Implementing XML-RPC Services
XML-RPC (Remote Procedure Call) is a simple and widely used protocol that enables communication between computers over a network using XML to encode calls and responses. It is one of the earliest methods for remote procedure calls (RPC) that facilitates the exchange of information between clients and servers using XML. XML-RPC is still relevant today because of its simplicity and ability to be used in a wide variety of languages and systems.
Introduction to XML-RPC
XML-RPC stands for XML Remote Procedure Call. It is a protocol that allows programs running on different computers to communicate with each other. The communication happens over HTTP, and the messages are encoded in XML. XML-RPC allows a client to call a function on a remote server and get the result, just as if the function were executed locally.
XML-RPC is simple to implement and is supported by most programming languages, making it an excellent choice for connecting distributed systems.
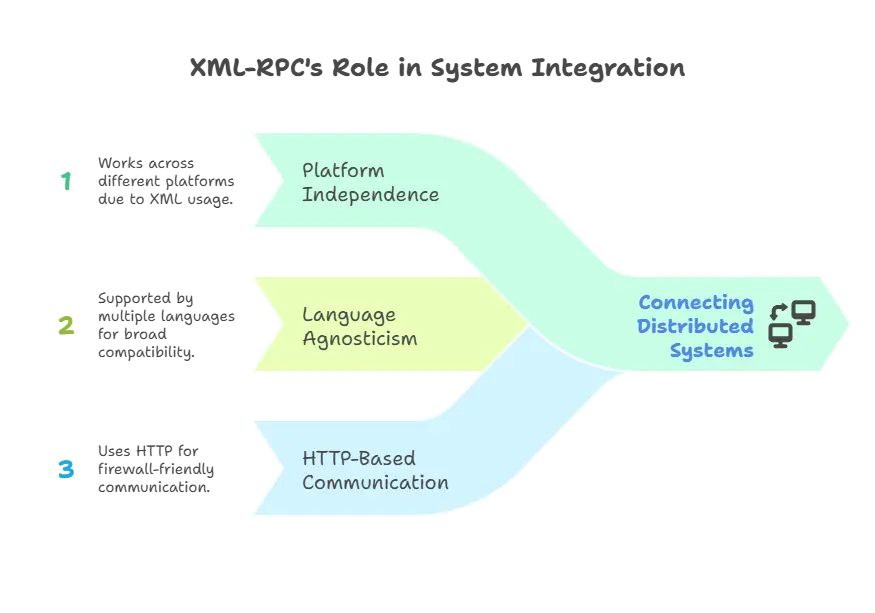
Key Characteristics of XML-RPC:
- Platform Independent: Since XML-RPC uses XML, it works across different platforms.
- Language Agnostic: It is supported by many languages such as Python, Java, PHP, Ruby, etc.
- HTTP-Based: Communication happens over HTTP, which is firewall-friendly.
Why Use XML-RPC?
XML-RPC is used because of its simplicity and efficiency in making remote calls. Its key use cases include:
- Inter-System Communication: When different applications (running on different platforms or written in different languages) need to communicate, XML-RPC acts as a middle ground.
- Lightweight Web Services: Compared to more complex protocols like SOAP, XML-RPC is much lighter and easier to implement.
- Cross-Platform Integration: XML-RPC can be used to integrate systems running on different platforms like Windows, Linux, and macOS.
How XML-RPC Works
XML-RPC works by wrapping remote procedure calls in an XML format and sending them over the HTTP protocol. The process can be broken down into these steps:
- Client Sends a Request: The client sends an XML-encoded request over HTTP, specifying the procedure to be called and any parameters required by that procedure.
- Server Receives and Processes the Request: The server interprets the XML, calls the specified procedure, and processes the input parameters.
- Server Sends a Response: The server encodes the result of the procedure in XML and sends it back to the client over HTTP.
- Client Receives the Response: The client decodes the XML response and retrieves the result of the remote procedure call.
XML-RPC vs SOAP vs REST
When choosing a communication protocol, it’s important to understand how XML-RPC differs from other protocols like SOAP and REST.
| Feature | XML-RPC | SOAP | REST |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Format | XML | XML | JSON, XML |
| Complexity | Simple | Complex | Simple |
| Transport | HTTP | HTTP, SMTP, others | HTTP |
| Messaging | RPC | RPC and Document | Resource-oriented |
| Ease of Use | Easy to implement | More complex | Very easy |
XML-RPC is generally simpler than SOAP and somewhat comparable to REST in simplicity, although REST is more flexible due to its use of different data formats (e.g., JSON). XML-RPC’s strength lies in its straightforwardness for making remote calls.
Components of XML-RPC
XML Request
An XML-RPC request contains a method name and parameters wrapped in an XML document. Here’s an example of a simple XML-RPC request calling a method sumNumbers with two parameters:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<methodCall>
<methodName>sumNumbers</methodName>
<params>
<param>
<value><int>5</int></value>
</param>
<param>
<value><int>3</int></value>
</param>
</params>
</methodCall>
XML Response
The XML-RPC response contains the result of the method call wrapped in XML. Here’s an example response for the sumNumbers method:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<methodResponse>
<params>
<param>
<value><int>8</int></value>
</param>
</params>
</methodResponse>
Data Types in XML-RPC
XML-RPC supports several data types:
- Integer:
<int>,<i4> - Boolean:
<boolean> - String:
<string> - Double:
<double> - DateTime:
<dateTime.iso8601> - Base64:
<base64> - Array:
<array> - Struct:
<struct>
Setting Up an XML-RPC Service
Setting up an XML-RPC service involves the following steps:
- Define the Remote Procedures: These are the methods that can be called by the client.
- Handle Requests: The server needs to parse the XML request, call the appropriate function, and send back the response.
- Run the Service: The XML-RPC service listens for incoming requests over HTTP.
Example: XML-RPC Request and Response
Request:
Let’s look at an example of an XML-RPC request where a client sends a request to multiply two numbers.
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<methodCall>
<methodName>multiplyNumbers</methodName>
<params>
<param>
<value><int>6</int></value>
</param>
<param>
<value><int>7</int></value>
</param>
</params>
</methodCall>
Response:
The server processes the request, multiplies the numbers, and returns the result:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<methodResponse>
<params>
<param>
<value><int>42</int></value>
</param>
</params>
</methodResponse>
Handling XML-RPC Requests in Python
To implement an XML-RPC server in Python, we can use the SimpleXMLRPCServer module, which provides a simple interface for handling XML-RPC requests.
Python Code Example:
from xmlrpc.server import SimpleXMLRPCServer
# Define the function to be called remotely
def multiply_numbers(x, y):
return x * y
# Create the server
server = SimpleXMLRPCServer(("localhost", 8000))
print("Server is running on port 8000...")
# Register the function with the server
server.register_function(multiply_numbers, "multiplyNumbers")
# Run the server
server.serve_forever()
Explanation:
- We define a function
multiply_numbersthat multiplies two numbers. - The server listens on port 8000 for XML-RPC requests.
- The function is registered with the name
multiplyNumbers.
Client Code Example:
import xmlrpc.client
# Connect to the server
proxy = xmlrpc.client.ServerProxy("http://localhost:8000/")
# Call the multiplyNumbers method
result = proxy.multiplyNumbers(6, 7)
print("Result:", result)
Output:
The client sends a request to the server, and the server returns the result:
Result: 42
Handling XML-RPC Requests in Java
For Java, we can use the Apache XML-RPC library to handle XML-RPC requests.
Java Code Example:
import org.apache.xmlrpc.WebServer;
public class XMLRPCServer {
public int multiplyNumbers(int x, int y) {
return x * y;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
System.out.println("Starting XML-RPC server...");
WebServer server = new WebServer(8000);
server.addHandler("sample", new XMLRPCServer());
server.start();
System.out.println("Server started successfully.");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("XML-RPC Server: " + e);
}
}
}
Explanation:
- We define the
multiplyNumbersmethod in theXMLRPCServerclass. - The server listens on port 8000.
- A handler is added to manage requests.
Error Handling in XML-RPC
Error handling is a crucial part of XML-RPC. If something goes wrong, the server returns a fault response.
Example of an XML-RPC Fault Response:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<methodResponse>
<fault>
<value>
<struct>
<member>
<name>faultCode</name>
<value><int>4</int></value>
</member>
<member>
<name>faultString</name>
<value><string>Too many parameters</string></value>
</member>
</struct>
</value>
</fault>
</methodResponse>
Advantages and Limitations of XML-RPC
Advantages:
- Simplicity: XML-RPC is easy to implement and understand.
- Cross-Language Support: Works well with many programming languages.
- Platform Independence: Can be used across different platforms and operating systems.
Limitations:
- XML Overhead: XML is verbose, which can lead to slower transmission compared to lighter formats like JSON.
- Limited Data Types: XML-RPC supports only a limited set of data types.
XML-RPC is a simple, yet effective protocol for enabling remote procedure calls across different systems and platforms. Its use of XML for encoding requests and responses makes it platform-independent, and the HTTP transport ensures that it works well across the internet. Happy Coding!❤️
