Aggregation Framework
The aggregation framework in MongoDB is a powerful tool for performing data processing and analysis on documents within a collection. It enables complex queries and transformations using a series of pipeline stages, each applying specific operations on the data. This chapter will provide a comprehensive overview of the aggregation framework, covering basic concepts, common stages, and advanced techniques. Each section will include detailed explanations and code examples.
Aggregation Framework
The aggregation framework processes data records and returns computed results. It is often used for tasks such as data transformation, statistical analysis, and data summarization. Aggregations are built on an extensible expression language and can perform a variety of operations, including filtering, grouping, sorting, and reshaping documents.
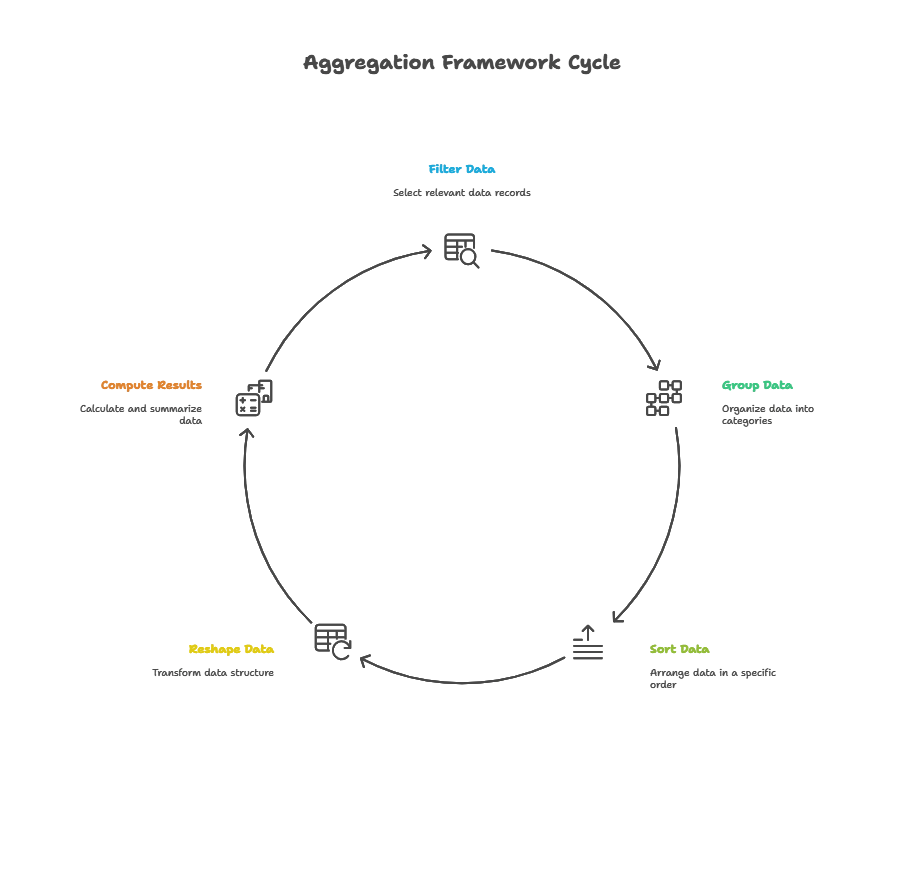
Basic Concepts
Aggregation Pipeline
The aggregation pipeline is a series of stages through which documents pass. Each stage transforms the documents in some way and passes the results to the next stage. The stages can filter, group, sort, and reshape documents.
Pipeline Stages
A pipeline stage is a MongoDB operator that performs an operation on the documents passed to it. Common stages include $match, $group, $sort, and $project.
Aggregation Pipeline Stages
$match
Filters documents to pass only those that match the specified condition.
Example:
db.collection.aggregate([
{ $match: { status: "A" } }
]);
Explanation:
$match: Filters documents wherestatusis “A”
// Output
[
{ _id: 1, status: "A", score: 85 },
{ _id: 2, status: "A", score: 90 }
]
$project
Shapes the documents by including, excluding, or adding new fields.
Example:
db.collection.aggregate([
{ $project: { item: 1, total: { $multiply: ["$price", "$quantity"] } } }
]);
Explanation:
$project: Includes theitemfield and adds a new fieldtotalcalculated by multiplyingpriceandquantity.
// Output
[
{ _id: 1, item: "apple", total: 60 },
{ _id: 2, item: "banana", total: 30 }
]
$group
Groups documents by a specified field and applies aggregate functions.
Example:
db.collection.aggregate([
{ $group: { _id: "$status", total: { $sum: "$score" } } }
]);
Explanation:
$group: Groups documents bystatusand calculates the totalscorefor each group.
// Output
[
{ _id: "A", total: 175 },
{ _id: "B", total: 70 }
]
$sort
Sorts the documents by a specified field.
Example:
db.collection.aggregate([
{ $sort: { score: -1 } }
]);
Explanation:
$sort: Orders the documents byscorein descending order.
// Output
[
{ _id: 2, status: "A", score: 90 },
{ _id: 1, status: "A", score: 85 },
{ _id: 3, status: "B", score: 70 }
]
$limit
Limits the number of documents passed to the next stage.
Example:
db.collection.aggregate([
{ $limit: 2 }
]);
Explanation:
$limit: Passes only the first 2 documents to the next stage.
// Output
[
{ _id: 1, status: "A", score: 85 },
{ _id: 2, status: "A", score: 90 }
]
$skip
Skips a specified number of documents and passes the rest to the next stage.
Example:
db.collection.aggregate([
{ $skip: 1 }
]);
Explanation:
$skip: Skips the first document and passes the remaining documents to the next stage.
// Output
[
{ _id: 2, status: "A", score: 90 },
{ _id: 3, status: "B", score: 70 }
]
$unwind
Deconstructs an array field from the input documents to output a document for each element.
Example:
db.collection.aggregate([
{ $unwind: "$items" }
]);
Explanation:
$unwind: Outputs a document for each element in theitemsarray field.
// Output
[
{ _id: 1, items: "apple" },
{ _id: 1, items: "banana" },
{ _id: 2, items: "orange" }
]
Common Aggregation Expressions
Arithmetic Expressions
Used for performing arithmetic operations on fields.
Example:
db.collection.aggregate([
{ $project: { total: { $add: ["$price", "$tax"] } } }
]);
Explanation:
$add: Adds thepriceandtaxfields.
// Output
[
{ _id: 1, total: 110 },
{ _id: 2, total: 220 }
]
Array Expressions
Used for performing operations on arrays.
Example:
db.collection.aggregate([
{ $project: { firstItem: { $arrayElemAt: ["$items", 0] } } }
]);
Explanation:
$arrayElemAt: Retrieves the first element of theitemsarray.
// Output
[
{ _id: 1, firstItem: "apple" },
{ _id: 2, firstItem: "orange" }
]
Boolean Expressions
Used for evaluating boolean conditions.
Example:
db.collection.aggregate([
{ $project: { isExpensive: { $gt: ["$price", 100] } } }
]);
Explanation:
$gt: Evaluates ifpriceis greater than 100.
// Output
[
{ _id: 1, isExpensive: true },
{ _id: 2, isExpensive: false }
]
Comparison Expressions
Used for comparing field values.
Example:
db.collection.aggregate([
{ $project: { isExpensive: { $gt: ["$price", 100] } } }
]);
Explanation:
$gt: Checks ifpriceis greater than 100.
// Output
[
{ _id: 1, isExpensive: true },
{ _id: 2, isExpensive: false }
]
Date Expressions
Used for manipulating dates.
Example:
db.collection.aggregate([
{ $project: { year: { $year: "$date" } } }
]);
Explanation:
$year: Extracts the year from thedatefield.
// Output
[
{ _id: 1, year: 2020 },
{ _id: 2, year: 2021 }
]
String Expressions
Used for manipulating strings.
Example:
db.collection.aggregate([
{ $project: { uppercaseName: { $toUpper: "$name" } } }
]);
Explanation:
$toUpper: Converts thenamefield to uppercase.
// Output
[
{ _id: 1, uppercaseName: "ALICE" },
{ _id: 2, uppercaseName: "BOB" }
]
Advanced Aggregation Techniques
$lookup (Joining Collections)
Performs a left outer join to a collection in the same database to filter in documents from the joined collection.
Example:
db.orders.aggregate([
{
$lookup: {
from: "inventory",
localField: "item",
foreignField: "item",
as: "inventory_docs"
}
}
]);
Explanation:
$lookup: Joins theorderscollection with theinventorycollection based on theitemfield.
// Output
[
{
_id: 1,
item: "apple",
inventory_docs: [
{ _id: 101, item: "apple", qty: 50 }
]
},
{
_id: 2,
item: "banana",
inventory_docs: [
{ _id: 102, item: "banana", qty: 30 }
]
}
]
$facet (Multiple Pipelines)
Processes multiple aggregation pipelines within a single stage and outputs a document that contains the results of each pipeline.
Example:
db.collection.aggregate([
{
$facet: {
"priceSummary": [
{ $group: { _id: null, avgPrice: { $avg: "$price" }, maxPrice: { $max: "$price" } } }
],
"categories": [
{ $group: { _id: "$category", count: { $sum: 1 } } }
]
}
}
]);
Explanation:
$facet: Runs multiple pipelines to get different summaries in a single query.
// Output
[
{
priceSummary: [
{ _id: null, avgPrice: 150, maxPrice: 200 }
],
categories: [
{ _id: "electronics", count: 10 },
{ _id: "appliances", count: 5 }
]
}
]
$bucket (Bucketization)
Categorizes documents into groups, called buckets, based on a specified expression and bucket boundaries.
Example:
db.collection.aggregate([
{
$bucket: {
groupBy: "$price",
boundaries: [0, 50, 100, 150, 200],
default: "Other",
output: {
"count": { $sum: 1 },
"items": { $push: "$name" }
}
}
}
]);
Explanation:
$bucket: Divides documents into price ranges and counts the number of documents in each range.
// Output
[
{ _id: 0, count: 2, items: ["item1", "item2"] },
{ _id: 50, count: 3, items: ["item3", "item4", "item5"] },
{ _id: 100, count: 1, items: ["item6"] },
{ _id: "Other", count: 1, items: ["item7"] }
]
$graphLookup (Recursive Search)
Performs a recursive search on a collection, searching a collection for documents that match a specified condition.
Example:
db.employees.aggregate([
{
$graphLookup: {
from: "employees",
startWith: "$reportsTo",
connectFromField: "reportsTo",
connectToField: "name",
as: "reportingHierarchy"
}
}
]);
Explanation:
$graphLookup: Recursively searches theemployeescollection to find the reporting hierarchy of each employee.
// Output
[
{
_id: 1,
name: "Alice",
reportsTo: "Bob",
reportingHierarchy: [
{ _id: 2, name: "Bob", reportsTo: "Charlie" },
{ _id: 3, name: "Charlie", reportsTo: null }
]
},
{
_id: 2,
name: "Bob",
reportsTo: "Charlie",
reportingHierarchy: [
{ _id: 3, name: "Charlie", reportsTo: null }
]
}
]
Performance Considerations
- Index Usage: Ensure indexes are used efficiently in
$matchstages. - Pipeline Order: Place
$matchand$sortstages early in the pipeline to reduce the number of documents processed in later stages. - Aggregation Memory Limit: Be aware of the 100 MB memory limit for aggregation operations and consider using the
allowDiskUseoption if necessary. - Sharded Collections: Aggregation pipelines that need to merge data from multiple shards can be more complex and less performant.
Practical Examples with Data
practical examples with sample data. We’ll use a collection of documents that represent sales records in a retail store.
Sample Data
Here’s a sample dataset of sales records:
db.sales.insertMany([
{ _id: 1, date: new Date("2023-07-25"), product: "Laptop", quantity: 2, amount: 1500, city: "New York" },
{ _id: 2, date: new Date("2023-07-25"), product: "Laptop", quantity: 1, amount: 750, city: "San Francisco" },
{ _id: 3, date: new Date("2023-07-26"), product: "Phone", quantity: 3, amount: 900, city: "New York" },
{ _id: 4, date: new Date("2023-07-26"), product: "Phone", quantity: 2, amount: 600, city: "San Francisco" },
{ _id: 5, date: new Date("2023-07-27"), product: "Tablet", quantity: 5, amount: 1250, city: "New York" },
{ _id: 6, date: new Date("2023-07-27"), product: "Tablet", quantity: 4, amount: 1000, city: "San Francisco" },
{ _id: 7, date: new Date("2023-07-28"), product: "Headphones", quantity: 10, amount: 500, city: "New York" },
{ _id: 8, date: new Date("2023-07-28"), product: "Headphones", quantity: 8, amount: 400, city: "San Francisco" }
]);
Example 1: Calculate Total Sales per Day
Objective
To calculate the total sales amount for each day.
Aggregation Pipeline
db.sales.aggregate([
{ $group: { _id: "$date", totalSales: { $sum: "$amount" } } },
{ $sort: { _id: 1 } }
]);
Explanation
$group: Groups the documents by thedatefield and calculates the total sales amount for each day using$sum.$sort: Sorts the grouped documents bydatein ascending order.
// Output
[
{ _id: ISODate("2023-07-25T00:00:00Z"), totalSales: 2250 },
{ _id: ISODate("2023-07-26T00:00:00Z"), totalSales: 1500 },
{ _id: ISODate("2023-07-27T00:00:00Z"), totalSales: 2250 },
{ _id: ISODate("2023-07-28T00:00:00Z"), totalSales: 900 }
]
Example 2: Find Average Sales Amount by City
Objective
To find the average sales amount for each city.
Aggregation Pipeline
db.sales.aggregate([
{ $group: { _id: "$city", avgSalesAmount: { $avg: "$amount" } } }
]);
Explanation
$group: Groups the documents by thecityfield and calculates the average sales amount for each city using$avg.
// Output
[
{ _id: "New York", avgSalesAmount: 1037.5 },
{ _id: "San Francisco", avgSalesAmount: 687.5 }
]
Example 3: Find Top 3 Most Sold Products
Objective
To find the top 3 most sold products based on the quantity sold.
Aggregation Pipeline
db.sales.aggregate([
{ $group: { _id: "$product", totalQuantity: { $sum: "$quantity" } } },
{ $sort: { totalQuantity: -1 } },
{ $limit: 3 }
]);
Explanation
$group: Groups the documents by theproductfield and calculates the total quantity sold for each product using$sum.$sort: Sorts the grouped documents bytotalQuantityin descending order.$limit: Limits the output to the top 3 products.
// Output
[
{ _id: "Headphones", totalQuantity: 18 },
{ _id: "Tablet", totalQuantity: 9 },
{ _id: "Phone", totalQuantity: 5 }
]
Example 4: Average Quantity Sold per Product per City
Objective
To find the average quantity sold per product for each city.
Aggregation Pipeline
db.sales.aggregate([
{ $group: { _id: { product: "$product", city: "$city" }, avgQuantity: { $avg: "$quantity" } } },
{ $sort: { "_id.city": 1, "_id.product": 1 } }
]);
Explanation
$group: Groups the documents by bothproductandcityand calculates the average quantity sold for each combination using$avg.$sort: Sorts the grouped documents first bycityand then byproductin ascending order.
// Output
[
{ _id: { product: "Headphones", city: "New York" }, avgQuantity: 10 },
{ _id: { product: "Headphones", city: "San Francisco" }, avgQuantity: 8 },
{ _id: { product: "Laptop", city: "New York" }, avgQuantity: 2 },
{ _id: { product: "Laptop", city: "San Francisco" }, avgQuantity: 1 },
{ _id: { product: "Phone", city: "New York" }, avgQuantity: 3 },
{ _id: { product: "Phone", city: "San Francisco" }, avgQuantity: 2 },
{ _id: { product: "Tablet", city: "New York" }, avgQuantity: 5 },
{ _id: { product: "Tablet", city: "San Francisco" }, avgQuantity: 4 }
]
Example 5: Monthly Sales Summary with $facet
Objective
To get a summary of total sales and average sales amount per product, all in one query.
Aggregation Pipeline
db.sales.aggregate([
{
$facet: {
totalSales: [
{ $group: { _id: null, totalAmount: { $sum: "$amount" } } }
],
averageSalesPerProduct: [
{ $group: { _id: "$product", avgAmount: { $avg: "$amount" } } }
]
}
}
]);
Explanation
$facet: Allows multiple aggregation pipelines within a single stage.totalSales: Aggregation pipeline to calculate the total sales amount.averageSalesPerProduct: Aggregation pipeline to calculate the average sales amount per product.
// Output
[
{
totalSales: [
{ _id: null, totalAmount: 6900 }
],
averageSalesPerProduct: [
{ _id: "Headphones", avgAmount: 450 },
{ _id: "Laptop", avgAmount: 1125 },
{ _id: "Phone", avgAmount: 750 },
{ _id: "Tablet", avgAmount: 1125 }
]
}
]
In this chapter, we delved into the MongoDB aggregation framework, exploring its basic concepts, common pipeline stages, and advanced techniques. The aggregation framework is a powerful tool for data transformation and analysis, enabling complex operations to be performed efficiently within MongoDB. Happy coding !❤️
