XML Serialization
XML Serialization is the process of converting an object’s data into an XML format that can be stored, transmitted, and later deserialized back into the object. It is widely used in data storage, configuration files, and communication between systems. Serialization makes it easy to save an object's state and recreate it later, making it useful in web services, APIs, and distributed applications.
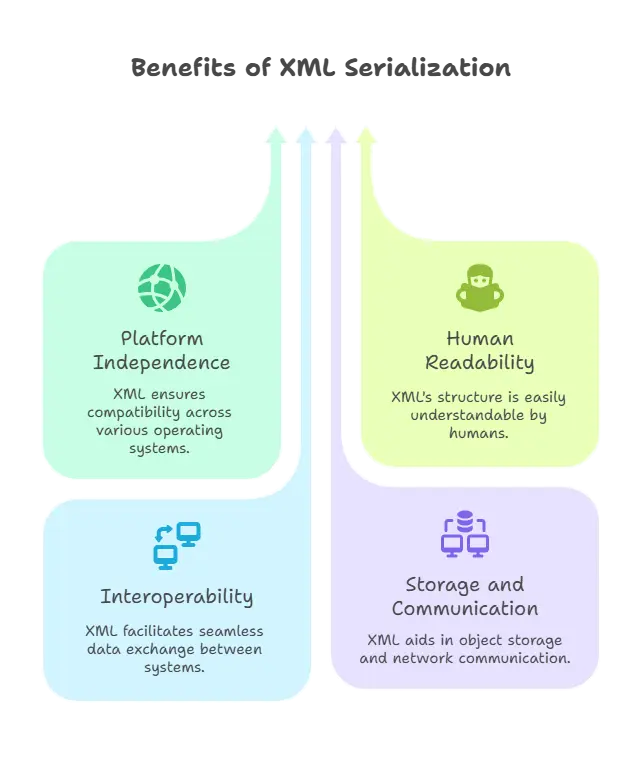
Why Use XML Serialization?
- Platform-Independent: XML is a universally accepted format that is easy to read and write across different platforms.
- Human-Readable: XML is structured in a way that is readable both by machines and humans.
- Interoperability: It allows data exchange between different programming languages and systems.
- Storage and Communication: XML serialization is useful for saving the state of objects, sending objects over networks, and reading configuration settings.
Basic Example of XML Serialization
Let’s assume we have a simple class in a programming language like Python, C#, or Java, and we want to serialize an object of this class into XML format.
Python Example
Suppose you have a class Book with attributes like title, author, and price.
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
class Book:
def __init__(self, title, author, price):
self.title = title
self.author = author
self.price = price
# Serialize Book object to XML
def serialize_to_xml(book):
book_element = ET.Element("book")
title = ET.SubElement(book_element, "title")
title.text = book.title
author = ET.SubElement(book_element, "author")
author.text = book.author
price = ET.SubElement(book_element, "price")
price.text = str(book.price)
return ET.tostring(book_element).decode()
# Create a Book object
book = Book("XML Developer's Guide", "Author Name", 44.95)
# Serialize the book object
xml_data = serialize_to_xml(book)
print(xml_data)
<book>
<title>XML Developer's Guide</title>
<author>Author Name</author>
<price>44.95</price>
</book>
In this example:
- A
Bookobject is created with attributestitle,author, andprice. - The
serialize_to_xml()function converts the object into an XML string. - The
ET.ElementandET.SubElementare used to create XML elements.
XML Deserialization
XML Deserialization is the reverse process of reading an XML document and converting it back into an object. This is useful for restoring the state of an object from XML.
Python Example
Continuing with the previous example, we now deserialize the XML back into a Book object.
def deserialize_from_xml(xml_string):
root = ET.fromstring(xml_string)
title = root.find("title").text
author = root.find("author").text
price = float(root.find("price").text)
return Book(title, author, price)
# Deserialize the XML string back to a Book object
deserialized_book = deserialize_from_xml(xml_data)
print(deserialized_book.title, deserialized_book.author, deserialized_book.price)
// Output
XML Developer's Guide Author Name 44.95
Here:
- The XML string is parsed back into an object using
ET.fromstring(). - The attributes
title,author, andpriceare extracted from the XML and used to recreate theBookobject.
XML Serialization in Other Languages
XML Serialization in C#
In C#, you can use the built-in XmlSerializer class to serialize and deserialize objects.
using System;
using System.Xml.Serialization;
using System.IO;
public class Book
{
public string Title { get; set; }
public string Author { get; set; }
public double Price { get; set; }
}
public class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
Book book = new Book { Title = "XML Developer's Guide", Author = "Author Name", Price = 44.95 };
// Serialize to XML
XmlSerializer serializer = new XmlSerializer(typeof(Book));
using (StringWriter writer = new StringWriter())
{
serializer.Serialize(writer, book);
Console.WriteLine(writer.ToString());
}
// Deserialize from XML
string xmlData = "<Book><Title>XML Developer's Guide</Title><Author>Author Name</Author><Price>44.95</Price></Book>";
using (StringReader reader = new StringReader(xmlData))
{
Book deserializedBook = (Book)serializer.Deserialize(reader);
Console.WriteLine($"{deserializedBook.Title}, {deserializedBook.Author}, {deserializedBook.Price}");
}
}
}
// Output
<Book>
<Title>XML Developer's Guide</Title>
<Author>Author Name</Author>
<Price>44.95</Price>
</Book>
This example shows how XmlSerializer in C# automatically handles the conversion between an object and XML.
XML Serialization in Java
In Java, you can use libraries like JAXB (Java Architecture for XML Binding) for XML serialization.
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlElement;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlRootElement;
import javax.xml.bind.JAXBContext;
import javax.xml.bind.Marshaller;
import javax.xml.bind.Unmarshaller;
import java.io.StringReader;
import java.io.StringWriter;
@XmlRootElement
public class Book {
private String title;
private String author;
private double price;
// Constructors, getters, and setters
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Book book = new Book("XML Developer's Guide", "Author Name", 44.95);
// Serialize to XML
JAXBContext context = JAXBContext.newInstance(Book.class);
Marshaller marshaller = context.createMarshaller();
StringWriter writer = new StringWriter();
marshaller.marshal(book, writer);
System.out.println(writer.toString());
// Deserialize from XML
String xmlData = writer.toString();
Unmarshaller unmarshaller = context.createUnmarshaller();
Book deserializedBook = (Book) unmarshaller.unmarshal(new StringReader(xmlData));
System.out.println(deserializedBook.getTitle() + ", " + deserializedBook.getAuthor() + ", " + deserializedBook.getPrice());
}
}
// Output
<book>
<title>XML Developer's Guide</title>
<author>Author Name</author>
<price>44.95</price>
</book>
Handling Complex Objects in XML Serialization
Serialization can handle more complex objects, including lists, arrays, and nested objects. For example, a Library object containing multiple Book objects can be serialized into XML with proper structure.
Example
class Library:
def __init__(self, books):
self.books = books
def serialize_library_to_xml(library):
library_element = ET.Element("library")
for book in library.books:
book_element = ET.SubElement(library_element, "book")
title = ET.SubElement(book_element, "title")
title.text = book.title
author = ET.SubElement(book_element, "author")
author.text = book.author
price = ET.SubElement(book_element, "price")
price.text = str(book.price)
return ET.tostring(library_element).decode()
# Create a Library object with multiple books
books = [
Book("XML Developer's Guide", "Author Name", 44.95),
Book("Learn XML", "Another Author", 39.95)
]
library = Library(books)
# Serialize the library object
xml_data = serialize_library_to_xml(library)
print(xml_data)
<library>
<book>
<title>XML Developer's Guide</title>
<author>Author Name</author>
<price>44.95</price>
</book>
<book>
<title>Learn XML</title>
<author>Another Author</author>
<price>39.95</price>
</book>
</library>
XML Serialization is a crucial technique for saving, transferring, and restoring the state of objects. It allows data to be easily stored and shared in a platform-agnostic format. Whether you're working in Python, C#, Java, or another language, the principles of serialization and deserialization remain the same. Happy coding !❤️
