Moving Data Between MongoDB Instances
Moving data between MongoDB instances is a crucial process when managing databases. You might need to transfer data for various reasons, such as migrating to a new server, splitting data across multiple instances, creating backups, or setting up a replica set. MongoDB provides tools and techniques to make this process efficient and secure.
Reasons for Moving Data Between MongoDB Instances
Understanding why data movement is necessary can help you determine the best approach for your needs.
Common Scenarios for Data Migration
- Server Migration: When upgrading or changing servers.
- Environment Setup: Moving data from development to production or vice versa.
- Load Balancing: Distributing data across multiple servers to balance the load.
- Backup and Restore: Moving data for backup or restoring data from a backup instance.
- Data Replication: Copying data to create replica sets for high availability and redundancy.
Choosing the Right Approach
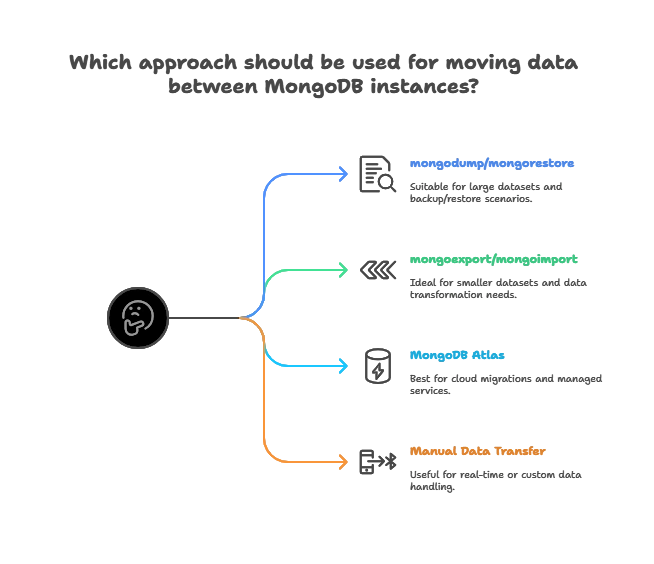
MongoDB offers several ways to move data, such as using mongodump and mongorestore, using mongoexport and mongoimport, using MongoDB’s Atlas for cloud migrations, and performing manual data transfers with find() and custom scripts. The best approach depends on factors like the volume of data, the need for downtime, and whether the transfer needs to be done in real-time or can be done in batches.
Using mongodump and mongorestore for Data Transfer
Overview of mongodump and mongorestore
mongodump and mongorestore are command-line tools provided by MongoDB. They are commonly used for creating backups and restoring data but are also ideal for transferring data between MongoDB instances.
Using mongodump to Create a Backup
The mongodump command creates a binary backup of your data. Here’s how to use it:
mongodump --host=source_host --port=source_port --db=your_database --out=/path/to/backup
Explanation:
--hostand--portspecify the source MongoDB instance.--dbspecifies the database to back up.--outspecifies the directory where the backup files will be stored.
For example, if we want to back up the exampleDB database on localhost port 27017, we would use:
mongodump --host=localhost --port=27017 --db=exampleDB --out=/backup
Using mongorestore to Restore Data
After creating a backup, use mongorestore to restore it on the destination MongoDB instance.
mongorestore --host=destination_host --port=destination_port --db=your_database /path/to/backup/your_database
For example, to restore the exampleDB database from /backup to a new server:
mongorestore --host=new_host --port=27017 --db=exampleDB /backup/exampleDB
Testing the Transfer
After restoring, connect to the destination instance and check that the data has been transferred successfully:
use exampleDB
db.collection_name.find().limit(5).pretty()
Output: This command will display a few documents from the restored database, confirming the migration’s success.
Using mongoexport and mongoimport for Data Transfer
Overview of mongoexport and mongoimport
While mongodump and mongorestore work with binary data, mongoexport and mongoimport work with JSON or CSV data, making them more flexible for transferring specific data.
Exporting Data with mongoexport
To export data in JSON format:
mongoexport --host=source_host --port=source_port --db=your_database --collection=your_collection --out=/path/to/file.json
Example:
mongoexport --host=localhost --port=27017 --db=exampleDB --collection=users --out=/backup/users.json
This exports the users collection from the exampleDB database to a JSON file.
Importing Data with mongoimport
To import the data to a new instance:
mongoimport --host=destination_host --port=destination_port --db=your_database --collection=your_collection --file=/path/to/file.json
Example:
mongoimport --host=new_host --port=27017 --db=exampleDB --collection=users --file=/backup/users.json
Verifying Data Import
After importing, verify the data by checking a few records:
mongoimport --host=new_host --port=27017 --db=exampleDB --collection=users --file=/backup/users.json
Output: This command outputs a few documents from the users collection, confirming that the data transfer was successful.
Data Transfer in MongoDB Atlas (Cloud Environment)
Using MongoDB Atlas for Data Migration
If you’re using MongoDB Atlas, MongoDB’s managed cloud database service, you can easily transfer data across clusters and between Atlas projects.
Migrating Between Atlas Clusters
- Cluster Link: Use MongoDB Atlas to link clusters within the same project for easy data migration.
- Live Migration: For migrating from an on-premises MongoDB to Atlas, use MongoDB’s Live Migration service.
Using Data Federation in Atlas
Data Federation in MongoDB Atlas allows you to query and aggregate data from different clusters or databases without moving data physically. This is helpful for cases where immediate data movement is not required.
Real-Time Data Transfer with Change Streams
Overview of Change Streams
Change Streams provide a way to listen for real-time changes in a MongoDB collection, making it useful for synchronizing data across instances.
Implementing Change Streams for Data Transfer
Here’s a simple example where we set up a Change Stream to listen for new inserts in a source collection and replicate them in a destination collection.
Example Code:
const { MongoClient } = require('mongodb');
const sourceClient = new MongoClient('mongodb://source_host:27017');
const destinationClient = new MongoClient('mongodb://destination_host:27017');
async function replicateChanges() {
await sourceClient.connect();
await destinationClient.connect();
const sourceCollection = sourceClient.db('exampleDB').collection('users');
const destinationCollection = destinationClient.db('exampleDB').collection('users');
const changeStream = sourceCollection.watch();
changeStream.on('change', async (change) => {
if (change.operationType === 'insert') {
await destinationCollection.insertOne(change.fullDocument);
console.log('Replicated new document:', change.fullDocument);
}
});
}
replicateChanges().catch(console.error);
Explanation:
- Change Stream Setup: The
watch()method listens for changes in theuserscollection. - Insert Operation: If a new document is inserted, it’s replicated in the destination collection.
Verifying Replication
Once running, this code will automatically replicate new documents from source_host to destination_host.
Best Practices for Data Transfer
Back Up Before Transferring
Always create a backup of your data before initiating any migration, especially for critical production data.
Ensure Network Security
Use secure connections, such as TLS/SSL, when transferring data between remote MongoDB instances to protect data during transfer.
Monitor and Test
Monitor the migration process for any errors and test the migrated data to ensure consistency.
Consider Downtime Requirements
Plan for downtime or perform a rolling migration if possible to avoid interruptions in application availability.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Handling Data Consistency Issues
Ensure that all documents were transferred correctly, and use tools like db.collection.count() to compare document counts before and after migration.
Network and Connectivity Issues
If connecting remotely, ensure firewalls are configured to allow communication between instances, and use VPNs or SSH tunnels for secure connections if required.
Large Data Volume Challenges
For large datasets, consider transferring data in batches, or using the mongodump and mongorestore binary approach, which is faster than mongoexport and mongoimport for large-scale data.
Moving data between MongoDB instances is an essential task for various scenarios, from backups to production migrations. MongoDB provides robust tools such as mongodump/mongorestore and mongoexport/mongoimport for flexible data transfer, as well as advanced solutions like Change Streams for real-time replication. Happy Coding!❤️
