
Modern Era: Machine ciphers (Enigma), digital encryption (RSA, AES)
Post-Quantum Era: Quantum-resistant algorithms
Core Principles of Cryptography
Confidentiality: Only authorized users can read the information.
Integrity: Data is not altered or tampered with.
Authentication: Verifying the identity of the sender or device.
Non-repudiation: Ensures a sender cannot deny their actions.
Types of Cryptographic Algorithms
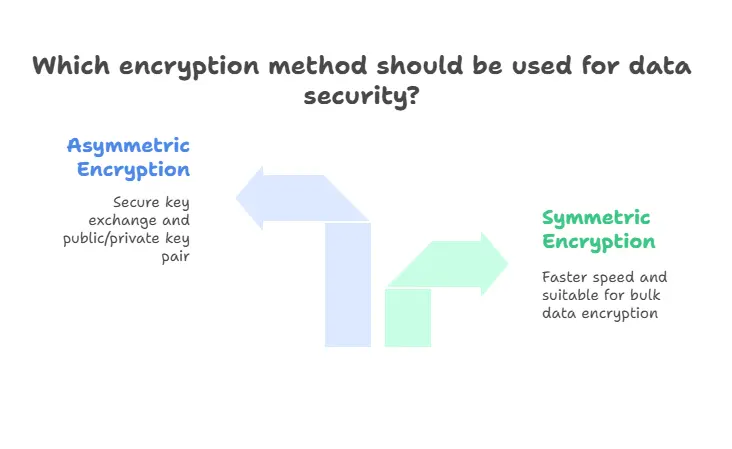
Symmetric Key Cryptography: One key for both encryption and decryption (e.g., AES, DES).
Asymmetric Key Cryptography: Public and private key pair (e.g., RSA, ECC).
Hash Functions: One-way functions for data integrity (e.g., SHA-256, MD5).
Symmetric vs. Asymmetric Encryption
| Feature | Symmetric Encryption | Asymmetric Encryption |
|---|---|---|
| Key Type | Single key | Public/private key pair |
| Speed | Faster | Slower |
| Use Case | Bulk data encryption | Secure key exchange |
| Example Algorithms | AES, Blowfish | RSA, ECC |
Common Cryptographic Techniques
Caesar Cipher – A simple substitution cipher.
RSA – Public-key cryptosystem used for secure data transmission.
AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) – Widely used for securing sensitive data.
Digital Signatures – Ensure authenticity and integrity.
Hashing Algorithms – Used in password storage and data verification.
Applications of Cryptography
Secure communication (emails, messaging apps)
Online transactions and digital payments
Digital signatures and certificates
Blockchain and cryptocurrencies
VPNs and secure network connections
Password protection and storage
Challenges and Limitations
Key management complexity
Performance overhead
Vulnerability to brute-force or side-channel attacks
Emerging threats like quantum computing
Emerging Trends in Cryptography
Post-Quantum Cryptography – Designing algorithms secure against quantum attacks
Homomorphic Encryption – Allows computation on encrypted data
Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKPs) – Used in privacy-preserving systems
Lightweight Cryptography – For IoT and embedded systems
Cryptography is the backbone of secure digital communication. From ancient ciphers to modern encryption standards, it plays a vital role in protecting data and ensuring trust. Understanding its principles, types, and real-world use cases equips professionals to build secure systems in an increasingly digital world.
