Exploring GraphQL Subscriptions with React
GraphQL Subscriptions is a query language for APIs and a runtime for executing those queries with your existing data. Unlike REST, which uses multiple endpoints, GraphQL provides a single endpoint and allows clients to request only the data they need.
Key Concepts
- Queries: Retrieve data.
- Mutations: Modify data.
- Subscriptions: Receive real-time updates.
Understanding GraphQL Subscription
GraphQL subscriptions are a way to get real-time updates from the server. Unlike queries and mutations, subscriptions maintain a persistent connection between the client and the server. This allows the server to push updates to the client whenever the data changes.
How Subscriptions Work
- WebSockets: Subscriptions typically use WebSocket connections to maintain a two-way communication channel.
- Server Push: The server pushes updates to the client based on subscription topics.
- Client Listening: The client listens for updates and processes them as they arrive.
Setting Up the Project
We’ll set up a simple project to demonstrate GraphQL subscriptions. This will include both the server and client sides.
Setting Up the GraphQL Server
1.Create a new directory for the server:
mkdir graphql-server
cd graphql-server
2.Initialize a Node.js project:
npm init -y
3.Install necessary dependencies:
npm install express graphql express-graphql graphql-subscriptions ws
4.Create a server file (server.js):
const express = require('express');
const { graphqlHTTP } = require('express-graphql');
const { buildSchema, GraphQLObjectType, GraphQLString, GraphQLSchema } = require('graphql');
const { PubSub } = require('graphql-subscriptions');
const WebSocket = require('ws');
const http = require('http');
const app = express();
const port = 4000;
const pubsub = new PubSub();
// GraphQL Schema
const MessageType = new GraphQLObjectType({
name: 'Message',
fields: {
content: { type: GraphQLString }
}
});
const RootQuery = new GraphQLObjectType({
name: 'RootQueryType',
fields: {
message: {
type: MessageType,
resolve() {
return { content: 'Hello world' };
}
}
}
});
const Mutation = new GraphQLObjectType({
name: 'Mutation',
fields: {
sendMessage: {
type: MessageType,
args: { content: { type: GraphQLString } },
resolve(parent, args) {
const message = { content: args.content };
pubsub.publish('MESSAGE_SENT', { messageSent: message });
return message;
}
}
}
});
const Subscription = new GraphQLObjectType({
name: 'Subscription',
fields: {
messageSent: {
type: MessageType,
subscribe: () => pubsub.asyncIterator(['MESSAGE_SENT'])
}
}
});
const schema = new GraphQLSchema({
query: RootQuery,
mutation: Mutation,
subscription: Subscription
});
app.use('/graphql', graphqlHTTP({
schema: schema,
graphiql: true
}));
const server = http.createServer(app);
const wss = new WebSocket.Server({ server });
wss.on('connection', ws => {
ws.on('message', message => {
console.log(`Received message => ${message}`);
});
});
server.listen(port, () => {
console.log(`Server is running on http://localhost:${port}/graphql`);
});
Explanation of Code
- Dependencies: We use
expressfor the server,graphqlfor schema definitions,graphql-subscriptionsfor handling subscriptions, andwsfor WebSocket support. - Schema Definition: Define
MessageType,RootQuery,Mutation, andSubscriptionto handle queries, mutations, and subscriptions. - PubSub:
PubSubfromgraphql-subscriptionshelps in publishing and subscribing to events. - Server and WebSocket: Set up an HTTP server and a WebSocket server.
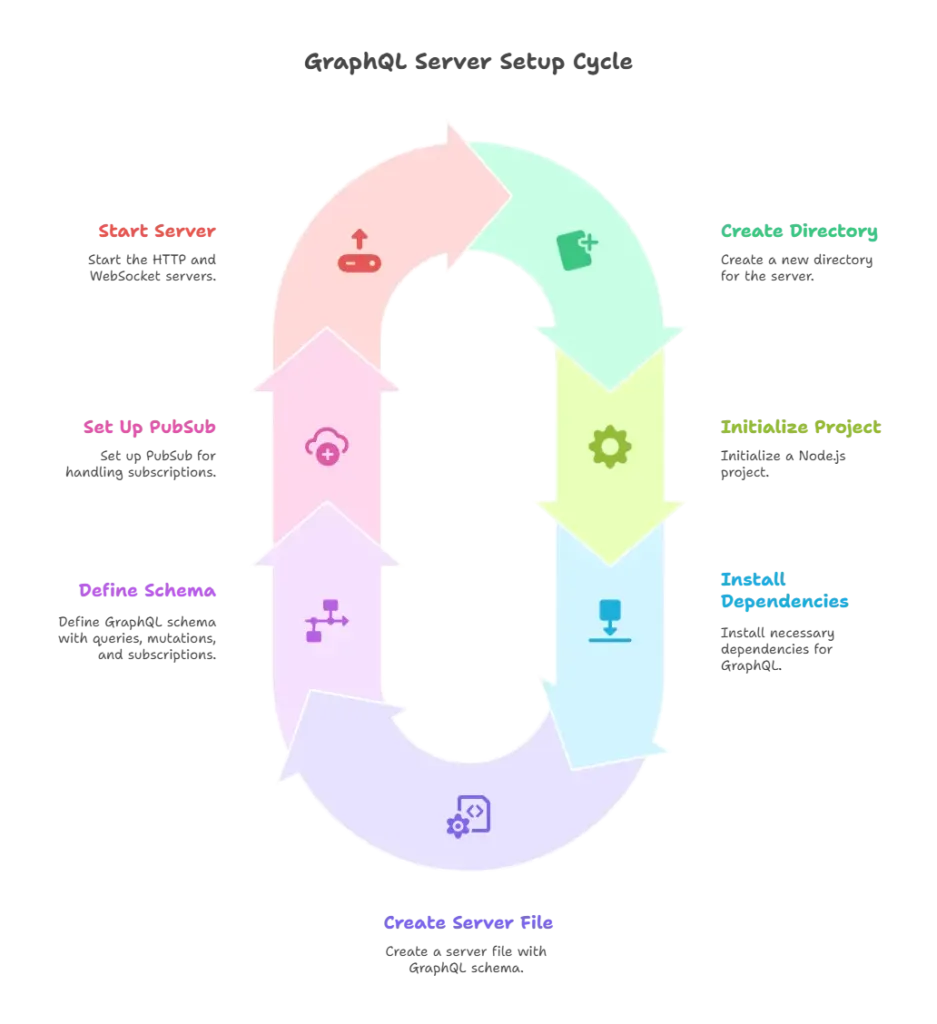
Creating a GraphQL Server with Subscriptions
With the basic server setup in place, let’s focus on the subscription logic. We already included the subscription part in the previous step.
Testing the Server
To test the server:
Run the server:
node server.js
Open GraphiQL at http://localhost:4000/graphql to test queries, mutations, and subscriptions.
Query:
{
message {
content
}
}
Mutation:
mutation {
sendMessage(content: "Hello from mutation!") {
content
}
}
Subscription:
subscription {
messageSent {
content
}
}
Open multiple instances of GraphiQL to test real-time updates.
Integrating GraphQL Client with Reac
Next, we’ll set up a React client that interacts with our GraphQL server.
Setting Up React Project
1.Create a React app:
npx create-react-app graphql-client
cd graphql-client
2.Install necessary dependencies:
npm install @apollo/client graphql subscriptions-transport-ws
Configure Apollo Client
In src/index.js, configure Apollo Client with WebSocket support:
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
import { ApolloProvider, InMemoryCache, ApolloClient, HttpLink, split } from '@apollo/client';
import { WebSocketLink } from 'subscriptions-transport-ws';
import { getMainDefinition } from '@apollo/client/utilities';
import App from './App';
// Create an HTTP Link
const httpLink = new HttpLink({
uri: 'http://localhost:4000/graphql'
});
// Create a WebSocket Link
const wsLink = new WebSocketLink({
uri: `ws://localhost:4000/graphql`,
options: {
reconnect: true
}
});
// Split links based on operation type
const splitLink = split(
({ query }) => {
const definition = getMainDefinition(query);
return (
definition.kind === 'OperationDefinition' &&
definition.operation === 'subscription'
);
},
wsLink,
httpLink
);
// Create an Apollo Client
const client = new ApolloClient({
link: splitLink,
cache: new InMemoryCache()
});
ReactDOM.render(
<ApolloProvider client={client}>
<App />
</ApolloProvider>,
document.getElementById('root')
);
Create a Basic React Component
In src/App.js, create a component to handle subscriptions:
import React, { useState } from 'react';
import { useMutation, useSubscription, gql } from '@apollo/client';
const MESSAGE_SUBSCRIPTION = gql`
subscription {
messageSent {
content
}
}
`;
const SEND_MESSAGE_MUTATION = gql`
mutation sendMessage($content: String!) {
sendMessage(content: $content) {
content
}
}
`;
function App() {
const [message, setMessage] = useState('');
const { data, loading } = useSubscription(MESSAGE_SUBSCRIPTION);
const [sendMessage] = useMutation(SEND_MESSAGE_MUTATION);
const handleSendMessage = () => {
sendMessage({ variables: { content: message } });
setMessage('');
};
return (
<div>
<h1>Real-Time Chat</h1>
<div>
{loading ? <p>Loading...</p> : data && <p>{data.messageSent.content}</p>}
</div>
<input
value={message}
onChange={(e) => setMessage(e.target.value)}
onKeyPress={(e) => {
if (e.key === 'Enter') {
handleSendMessage();
}
}}
/>
<button onClick={handleSendMessage}>Send</button>
</div>
);
}
export default App;
Explanation of Code
- Apollo Client Configuration: Sets up HTTP and WebSocket links and integrates them with Apollo Client.
- Subscriptions and Mutations: Uses
useSubscriptionto listen for incoming messages anduseMutationto send messages. - UI Rendering: Displays real-time updates and provides an input field to send messages.
Implementing GraphQL Subscriptions in React
With the basic setup done, let’s dive into how the subscription and mutation work in detail.
Handling Real-Time Updates
In the App.js component, the useSubscription hook listens for new messages. When a new message is published from the server, it automatically updates the UI.
Sending Messages
The handleSendMessage function triggers the sendMessage mutation. This mutation publishes the message to all clients subscribed to the MESSAGE_SENT subscription topic.
Handling Real-Time Updates
Handling real-time updates involves ensuring that your application efficiently processes and displays incoming data.
Optimizing Performance
- Debouncing Input: Prevent sending too many messages in quick succession.
- Efficient Rendering: Use React’s
memoanduseCallbackto optimize rendering performance.
Error Handling
Handle potential errors from GraphQL operations using Apollo Client’s error handling mechanisms.
Advanced Topics and Optimizations
Authentication and Authorization
For secure applications, implement authentication and authorization:
- Frontend: Use authentication tokens with Apollo Client.
- Backend: Validate tokens and restrict access to certain subscriptions and mutations.
Scaling Subscriptions
- Handling Large Data: Implement pagination and efficient data querying.
- Scaling WebSockets: Use a scalable WebSocket server or message broker (e.g., Redis).
Testing and Deployment
Testing
- Frontend Testing: Use tools like Jest and React Testing Library to test components and GraphQL operations.
- Backend Testing: Use libraries like Mocha or Jest for server-side testing.
Deployment
- Frontend Deployment: Deploy your React app to platforms like Vercel or Netlify.
- Backend Deployment: Deploy your GraphQL server to platforms like Heroku or AWS.
In this chapter, we explored GraphQL subscriptions with React, covering the setup of both server and client, handling real-time updates, and implementing advanced features. By integrating GraphQL subscriptions, you can build powerful real-time applications that provide a dynamic and engaging user experience. Happy coding !❤️
