Redux Thunk or Redux Saga
In the world of Redux, managing asynchronous actions is crucial for handling side effects like fetching data from APIs or performing complex operations. Redux Thunk and Redux Saga are two popular middleware solutions that address this need. This chapter delves into both Redux Thunk and Redux Saga, explaining their basic concepts, advanced features, and practical examples to help you understand their usage in depth.
Understanding Asynchronous Actions in Redux
Redux itself is synchronous, meaning it processes actions and updates the state immediately. However, for handling asynchronous operations like API calls or timeouts, Redux requires middleware to extend its capabilities.
Introduction to Redux Thunk
Redux Thunk is a middleware for Redux that enables handling of asynchronous logic in action creators. It allows action creators to return functions instead of plain objects, thus providing more flexibility and control over side effects like AJAX requests or setTimeout calls.
Setup and Basic Usage
To use Redux Thunk, you need to configure it in your Redux store setup (store.js). Here’s how you set it up and its basic usage:
Setup in store.js:
import { createStore, applyMiddleware } from 'redux';
import thunk from 'redux-thunk';
import rootReducer from './reducers'; // assuming you have a rootReducer
const store = createStore(
rootReducer,
applyMiddleware(thunk)
);
export default store;
Explanation
- Middleware Application: Redux Thunk is applied as middleware using
applyMiddleware(thunk). This middleware intercepts Redux actions before they reach the reducers, allowing asynchronous action creators.
Handling Asynchronous Actions
Redux Thunk allows you to write action creators that return a function instead of an action object. This function receives dispatch and getState as arguments, enabling you to dispatch actions asynchronously.
Example of an asynchronous action creator using Redux Thunk:
// actions.js
import axios from 'axios';
export const fetchData = () => {
return async (dispatch, getState) => {
dispatch({ type: 'FETCH_DATA_REQUEST' });
try {
const response = await axios.get('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts');
dispatch({ type: 'FETCH_DATA_SUCCESS', payload: response.data });
} catch (error) {
dispatch({ type: 'FETCH_DATA_FAILURE', payload: error.message });
}
};
};
Explanation
Action Creator Function:
fetchData()is an action creator that returns a function instead of an action object.Asynchronous Logic: Within this function, you have access to
dispatchto dispatch actions (FETCH_DATA_REQUEST,FETCH_DATA_SUCCESS,FETCH_DATA_FAILURE) based on the result of an asynchronous operation (in this case, fetching data from an API using Axios).
Practical Example: Fetching Data
Let’s see how you can use Redux Thunk in a React component (App.js) to fetch data asynchronously and update the Redux state accordingly.
Example in React Component (App.js):
import React, { useEffect } from 'react';
import { useSelector, useDispatch } from 'react-redux';
import { fetchData } from './actions';
function App() {
const dispatch = useDispatch();
const data = useSelector(state => state.data);
const loading = useSelector(state => state.loading);
const error = useSelector(state => state.error);
useEffect(() => {
dispatch(fetchData());
}, [dispatch]);
return (
<div>
{loading ? (
<p>Loading...</p>
) : error ? (
<p>Error: {error}</p>
) : (
<ul>
{data.map(item => (
<li key={item.id}>{item.title}</li>
))}
</ul>
)}
</div>
);
}
export default App;
Explanation
Component Setup: The
Appcomponent usesuseSelectorto accessdata,loading, anderrorstates from Redux store.Effect Hook:
useEffecthook dispatchesfetchData()action creator when the component mounts, triggering an asynchronous data fetch.Rendering: Depending on the
loadinganderrorstates, different UI components (Loading..., error message, or list of fetched data) are rendered.
Introduction to Redux Saga
Redux Saga is a middleware library for Redux that helps manage side effects (e.g., asynchronous actions like data fetching, accessing browser storage) in a more efficient and manageable way. It uses ES6 Generators to make asynchronous flow control easier to read, write, and test.
Setup and Basic Usage
To use Redux Saga, you need to configure it in your Redux store setup (store.js). Here’s how you set it up and its basic usage:
Setup in store.js:
import { createStore, applyMiddleware } from 'redux';
import createSagaMiddleware from 'redux-saga';
import rootReducer from './reducers'; // assuming you have a rootReducer
import rootSaga from './sagas'; // assuming you have a rootSaga
const sagaMiddleware = createSagaMiddleware();
const store = createStore(
rootReducer,
applyMiddleware(sagaMiddleware)
);
sagaMiddleware.run(rootSaga);
export default store;
Explanation
Middleware Application: Redux Saga is applied as middleware using
applyMiddleware(sagaMiddleware). This middleware intercepts dispatched actions and executes saga functions.Running Root Saga:
sagaMiddleware.run(rootSaga)starts the root saga (rootSaga), which is a collection of all your sagas combined.
Handling Asynchronous Actions with Generators
Redux Saga uses ES6 Generators to manage complex asynchronous flows in a synchronous-looking manner. Generators allow you to pause and resume functions, making it easier to handle async operations like API calls, delays, and more.
Example of a saga for fetching data using Redux Saga:
// sagas.js
import { call, put, takeEvery } from 'redux-saga/effects';
import axios from 'axios';
function* fetchData(action) {
try {
const response = yield call(axios.get, 'https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts');
yield put({ type: 'FETCH_DATA_SUCCESS', payload: response.data });
} catch (error) {
yield put({ type: 'FETCH_DATA_FAILURE', payload: error.message });
}
}
function* rootSaga() {
yield takeEvery('FETCH_DATA_REQUEST', fetchData);
}
export default rootSaga;
Explanation
Saga Function:
fetchData()is a saga function defined using a generator (function*). It listens forFETCH_DATA_REQUESTactions.Effect Creators: Inside the saga function,
callis used to call asynchronous functions (like Axios requests), andputis used to dispatch actions (FETCH_DATA_SUCCESS,FETCH_DATA_FAILURE) based on the API response or error.
Practical Example: Handling Complex Flows
Redux Saga excels in managing complex asynchronous flows, such as handling race conditions, cancellation, and chaining multiple async operations.
Example in React Component (App.js):
import React, { useEffect } from 'react';
import { useSelector, useDispatch } from 'react-redux';
import { fetchData } from './actions';
function App() {
const dispatch = useDispatch();
const data = useSelector(state => state.data);
const loading = useSelector(state => state.loading);
const error = useSelector(state => state.error);
useEffect(() => {
dispatch({ type: 'FETCH_DATA_REQUEST' });
}, [dispatch]);
return (
<div>
{loading ? (
<p>Loading...</p>
) : error ? (
<p>Error: {error}</p>
) : (
<ul>
{data.map(item => (
<li key={item.id}>{item.title}</li>
))}
</ul>
)}
</div>
);
}
export default App;
Explanation
Component Setup: The
Appcomponent dispatchesFETCH_DATA_REQUESTaction on mount to trigger the data fetching saga (fetchData()).Rendering: Based on Redux state (
loading,error,data), different UI components (Loading..., error message, or list of fetched data) are rendered.
Comparing Redux Thunk and Redux Saga
Redux Thunk and Redux Saga are two middleware solutions for handling asynchronous logic in Redux applications. Each has its strengths and is suited for different scenarios based on complexity, control over asynchronous flow, and developer preferences.
Use Cases and Scenarios
Redux Thunk:
- Use Cases: Redux Thunk is ideal for applications with straightforward asynchronous requirements, such as simple data fetching from APIs or dispatching multiple actions sequentially.
- Scenarios: It’s suitable when you primarily need to handle basic async operations without the need for complex flow control or coordination between multiple tasks.
Redux Saga:
- Use Cases: Redux Saga shines in managing complex asynchronous flows and handling advanced use cases like race conditions, cancellation, and complex data transformations before updating the Redux state.
- Scenarios: It’s recommended for applications with intricate business logic that involves multiple asynchronous tasks, real-time data synchronization, or when actions need to be coordinated in specific sequences.
Performance Considerations
Redux Thunk:
- Performance: Redux Thunk is lightweight and has minimal overhead since it directly invokes asynchronous operations and dispatches actions within action creators.
- Suitability: It’s generally suitable for most applications without significant performance concerns, especially when dealing with a limited number of asynchronous tasks.
Redux Saga:
- Performance: Redux Saga introduces a slightly higher initialization cost due to its reliance on generators and the additional middleware layer.
- Suitability: While it may have a marginally higher runtime cost compared to Redux Thunk, Redux Saga’s benefits in managing complex asynchronous flows outweigh this cost in applications requiring extensive async logic.
Debugging and Testing
Redux Thunk:
- Debugging: Redux Thunk is straightforward to debug since async logic resides directly within action creators, making it easier to trace and debug actions using standard debugging tools.
- Testing: Unit testing Thunk action creators involves mocking asynchronous operations, which is manageable and aligns with traditional Redux testing practices.
Redux Saga:
- Debugging: Redux Saga can be more challenging to debug due to its reliance on generators and the non-linear flow of async tasks. However, Redux Saga provides extensive logging and debugging tools like
redux-saga-devtoolsto inspect saga execution and state changes. - Testing: Testing Sagas involves using libraries like
redux-saga-test-planfor mocking and controlling saga execution, ensuring predictable and isolated testing of complex async logic.
Decision Factors and Best Practices
Choosing Redux Thunk:
- Factors: Opt for Redux Thunk in projects with simpler async requirements, where straightforward data fetching or sequential action dispatching suffices.
- Best Practices: Stick to Redux Thunk if your team is more comfortable with traditional Redux patterns and prefers a simpler setup without additional learning overhead.
Choosing Redux Saga:
- Factors: Consider Redux Saga for projects requiring advanced async flow control, such as complex data synchronization, real-time updates, or handling long-lived transactions.
- Best Practices: Invest in Redux Saga if your application demands precise control over async operations, and your team is willing to learn and leverage its powerful capabilities for managing side effects.
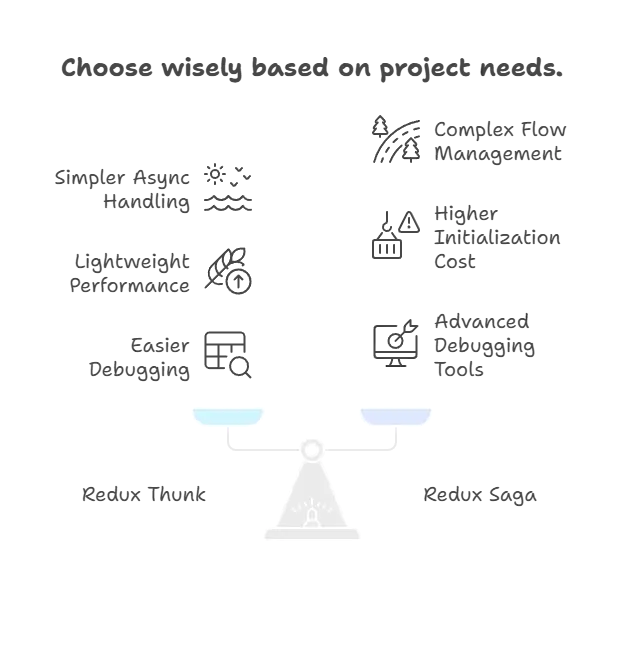
Summary
Redux Thunk and Redux Saga are both middleware solutions for managing asynchronous logic in Redux applications. Each has distinct characteristics, use cases, and considerations, making them suitable for different scenarios based on project requirements and developer preferences.
Redux Thunk
- Overview: Redux Thunk allows action creators to return functions instead of plain objects, enabling asynchronous operations like data fetching or dispatching multiple actions sequentially.
- Use Cases: Ideal for applications with straightforward asynchronous requirements, where basic data fetching or sequential action dispatching suffices.
- Performance: Lightweight with minimal overhead, making it suitable for most applications without significant performance concerns.
- Debugging and Testing: Relatively easy to debug since async logic resides within action creators, aligning well with standard Redux testing practices.
- Best Practices: Recommended for teams familiar with traditional Redux patterns and seeking simplicity in handling basic async operations.
Redux Saga
- Overview: Redux Saga uses ES6 Generators to manage complex asynchronous flows, offering advanced capabilities like handling race conditions, cancellation, and coordinating multiple async tasks.
- Use Cases: Best suited for applications requiring precise control over async operations, complex data synchronization, real-time updates, or long-lived transaction handling.
- Performance: Introduces slightly higher initialization and runtime costs due to generator functions and middleware layer, but excels in managing complex async flows effectively.
- Debugging and Testing: Can be more challenging to debug due to the non-linear flow of generators, but offers extensive debugging tools and testing libraries like
redux-saga-test-plan. - Best Practices: Recommended for projects needing advanced async flow control and where teams are willing to invest time in learning and leveraging its powerful capabilities.
Practical Example 1: Using Redux Thunk for Data Fetching
In this example, we’ll demonstrate how to use Redux Thunk to fetch data from an API and update the Redux store accordingly.
Step-by-Step Implementation
1. Setting up Redux and Redux Thunk
Assume you have already set up your Redux store with Redux Thunk middleware, as shown in the previous examples.
2. Creating Action Types
Define action types to manage the data fetching process:
// actionTypes.js
export const FETCH_DATA_REQUEST = 'FETCH_DATA_REQUEST';
export const FETCH_DATA_SUCCESS = 'FETCH_DATA_SUCCESS';
export const FETCH_DATA_FAILURE = 'FETCH_DATA_FAILURE';
3. Implementing Action Creators
Create action creators to handle data fetching using Redux Thunk:
// actions.js
import axios from 'axios';
import {
FETCH_DATA_REQUEST,
FETCH_DATA_SUCCESS,
FETCH_DATA_FAILURE
} from './actionTypes';
export const fetchData = () => {
return async (dispatch) => {
dispatch({ type: FETCH_DATA_REQUEST });
try {
const response = await axios.get('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts');
dispatch({ type: FETCH_DATA_SUCCESS, payload: response.data });
} catch (error) {
dispatch({ type: FETCH_DATA_FAILURE, payload: error.message });
}
};
};
4. Reducer Setup
Define a reducer to handle state updates based on the actions dispatched:
// reducer.js
import {
FETCH_DATA_REQUEST,
FETCH_DATA_SUCCESS,
FETCH_DATA_FAILURE
} from './actionTypes';
const initialState = {
data: [],
loading: false,
error: null
};
const reducer = (state = initialState, action) => {
switch (action.type) {
case FETCH_DATA_REQUEST:
return {
...state,
loading: true,
error: null
};
case FETCH_DATA_SUCCESS:
return {
...state,
loading: false,
data: action.payload,
error: null
};
case FETCH_DATA_FAILURE:
return {
...state,
loading: false,
error: action.payload
};
default:
return state;
}
};
export default reducer;
5. Connecting Redux to React Component
Integrate Redux with a React component to display fetched data:
// App.js
import React, { useEffect } from 'react';
import { useSelector, useDispatch } from 'react-redux';
import { fetchData } from './actions';
function App() {
const dispatch = useDispatch();
const data = useSelector(state => state.data);
const loading = useSelector(state => state.loading);
const error = useSelector(state => state.error);
useEffect(() => {
dispatch(fetchData());
}, [dispatch]);
return (
<div>
{loading ? (
<p>Loading...</p>
) : error ? (
<p>Error: {error}</p>
) : (
<ul>
{data.map(item => (
<li key={item.id}>{item.title}</li>
))}
</ul>
)}
</div>
);
}
export default App;
Explanation
- Redux Thunk: The
fetchDataaction creator is an async function that dispatches actions (FETCH_DATA_REQUEST,FETCH_DATA_SUCCESS,FETCH_DATA_FAILURE) based on the result of the Axios request. - Redux Store: The reducer manages state updates based on these actions, updating
data,loading, anderrorstates. - React Component: The
Appcomponent connects to Redux usinguseSelectoranduseDispatchhooks to fetch data on component mount and render based on Redux state.
Practical Example 2: Using Redux Saga for Advanced Async Flows
In this example, we’ll demonstrate how Redux Saga handles more complex asynchronous operations, such as handling race conditions and managing multiple async tasks.
Step-by-Step Implementation
1. Setting up Redux and Redux Saga
Ensure Redux Saga is integrated into your Redux store setup, as shown in the previous examples.
2. Creating Saga Functions
Implement a saga to manage data fetching with additional complex async logic:
// sagas.js
import { call, put, takeLatest } from 'redux-saga/effects';
import axios from 'axios';
import {
FETCH_DATA_REQUEST,
FETCH_DATA_SUCCESS,
FETCH_DATA_FAILURE
} from './actionTypes';
function* fetchDataSaga(action) {
try {
const response = yield call(axios.get, 'https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts');
yield put({ type: FETCH_DATA_SUCCESS, payload: response.data });
} catch (error) {
yield put({ type: FETCH_DATA_FAILURE, payload: error.message });
}
}
function* rootSaga() {
yield takeLatest(FETCH_DATA_REQUEST, fetchDataSaga);
}
export default rootSaga;
3. Reducer Setup
Update the reducer to handle new action types for advanced async flows:
// reducer.js
import {
FETCH_DATA_REQUEST,
FETCH_DATA_SUCCESS,
FETCH_DATA_FAILURE
} from './actionTypes';
const initialState = {
data: [],
loading: false,
error: null
};
const reducer = (state = initialState, action) => {
switch (action.type) {
case FETCH_DATA_REQUEST:
return {
...state,
loading: true,
error: null
};
case FETCH_DATA_SUCCESS:
return {
...state,
loading: false,
data: action.payload,
error: null
};
case FETCH_DATA_FAILURE:
return {
...state,
loading: false,
error: action.payload
};
default:
return state;
}
};
export default reducer;
4. Connecting Redux Saga to React Component
Integrate Redux Saga with a React component to handle complex async flows:
// App.js
import React, { useEffect } from 'react';
import { useSelector, useDispatch } from 'react-redux';
import { fetchData } from './actions';
function App() {
const dispatch = useDispatch();
const data = useSelector(state => state.data);
const loading = useSelector(state => state.loading);
const error = useSelector(state => state.error);
useEffect(() => {
dispatch({ type: 'FETCH_DATA_REQUEST' });
}, [dispatch]);
return (
<div>
{loading ? (
<p>Loading...</p>
) : error ? (
<p>Error: {error}</p>
) : (
<ul>
{data.map(item => (
<li key={item.id}>{item.title}</li>
))}
</ul>
)}
</div>
);
}
export default App;
Explanation
- Redux Saga: The
fetchDataSagagenerator function usescallto perform an Axios GET request andputto dispatch success or failure actions (FETCH_DATA_SUCCESS,FETCH_DATA_FAILURE). - React Component: The
Appcomponent dispatchesFETCH_DATA_REQUESTaction on mount, triggering the saga to handle the data fetch with advanced async flow control.
Redux Thunk and Redux Saga are powerful middleware solutions that enhance Redux's capabilities for handling asynchronous operations. By understanding their strengths, use cases, and integration patterns, you can make informed decisions on choosing the right middleware for your project. Whether opting for the simplicity of Redux Thunk or the sophistication of Redux Saga, both provide robust tools for managing complex state and side effects in React applications.Happy coding !❤️
Table of Contents

