Cyber Security vs Information Security vs IT Security
In today’s digital-first world, terms like Cyber Security, Information Security, and IT Security are often used interchangeably, creating confusion among professionals and learners alike. While these concepts are interconnected and sometimes overlap, each has a distinct focus, scope, and objective. This chapter explores these three crucial domains, compares them, and clarifies their unique roles in securing data and systems.
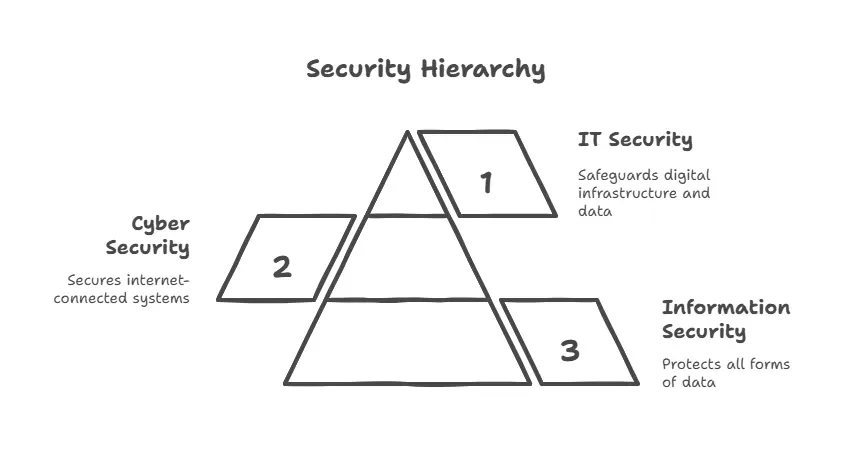
Information Security (InfoSec)
Definition:
Information Security is the umbrella discipline that deals with protecting all forms of information, whether digital or physical, from unauthorized access, disclosure, alteration, or destruction.
Key Focus:
Confidentiality
Integrity
Availability
(Often referred to as the CIA Triad)
Scope:
Protecting paper records, biometric data, and digital files.
Ensuring policies and procedures secure sensitive business and personal information.
Examples:
Locking file cabinets containing sensitive employee records.
Encrypting hard drives that store financial data.
Implementing access control policies across an organization.
Cyber Security
Definition:
Cyber Security is a subset of Information Security that specifically deals with protecting internet-connected systems, including networks, computers, servers, and mobile devices, from cyber threats and attacks.
Key Focus:
Preventing cyber attacks like malware, ransomware, phishing, DDoS attacks.
Securing online transactions, cloud platforms, and digital communications.
Scope:
Primarily concerned with the digital world and cyber space.
Defense against hackers, cyber terrorists, and other malicious actors.
Examples:
Installing antivirus software and firewalls.
Monitoring network traffic for intrusion attempts.
Training employees to identify phishing emails.
IT Security (Information Technology Security)
Definition:
IT Security focuses on safeguarding the digital infrastructure—such as hardware, software, and network resources—against threats that may compromise their functionality or data.
Key Focus:
Protection of technology systems and the data they process.
Ensuring operational resilience and technical defense mechanisms.
Scope:
Covers both cyber security tools and IT-specific controls.
Encompasses physical security (e.g., securing servers) and technical policies.
Examples:
Ensuring only authorized personnel can access server rooms.
Applying software patches to prevent vulnerabilities.
Managing firewalls, IDS/IPS, and secure configuration of systems.
| Feature | Information Security | Cyber Security | IT Security |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scope | All forms of data (digital + physical) | Only digital and online data | Digital infrastructure & technology |
| Focus | Data protection | Internet threats & online attacks | Systems and networks security |
| Medium | Both online and offline | Only online | Hardware, software, and network |
| Includes | Policies, physical & digital security | Cyber threats (malware, hacking) | Technical configurations & controls |
| Subset Of | Broadest field | Subset of InfoSec | Overlaps with InfoSec and Cyber Security |
Overlap and Integration
While the distinctions are important, in practice, these domains often work together:
Cyber Security relies on IT Security tools to detect and prevent threats.
Information Security defines the governance policies which Cyber and IT Security enforce.
All three help achieve compliance (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA, ISO 27001) and ensure business continuity.
Real-World Analogy
Imagine your organization as a building:
Information Security is the overall security policy—it decides what needs protection (rooms, files, documents).
Cyber Security is like securing the internet-connected surveillance cameras, email systems, and cloud platforms.
IT Security includes the locks on doors, keycard systems, fire alarms, and server room access—all technical and hardware-based controls.
Understanding the differences between Cyber Security, Information Security, and IT Security is crucial for creating a robust defense strategy in any organization. While their roles may overlap, their focus areas differ significantly, and each plays a critical part in maintaining the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of organizational assets.A clear grasp of these distinctions will help professionals, policy-makers, and students make informed decisions regarding risk management, compliance, and organizational resilience in an increasingly digital world.
