Scalability and Load Balancing with Express.js
In modern web applications, scalability is key to ensuring that an application can handle an increasing number of users without a drop in performance.
Introduction to Scalability and Load Balancing
Scalability ensures that an application can handle increasing numbers of users or requests by adding resources. In a scalable system, as more users connect, the system continues to operate effectively without degradation. Load balancing is a technique that distributes incoming requests across multiple servers to prevent overloading any one server, ensuring high performance and reliability.
Vertical Scaling vs. Horizontal Scaling
Scalability can be achieved through two main approaches: Vertical Scaling and Horizontal Scaling.
Vertical Scaling (Scaling Up)
Vertical scaling involves adding more power (CPU, RAM) to a single server to handle more requests. It’s relatively simple to implement but has limitations, as there’s a ceiling to how much hardware can be added to a single server.
Horizontal Scaling (Scaling Out)
Horizontal scaling involves adding more servers (or instances) to distribute the load. Each server, running an instance of the application, shares the traffic load, allowing for better resource distribution and improved fault tolerance.
Setting Up Load Balancing
Load balancing is a method to distribute requests across multiple servers, improving performance, reliability, and availability.
Reverse Proxy with Nginx
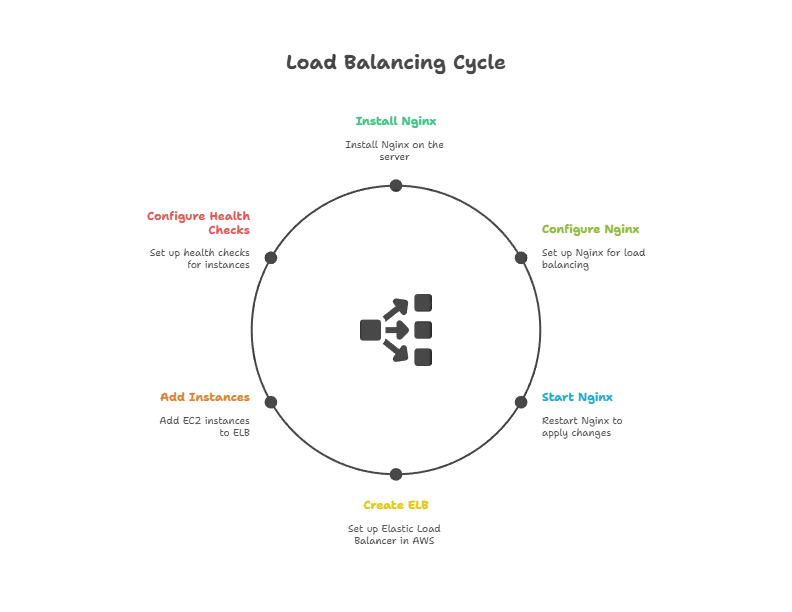
Nginx is a popular choice for load balancing. Acting as a reverse proxy, Nginx forwards client requests to multiple application servers, balancing the load.
1. Install Nginx
On Ubuntu, install Nginx with:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install nginx
2. Configure Nginx for Load Balancing
Open the Nginx configuration file:
sudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/default
3. Edit Configuration
In the configuration file, add your Express.js server instances as upstream servers:
http {
upstream express_app {
server 127.0.0.1:3000;
server 127.0.0.1:3001;
server 127.0.0.1:3002;
}
server {
listen 80;
location / {
proxy_pass http://express_app;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
}
}
}
4. Start Nginx
Save the configuration and restart Nginx:
sudo systemctl restart nginx
Output: Now, Nginx will distribute incoming requests across the servers defined in the upstream directive.
Load Balancing with AWS ELB
Amazon Web Services offers Elastic Load Balancing (ELB), which automatically distributes incoming traffic across multiple Amazon EC2 instances.
- Create a Load Balancer: In the AWS Console, go to the EC2 dashboard and create an ELB.
- Add Instances: Add your EC2 instances running Express.js to the load balancer.
- Configure Health Checks: Set up health checks to monitor the health of each instance.
AWS ELB manages the distribution of requests and scales based on traffic automatically, making it ideal for production.
Using Clusters in Express.js
Node.js runs on a single-threaded event loop, but you can use clustering to leverage multiple CPU cores.
Creating a Basic Cluster
1. Set Up a Cluster: Create a cluster.js file:
// cluster.js
const cluster = require('cluster');
const os = require('os');
const express = require('express');
if (cluster.isMaster) {
const numCPUs = os.cpus().length;
console.log(`Master ${process.pid} is running`);
// Fork workers
for (let i = 0; i < numCPUs; i++) {
cluster.fork();
}
cluster.on('exit', (worker) => {
console.log(`Worker ${worker.process.pid} died`);
cluster.fork(); // Replace the dead worker
});
} else {
const app = express();
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.send(`Hello from worker ${process.pid}`);
});
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log(`Worker ${process.pid} started`);
});
}
2. Run the Clustered App
Run the app with node cluster.js. Each CPU core will run an instance, allowing the app to handle multiple requests.
Output: The app should print the PID of each worker process, showing that it’s distributed across CPU cores.
Scaling with Containerization (Docker)
Docker allows you to create isolated containers for your applications, making scaling easier.
1. Create a Dockerfile:
FROM node:14
WORKDIR /app
COPY package*.json ./
RUN npm install
COPY . .
EXPOSE 3000
CMD ["node", "app.js"]
2. Build and Run the Docker Image
docker build -t express-app .
docker run -p 3000:3000 express-app
3. Scaling with Docker Compose
Create a docker-compose.yml file to define multiple instances:
version: '3'
services:
app:
image: express-app
deploy:
replicas: 3
ports:
- "3000:3000"
4. Deploy with Docker Compose
docker-compose up -d
Output: Docker Compose will create three instances of your Express.js app, accessible on port 3000.
Scaling with Microservices
Microservices architecture involves breaking down an application into small, independently deployable services. Each service performs a specific function and communicates with others through APIs.
- Define Services: Identify core functionalities (e.g., user management, billing) and build separate Express apps for each.
- Communication: Use REST or message queues (e.g., RabbitMQ) for communication between services.
- Deploy Separately: Deploy each service independently, allowing them to scale based on specific needs.
Auto-Scaling with Cloud Providers
Most cloud providers offer auto-scaling, which automatically adjusts the number of instances based on demand.
- AWS Auto Scaling: Scales EC2 instances automatically.
- Google Cloud AutoScaler: Similar to AWS, but for Google Compute Engine.
- Azure Autoscale: Scales based on metrics like CPU usage.
Auto-scaling ensures that your application can handle traffic spikes by adding or removing instances as needed.
Best Practices for Scalability and Load Balancing
- Monitor Performance: Use monitoring tools like Prometheus or New Relic to monitor application health and performance.
- Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN): Offload static assets to a CDN to reduce server load.
- Implement Health Checks: Ensure that load balancers route traffic only to healthy instances.
- Cache Responses: Use caching (e.g., Redis) for frequently accessed data to reduce server load.
Scaling and load balancing are essential for high-traffic Express.js applications. By using load balancers, clusters, containerization, microservices, and cloud auto-scaling, you can create a scalable, resilient, and efficient architecture. Following these best practices will ensure that your application remains fast and available, even as user demand grows. Happy Coding!❤️
