Leveraging Expressive Aggregation Framework Features
The Aggregation Framework in MongoDB is a powerful and flexible tool that enables advanced data processing and analysis by chaining stages to transform documents in various ways.
Introduction to MongoDB’s Aggregation Framework
What is Aggregation?
Aggregation is the process of processing data records and returning computed results. MongoDB’s Aggregation Framework allows for complex data manipulation by utilizing a series of transformation stages, making it suitable for tasks like analytics and reporting.
The Structure of an Aggregation Pipeline
The Aggregation Pipeline consists of multiple stages. Each stage performs a specific operation on documents, passing the transformed documents to the next stage.
Basic Syntax:
db.collection.aggregate([
{ stage1 },
{ stage2 },
...
])
Core Aggregation Pipeline Stages
Essential Stages
$match: Filters documents by specified criteria.$project: Shapes the documents by including or excluding fields.$group: Groups documents by a specified field, performing operations on grouped data.$sort: Orders documents based on specified fields.$limit: Limits the number of documents in the output.
How Each Stage Works
Example – Filtering and Grouping:
db.sales.aggregate([
{ $match: { status: "completed" } },
{ $group: { _id: "$customer", totalAmount: { $sum: "$amount" } } }
])
Output Explanation: This pipeline filters sales to include only completed orders, then groups by customer and calculates the total amount for each customer.
Advanced Aggregation Pipeline Stages
The $lookup Stage for Joins
$lookup allows joining data from multiple collections, similar to SQL joins.
Example:
db.orders.aggregate([
{
$lookup: {
from: "customers",
localField: "customerId",
foreignField: "_id",
as: "customerData"
}
}
])
Output Explanation: This query joins orders with customers using the customerId field, adding customer details to each order.
The $unwind Stage for Flattening Arrays
$unwind breaks an array field in a document into separate documents for each element.
Example:
db.orders.aggregate([
{ $unwind: "$items" }
])
Output Explanation: If an order document has an array field items, each item in the array is output as a separate document.
Advanced Expressions and Operators
Mathematical and Logical Operators
Operators like $sum, $multiply, $divide, $cond, and $ifNull allow mathematical calculations and conditional logic.
Example:
db.sales.aggregate([
{
$project: {
revenue: { $multiply: ["$price", "$quantity"] },
isHighValue: { $cond: { if: { $gte: ["$revenue", 1000] }, then: true, else: false } }
}
}
])
Explanation: This pipeline calculates revenue for each sale and adds a boolean isHighValue field based on a revenue threshold.
Date Operators
Date operators like $year, $month, $dayOfWeek, and $dateToString are helpful for extracting and formatting date fields.
Example:
db.orders.aggregate([
{ $project: { year: { $year: "$orderDate" }, month: { $month: "$orderDate" } } }
])
Explanation: Extracts year and month from the orderDate field, making it easier to perform time-based analysis.
Array Manipulation with Aggregation
Using $push and $addToSet for Arrays
$push: Adds values to an array.$addToSet: Adds unique values only.
Example:
db.orders.aggregate([
{
$group: {
_id: "$customerId",
orders: { $push: "$_id" },
uniqueProducts: { $addToSet: "$product" }
}
}
])
Explanation: Groups orders by customer, collecting order IDs in an array and ensuring unique products.
Working with $filter to Conditionally Include Array Elements
$filter applies conditions to include specific elements in an array.
Example:
db.products.aggregate([
{
$project: {
highRatedReviews: {
$filter: {
input: "$reviews",
as: "review",
cond: { $gte: ["$$review.rating", 4] }
}
}
}
}
])
Explanation: This extracts only reviews with ratings of 4 or higher.
Conditional Expressions and Transformations
Using $cond for Conditional Logic
The $cond operator is a conditional expression similar to an “if-else” statement.
Example:
db.orders.aggregate([
{
$project: {
customerType: {
$cond: { if: { $gte: ["$totalAmount", 500] }, then: "Premium", else: "Standard" }
}
}
}
])
Explanation: Classifies customers as “Premium” or “Standard” based on totalAmount.
Transforming Data with $switch
$switch provides a multi-branch conditional similar to a “switch-case” statement.
Example:
db.orders.aggregate([
{
$project: {
category: {
$switch: {
branches: [
{ case: { $gte: ["$totalAmount", 1000] }, then: "High" },
{ case: { $gte: ["$totalAmount", 500] }, then: "Medium" }
],
default: "Low"
}
}
}
}
])
Explanation: Categorizes orders as “High,” “Medium,” or “Low” based on totalAmount.
Text Search and Aggregation
Full-Text Search with Aggregation
MongoDB supports full-text search with the $text operator.
Example:
db.products.aggregate([
{ $match: { $text: { $search: "laptop" } } },
{ $project: { name: 1, score: { $meta: "textScore" } } },
{ $sort: { score: -1 } }
])
Explanation: This pipeline finds products containing the word “laptop” and sorts them by relevance.
Practical Examples of Expressive Aggregation Features
Example – Monthly Sales Summary
Calculates monthly sales totals with grouping and date operators.
db.sales.aggregate([
{ $match: { year: 2024 } },
{ $group: { _id: { month: { $month: "$saleDate" } }, totalSales: { $sum: "$amount" } } },
{ $sort: { "_id.month": 1 } }
])
Explanation: This pipeline provides total sales per month for 2024, sorted by month.
Example – Customer Segmentation
Segments customers based on total spending using $group and $project.
db.sales.aggregate([
{ $group: { _id: "$customerId", totalSpent: { $sum: "$amount" } } },
{
$project: {
customerType: {
$cond: { if: { $gte: ["$totalSpent", 1000] }, then: "VIP", else: "Regular" }
}
}
}
])
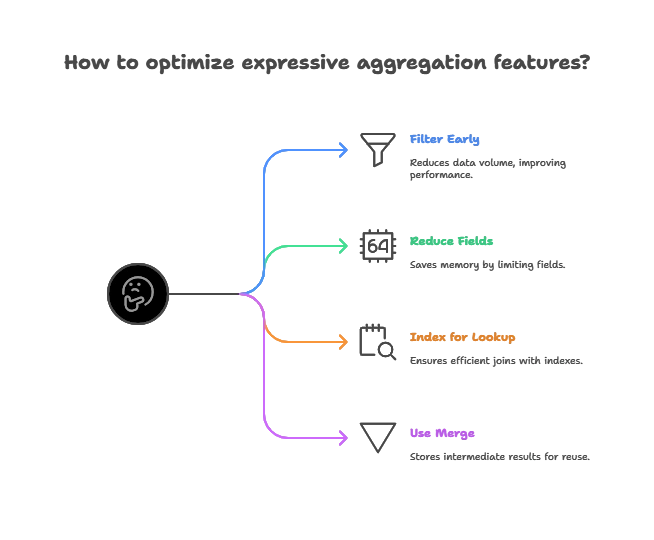
Best Practices for Using Expressive Aggregation Features
- Filter Early: Use
$matchat the beginning to reduce data volume. - Reduce Fields with
$project: Limit fields to save memory. - Index for
$lookup: Ensure indexes exist on fields used in joins. - Use
$mergefor Complex Pipelines: Store intermediate results for reusability.
The expressive features of MongoDB’s Aggregation Framework unlock powerful capabilities for data analysis and transformation. From basic filtering and grouping to advanced expressions, conditional logic, and array manipulation, the aggregation framework allows you to perform complex operations directly within the database. Happy Coding!❤️
