Storing and Indexing Geospatial Data
MongoDB provides robust support for geospatial data, enabling applications to store, index, and query location-based data efficiently. This capability is invaluable for location-based services like ride-hailing, mapping, logistics, and more.
Understanding Geospatial Data
What is Geospatial Data?
Geospatial data describes the geographical position and characteristics of objects on Earth. Types include:
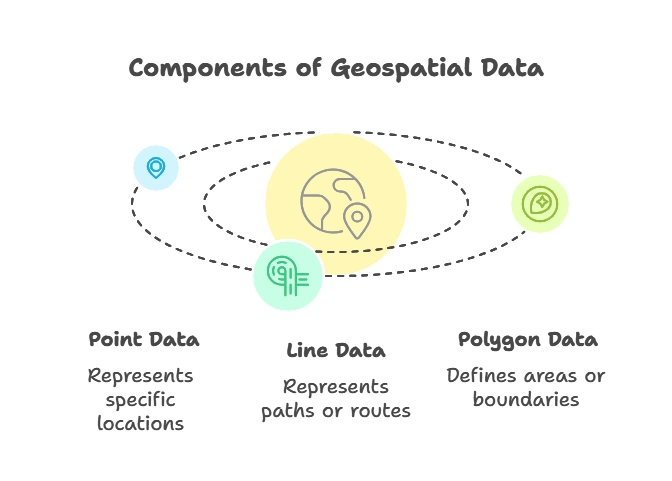
- Point Data: Represents a specific location (latitude, longitude), like a store location.
- Line Data: Represents paths, like roads or rivers.
- Polygon Data: Defines areas, like a city boundary or a lake.
Importance of Geospatial Data in MongoDB
MongoDB’s geospatial indexing and querying capabilities allow applications to handle location data more efficiently. This is essential for:
- Location-based Recommendations: Showing nearby stores, restaurants, or events.
- Mapping Applications: Visualizing geographical data.
- Route Optimization: Finding shortest paths, ideal for logistics and delivery.
Setting Up Geospatial Data Types in MongoDB
MongoDB supports different data types to store geospatial data, making it versatile for handling various location-based data structures.
Supported Geospatial Data Types
MongoDB has two main data types for geospatial data:
- Point: Represents a single coordinate pair (longitude, latitude).
- LineString: Represents a series of points connected in sequence (useful for paths).
- Polygon: Defines an enclosed area using a series of points.
Example of Geospatial Data Types
1. Point Example: Represents a single coordinate, like a restaurant location.
{ "type": "Point", "coordinates": [ -73.97, 40.77 ] }
2. LineString Example: Represents a path or line, like a hiking trail.
{ "type": "LineString", "coordinates": [ [ -73.97, 40.77 ], [ -73.98, 40.78 ] ] }
3. Polygon Example: Defines an area, like a park boundary.
{
"type": "Polygon",
"coordinates": [
[ [ -73.97, 40.77 ], [ -73.98, 40.77 ], [ -73.98, 40.78 ], [ -73.97, 40.77 ] ]
]
}
Storing Geospatial Data in MongoDB
Store geospatial data in a field within your document, making it easier to index and query. For example:
db.places.insertOne({
name: "Central Park",
location: { type: "Point", coordinates: [ -73.97, 40.77 ] }
})
Creating Geospatial Indexes
Indexes are crucial for efficiently querying geospatial data in MongoDB.
Understanding 2D and 2dsphere Indexes
- 2D Index: For flat, 2D coordinate systems, often used for simple, non-spherical data.
- 2dsphere Index: For spherical (Earth-like) data, accommodating latitude and longitude for real-world locations.
Creating a 2dsphere Index
The 2dsphere index is more commonly used for real-world applications, as it accommodates spherical coordinates.
Syntax:
db.collection.createIndex({ location: "2dsphere" })
Example: Let’s index the location field in a collection named places.
db.places.createIndex({ location: "2dsphere" })
Verifying Indexes
After creating an index, you can view it using the getIndexes() method.
db.places.getIndexes()
Output: The output shows that a 2dsphere index has been created on the location field.
Basic Geospatial Queries
With the geospatial index in place, you can perform queries such as finding locations near a point or within a specified area.
Finding Nearby Locations with $near
The $near operator finds documents close to a given point, useful for applications like “find nearest restaurants.”
Syntax:
db.collection.find({
location: {
$near: {
$geometry: { type: "Point", coordinates: [ <longitude>, <latitude> ] },
$maxDistance: <distance_in_meters>
}
}
})
Example: Find locations within 1 km of a given point.
db.places.find({
location: {
$near: {
$geometry: { type: "Point", coordinates: [ -73.97, 40.77 ] },
$maxDistance: 1000
}
}
})
Explanation:
- $geometry specifies the type and coordinates of the point.
- $maxDistance limits results to within 1,000 meters of the given point.
Output: This query returns locations ordered by proximity to the specified point.
Finding Locations Within an Area Using $geoWithin
The $geoWithin operator retrieves documents within a specified shape, like a polygon or a circle.
Syntax:
db.collection.find({
location: {
$geoWithin: {
$geometry: { type: "Polygon", coordinates: [ [ [ <longitude>, <latitude> ], … ] ] }
}
}
})
Example: Find locations within a defined polygon area.
db.places.find({
location: {
$geoWithin: {
$geometry: {
type: "Polygon",
coordinates: [
[ [ -73.99, 40.75 ], [ -73.98, 40.75 ], [ -73.98, 40.76 ], [ -73.99, 40.76 ], [ -73.99, 40.75 ] ]
]
}
}
}
})
Advanced Geospatial Queries
Combining Geospatial Queries with Other Filters
MongoDB allows combining geospatial queries with other fields in a document. For example, finding locations near a point with a specific name or property.
Example: Find places near a point that are parks.
db.places.find({
location: {
$near: {
$geometry: { type: "Point", coordinates: [ -73.97, 40.77 ] },
$maxDistance: 1000
}
},
type: "park"
})
Using $centerSphere for Circular Queries
The $centerSphere operator defines a circular search area by specifying a center point and radius in radians.
Example: Find locations within a 10 km radius of a point.
db.places.find({
location: {
$geoWithin: {
$centerSphere: [ [ -73.97, 40.77 ], 10 / 6378.1 ] // 10 km in radians
}
}
})
Practical Applications of Geospatial Data in MongoDB
Geospatial data is widely used across industries:
- Mapping and Navigation: Using real-time data for routes.
- Logistics and Delivery: Tracking shipments and optimizing routes.
- Social and Marketing: Offering location-based recommendations.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Indexing Errors
If MongoDB raises an error when creating a 2dsphere index, verify that your documents use correct geoJSON types.
Invalid Data Types
Ensure that your data follows the correct GeoJSON format (e.g., Point, Polygon). Invalid data types can result in errors.
Query Performance
Ensure your queries use indexed fields, as geospatial queries can be resource-intensive without indexing.
MongoDB’s geospatial capabilities offer a robust solution for applications requiring efficient location-based data handling. By leveraging the indexing and querying capabilities described in this chapter, developers can build powerful, real-time geospatial applications that are essential for modern data-driven services. Happy Coding!❤️
