MiddleWare in Express.js
In this chapter, we'll delve into the concept of middleware in Express.js, exploring its basics and advanced usage with practical examples. Middleware is a fundamental part of Express.js, playing a crucial role in building robust web applications. Understanding middleware will help you handle various tasks such as request processing, authentication, logging, error handling, and more.
What is Middleware?
Middleware functions are functions that have access to the request object (req), the response object (res), and the next middleware function in the application’s request-response cycle. These functions can perform a variety of tasks:
- Execute any code.
- Make changes to the request and response objects.
- End the request-response cycle.
- Call the next middleware function in the stack.
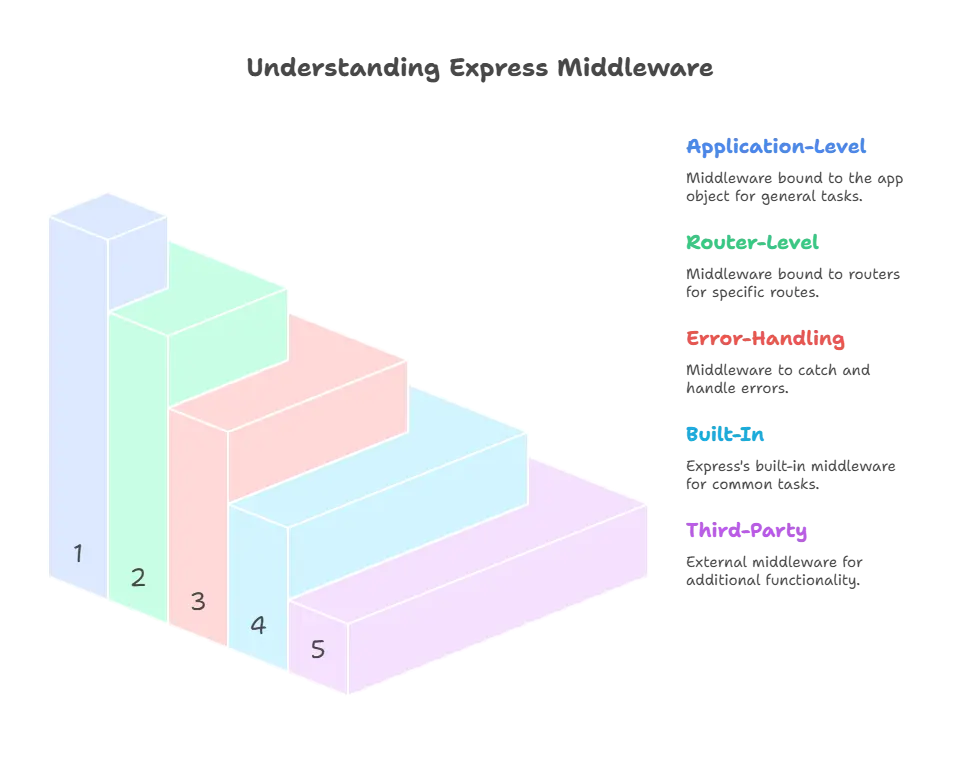
Types of Middleware
Application-Level Middleware
Application-level middleware is bound to an instance of the app object using app.use() or app.METHOD(), where METHOD is an HTTP method such as GET, POST, PUT, etc.
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
app.use((req, res, next) => {
console.log('Time:', Date.now());
next();
});
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.send('Hello, World!');
});
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('Server is running on port 3000');
});
Explanation:
- The middleware function logs the current time and then passes control to the next middleware function using
next(). - The route handler for the root URL sends a “Hello, World!” message.
Output: When you navigate to http://localhost:3000/, the server logs the current time and responds with “Hello, World!”.
Router-Level Middleware
Router-level middleware works in the same way as application-level middleware, except it is bound to an instance of express.Router().
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
const router = express.Router();
router.use((req, res, next) => {
console.log('Request URL:', req.originalUrl);
next();
});
router.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.send('Router Home');
});
app.use('/router', router);
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('Server is running on port 3000');
});
Explanation:
- The middleware logs the requested URL.
- The router handles requests to the
/routerpath and responds with “Router Home”.
Output: When you navigate to http://localhost:3000/router, the server logs the requested URL and responds with “Router Home”.
Error-Handling Middleware
Error-handling middleware functions have four arguments: (err, req, res, next). They are used to catch and handle errors.
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
throw new Error('Something went wrong!');
});
app.use((err, req, res, next) => {
console.error(err.stack);
res.status(500).send('Something broke!');
});
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('Server is running on port 3000');
});
Explanation:
- An error is thrown in the route handler.
- The error-handling middleware catches the error, logs the stack trace, and sends a 500 status with the message “Something broke!”.
Output: Navigating to http://localhost:3000/ will result in a 500 status response with the message “Something broke!”.
Built-In Middleware
Express has several built-in middleware functions, such as express.static, express.json, and express.urlencoded.
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
app.use(express.static('public'));
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('Server is running on port 3000');
});
Explanation:
- The
express.staticmiddleware serves static files from thepublicdirectory.
You can also use third-party middleware, such as morgan for logging, helmet for security, and cors for enabling Cross-Origin Resource Sharing.
Third-Party Middleware
Express has several built-in middleware functions, such as express.static, express.json, and express.urlencoded.
How Middleware Works
Middleware functions are executed in the order they are added. Each middleware function receives three arguments: req, res, and next. The next function is a callback that passes control to the next middleware function.
Creating and Using Middleware
To create middleware, you simply define a function with req, res, and next as parameters.
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
const myMiddleware = (req, res, next) => {
console.log('Request received');
next();
};
app.use(myMiddleware);
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.send('Hello, World!');
});
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('Server is running on port 3000');
});
Output: Navigating to http://localhost:3000/ logs “Request received” and responds with “Hello, World!”.
Order of Middleware Execution
The order in which middleware functions are defined is important because they are executed sequentially.
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
app.use((req, res, next) => {
console.log('First middleware');
next();
});
app.use((req, res, next) => {
console.log('Second middleware');
next();
});
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.send('Hello, World!');
});
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('Server is running on port 3000');
});
Output: Navigating to http://localhost:3000/ logs “First middleware”, then “Second middleware”, and responds with “Hello, World!”.
Middleware for Static Files
The express.static middleware serves static files, such as HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files, from a directory.
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
app.use(express.static('public'));
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('Server is running on port 3000');
});
Output: If you have an index.html file in the public directory, navigating to http://localhost:3000/ will serve that file.
Middleware for Request Data Parsing
Express provides middleware to parse incoming request bodies.
Body-Parser Middleware
Body-parser is now part of the core express package, allowing you to parse incoming request bodies.
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
app.use(express.json());
app.post('/data', (req, res) => {
res.send(req.body);
});
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('Server is running on port 3000');
});
Output: Using Postman, send a POST request to http://localhost:3000/data with a JSON body { "name": "John" }. The response will be { "name": "John" }.
URL-Encoded Middleware
This middleware is used to parse URL-encoded bodies, which are typically sent via HTML forms.
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
app.use(express.urlencoded({ extended: true }));
app.post('/form', (req, res) => {
res.send(req.body);
});
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('Server is running on port 3000');
});
Output: Using Postman or an HTML form, send a POST request to http://localhost:3000/form with form data name=John. The response will be { "name": "John" }.
Custom Middleware
Custom middleware allows you to add any functionality you need.
Logging Middleware
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
const logger = (req, res, next) => {
console.log(`${req.method} ${req.url}`);
next();
};
app.use(logger);
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.send('Hello, World!');
});
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('Server is running on port 3000');
});
Output: Every time you navigate to any endpoint, the method and URL will be logged to the console.
Authentication Middleware
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
const authenticate = (req, res, next) => {
const token = req.headers['authorization'];
if (token === 'mysecrettoken') {
next();
} else {
res.status(401).send('Unauthorized');
}
};
app.use(authenticate);
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.send('Hello, World!');
});
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('Server is running on port 3000');
});
Output: Navigate to http://localhost:3000/ with an authorization header set to mysecrettoken to receive “Hello, World!”. Otherwise, you receive a 401 status with “Unauthorized”.
Request Time Middleware
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
const requestTime = (req, res, next) => {
req.requestTime = Date.now();
next();
};
app.use(requestTime);
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.send(`Current Time: ${req.requestTime}`);
});
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('Server is running on port 3000');
});
Output: Navigate to http://localhost:3000/ to see the current request time.
Error-Handling Middleware
Error-handling middleware catches errors and prevents them from crashing the server.
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
throw new Error('Something went wrong!');
});
app.use((err, req, res, next) => {
console.error(err.stack);
res.status(500).send('Something broke!');
});
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('Server is running on port 3000');
});
Output: Navigating to http://localhost:3000/ logs the error stack and responds with “Something broke!”.
Third-Party Middleware Examples
Morgan for Logging
Morgan is a popular logging middleware.
const express = require('express');
const morgan = require('morgan');
const app = express();
app.use(morgan('tiny'));
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.send('Hello, World!');
});
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('Server is running on port 3000');
});
Output: Each request is logged in a ‘tiny’ format.
Helmet for Security
Helmet helps secure your Express apps by setting various HTTP headers.
const express = require('express');
const helmet = require('helmet');
const app = express();
app.use(helmet());
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.send('Hello, Secure World!');
});
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('Server is running on port 3000');
});
Output: HTTP headers for security are automatically set.
Cors for Cross-Origin Resource Sharing
Cors middleware allows you to enable CORS with various options.
const express = require('express');
const cors = require('cors');
const app = express();
app.use(cors());
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.send('CORS enabled!');
});
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('Server is running on port 3000');
});
Output: CORS is enabled for all routes.
Advanced Middleware Concepts
Chaining Middleware
Middleware functions can be chained by calling next() within each function.
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
app.use((req, res, next) => {
console.log('First middleware');
next();
});
app.use((req, res, next) => {
console.log('Second middleware');
next();
});
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.send('Hello, World!');
});
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('Server is running on port 3000');
});
Output: Navigating to http://localhost:3000/ logs “First middleware”, then “Second middleware”, and responds with “Hello, World!”.
Middleware Composition
Middleware composition allows you to group multiple middleware functions into a single function.
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
const middleware1 = (req, res, next) => {
console.log('Middleware 1');
next();
};
const middleware2 = (req, res, next) => {
console.log('Middleware 2');
next();
};
const composedMiddleware = [middleware1, middleware2];
app.use(composedMiddleware);
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.send('Hello, World!');
});
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('Server is running on port 3000');
});
Output: Navigating to http://localhost:3000/ logs “Middleware 1”, then “Middleware 2”, and responds with “Hello, World!”.
Practical Example
Let’s create a practical example of an Express.js application that demonstrates various types of middleware. We’ll build a simple user management system with the following features:
- Static file serving.
- Request logging.
- JSON body parsing.
- Basic authentication.
- Error handling.
Setting Up the Project
First, create a new directory for your project and initialize it with npm:
mkdir express-middleware-example
cd express-middleware-example
npm init -y
Then, install Express and other necessary middleware:
npm install express morgan body-parser helmet cors
Creating the Server
Create a new file named server.js and start by setting up the basic Express server:
const express = require('express');
const morgan = require('morgan');
const bodyParser = require('body-parser');
const helmet = require('helmet');
const cors = require('cors');
const app = express();
const PORT = 3000;
// Middleware setup
app.use(helmet()); // Security headers
app.use(cors()); // Enable CORS
app.use(morgan('tiny')); // Request logging
app.use(bodyParser.json()); // JSON body parsing
app.use(express.static('public')); // Serve static files
// Custom middleware for logging request details
app.use((req, res, next) => {
console.log(`Request Method: ${req.method}, Request URL: ${req.url}`);
next();
});
// Basic authentication middleware
const authenticate = (req, res, next) => {
const authHeader = req.headers.authorization;
if (authHeader && authHeader === 'Bearer mysecrettoken') {
next();
} else {
res.status(401).send('Unauthorized');
}
};
// Routes
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.send('Welcome to the User Management System!');
});
app.post('/login', (req, res) => {
const { username, password } = req.body;
if (username === 'admin' && password === 'password') {
res.send({ token: 'mysecrettoken' });
} else {
res.status(401).send('Invalid credentials');
}
});
app.get('/users', authenticate, (req, res) => {
res.send(['User1', 'User2', 'User3']);
});
// Error-handling middleware
app.use((err, req, res, next) => {
console.error(err.stack);
res.status(500).send('Something broke!');
});
// Start the server
app.listen(PORT, () => {
console.log(`Server is running on port ${PORT}`);
});
Creating the Public Directory
Create a directory named public in the root of your project and add an index.html file inside it:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>User Management System</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome to the User Management System</h1>
<p>Navigate to <code>/users</code> to see the list of users.</p> <script data-no-optimize="1">window.lazyLoadOptions=Object.assign({},{threshold:300},window.lazyLoadOptions||{});!function(t,e){"object"==typeof exports&&"undefined"!=typeof module?module.exports=e():"function"==typeof define&&define.amd?define(e):(t="undefined"!=typeof globalThis?globalThis:t||self).LazyLoad=e()}(this,function(){"use strict";function e(){return(e=Object.assign||function(t){for(var e=1;e<arguments.length;e++){var n,a=arguments[e];for(n in a)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(a,n)&&(t[n]=a[n])}return t}).apply(this,arguments)}function o(t){return e({},at,t)}function l(t,e){return t.getAttribute(gt+e)}function c(t){return l(t,vt)}function s(t,e){return function(t,e,n){e=gt+e;null!==n?t.setAttribute(e,n):t.removeAttribute(e)}(t,vt,e)}function i(t){return s(t,null),0}function r(t){return null===c(t)}function u(t){return c(t)===_t}function d(t,e,n,a){t&&(void 0===a?void 0===n?t(e):t(e,n):t(e,n,a))}function f(t,e){et?t.classList.add(e):t.className+=(t.className?" ":"")+e}function _(t,e){et?t.classList.remove(e):t.className=t.className.replace(new RegExp("(^|\\s+)"+e+"(\\s+|$)")," ").replace(/^\s+/,"").replace(/\s+$/,"")}function g(t){return t.llTempImage}function v(t,e){!e||(e=e._observer)&&e.unobserve(t)}function b(t,e){t&&(t.loadingCount+=e)}function p(t,e){t&&(t.toLoadCount=e)}function n(t){for(var e,n=[],a=0;e=t.children[a];a+=1)"SOURCE"===e.tagName&&n.push(e);return n}function h(t,e){(t=t.parentNode)&&"PICTURE"===t.tagName&&n(t).forEach(e)}function a(t,e){n(t).forEach(e)}function m(t){return!!t[lt]}function E(t){return t[lt]}function I(t){return delete t[lt]}function y(e,t){var n;m(e)||(n={},t.forEach(function(t){n[t]=e.getAttribute(t)}),e[lt]=n)}function L(a,t){var o;m(a)&&(o=E(a),t.forEach(function(t){var e,n;e=a,(t=o[n=t])?e.setAttribute(n,t):e.removeAttribute(n)}))}function k(t,e,n){f(t,e.class_loading),s(t,st),n&&(b(n,1),d(e.callback_loading,t,n))}function A(t,e,n){n&&t.setAttribute(e,n)}function O(t,e){A(t,rt,l(t,e.data_sizes)),A(t,it,l(t,e.data_srcset)),A(t,ot,l(t,e.data_src))}function w(t,e,n){var a=l(t,e.data_bg_multi),o=l(t,e.data_bg_multi_hidpi);(a=nt&&o?o:a)&&(t.style.backgroundImage=a,n=n,f(t=t,(e=e).class_applied),s(t,dt),n&&(e.unobserve_completed&&v(t,e),d(e.callback_applied,t,n)))}function x(t,e){!e||0<e.loadingCount||0<e.toLoadCount||d(t.callback_finish,e)}function M(t,e,n){t.addEventListener(e,n),t.llEvLisnrs[e]=n}function N(t){return!!t.llEvLisnrs}function z(t){if(N(t)){var e,n,a=t.llEvLisnrs;for(e in a){var o=a[e];n=e,o=o,t.removeEventListener(n,o)}delete t.llEvLisnrs}}function C(t,e,n){var a;delete t.llTempImage,b(n,-1),(a=n)&&--a.toLoadCount,_(t,e.class_loading),e.unobserve_completed&&v(t,n)}function R(i,r,c){var l=g(i)||i;N(l)||function(t,e,n){N(t)||(t.llEvLisnrs={});var a="VIDEO"===t.tagName?"loadeddata":"load";M(t,a,e),M(t,"error",n)}(l,function(t){var e,n,a,o;n=r,a=c,o=u(e=i),C(e,n,a),f(e,n.class_loaded),s(e,ut),d(n.callback_loaded,e,a),o||x(n,a),z(l)},function(t){var e,n,a,o;n=r,a=c,o=u(e=i),C(e,n,a),f(e,n.class_error),s(e,ft),d(n.callback_error,e,a),o||x(n,a),z(l)})}function T(t,e,n){var a,o,i,r,c;t.llTempImage=document.createElement("IMG"),R(t,e,n),m(c=t)||(c[lt]={backgroundImage:c.style.backgroundImage}),i=n,r=l(a=t,(o=e).data_bg),c=l(a,o.data_bg_hidpi),(r=nt&&c?c:r)&&(a.style.backgroundImage='url("'.concat(r,'")'),g(a).setAttribute(ot,r),k(a,o,i)),w(t,e,n)}function G(t,e,n){var a;R(t,e,n),a=e,e=n,(t=Et[(n=t).tagName])&&(t(n,a),k(n,a,e))}function D(t,e,n){var a;a=t,(-1<It.indexOf(a.tagName)?G:T)(t,e,n)}function S(t,e,n){var a;t.setAttribute("loading","lazy"),R(t,e,n),a=e,(e=Et[(n=t).tagName])&&e(n,a),s(t,_t)}function V(t){t.removeAttribute(ot),t.removeAttribute(it),t.removeAttribute(rt)}function j(t){h(t,function(t){L(t,mt)}),L(t,mt)}function F(t){var e;(e=yt[t.tagName])?e(t):m(e=t)&&(t=E(e),e.style.backgroundImage=t.backgroundImage)}function P(t,e){var n;F(t),n=e,r(e=t)||u(e)||(_(e,n.class_entered),_(e,n.class_exited),_(e,n.class_applied),_(e,n.class_loading),_(e,n.class_loaded),_(e,n.class_error)),i(t),I(t)}function U(t,e,n,a){var o;n.cancel_on_exit&&(c(t)!==st||"IMG"===t.tagName&&(z(t),h(o=t,function(t){V(t)}),V(o),j(t),_(t,n.class_loading),b(a,-1),i(t),d(n.callback_cancel,t,e,a)))}function $(t,e,n,a){var o,i,r=(i=t,0<=bt.indexOf(c(i)));s(t,"entered"),f(t,n.class_entered),_(t,n.class_exited),o=t,i=a,n.unobserve_entered&&v(o,i),d(n.callback_enter,t,e,a),r||D(t,n,a)}function q(t){return t.use_native&&"loading"in HTMLImageElement.prototype}function H(t,o,i){t.forEach(function(t){return(a=t).isIntersecting||0<a.intersectionRatio?$(t.target,t,o,i):(e=t.target,n=t,a=o,t=i,void(r(e)||(f(e,a.class_exited),U(e,n,a,t),d(a.callback_exit,e,n,t))));var e,n,a})}function B(e,n){var t;tt&&!q(e)&&(n._observer=new IntersectionObserver(function(t){H(t,e,n)},{root:(t=e).container===document?null:t.container,rootMargin:t.thresholds||t.threshold+"px"}))}function J(t){return Array.prototype.slice.call(t)}function K(t){return t.container.querySelectorAll(t.elements_selector)}function Q(t){return c(t)===ft}function W(t,e){return e=t||K(e),J(e).filter(r)}function X(e,t){var n;(n=K(e),J(n).filter(Q)).forEach(function(t){_(t,e.class_error),i(t)}),t.update()}function t(t,e){var n,a,t=o(t);this._settings=t,this.loadingCount=0,B(t,this),n=t,a=this,Y&&window.addEventListener("online",function(){X(n,a)}),this.update(e)}var Y="undefined"!=typeof window,Z=Y&&!("onscroll"in window)||"undefined"!=typeof navigator&&/(gle|ing|ro)bot|crawl|spider/i.test(navigator.userAgent),tt=Y&&"IntersectionObserver"in window,et=Y&&"classList"in document.createElement("p"),nt=Y&&1<window.devicePixelRatio,at={elements_selector:".lazy",container:Z||Y?document:null,threshold:300,thresholds:null,data_src:"src",data_srcset:"srcset",data_sizes:"sizes",data_bg:"bg",data_bg_hidpi:"bg-hidpi",data_bg_multi:"bg-multi",data_bg_multi_hidpi:"bg-multi-hidpi",data_poster:"poster",class_applied:"applied",class_loading:"litespeed-loading",class_loaded:"litespeed-loaded",class_error:"error",class_entered:"entered",class_exited:"exited",unobserve_completed:!0,unobserve_entered:!1,cancel_on_exit:!0,callback_enter:null,callback_exit:null,callback_applied:null,callback_loading:null,callback_loaded:null,callback_error:null,callback_finish:null,callback_cancel:null,use_native:!1},ot="src",it="srcset",rt="sizes",ct="poster",lt="llOriginalAttrs",st="loading",ut="loaded",dt="applied",ft="error",_t="native",gt="data-",vt="ll-status",bt=[st,ut,dt,ft],pt=[ot],ht=[ot,ct],mt=[ot,it,rt],Et={IMG:function(t,e){h(t,function(t){y(t,mt),O(t,e)}),y(t,mt),O(t,e)},IFRAME:function(t,e){y(t,pt),A(t,ot,l(t,e.data_src))},VIDEO:function(t,e){a(t,function(t){y(t,pt),A(t,ot,l(t,e.data_src))}),y(t,ht),A(t,ct,l(t,e.data_poster)),A(t,ot,l(t,e.data_src)),t.load()}},It=["IMG","IFRAME","VIDEO"],yt={IMG:j,IFRAME:function(t){L(t,pt)},VIDEO:function(t){a(t,function(t){L(t,pt)}),L(t,ht),t.load()}},Lt=["IMG","IFRAME","VIDEO"];return t.prototype={update:function(t){var e,n,a,o=this._settings,i=W(t,o);{if(p(this,i.length),!Z&&tt)return q(o)?(e=o,n=this,i.forEach(function(t){-1!==Lt.indexOf(t.tagName)&&S(t,e,n)}),void p(n,0)):(t=this._observer,o=i,t.disconnect(),a=t,void o.forEach(function(t){a.observe(t)}));this.loadAll(i)}},destroy:function(){this._observer&&this._observer.disconnect(),K(this._settings).forEach(function(t){I(t)}),delete this._observer,delete this._settings,delete this.loadingCount,delete this.toLoadCount},loadAll:function(t){var e=this,n=this._settings;W(t,n).forEach(function(t){v(t,e),D(t,n,e)})},restoreAll:function(){var e=this._settings;K(e).forEach(function(t){P(t,e)})}},t.load=function(t,e){e=o(e);D(t,e)},t.resetStatus=function(t){i(t)},t}),function(t,e){"use strict";function n(){e.body.classList.add("litespeed_lazyloaded")}function a(){console.log("[LiteSpeed] Start Lazy Load"),o=new LazyLoad(Object.assign({},t.lazyLoadOptions||{},{elements_selector:"[data-lazyloaded]",callback_finish:n})),i=function(){o.update()},t.MutationObserver&&new MutationObserver(i).observe(e.documentElement,{childList:!0,subtree:!0,attributes:!0})}var o,i;t.addEventListener?t.addEventListener("load",a,!1):t.attachEvent("onload",a)}(window,document);</script><script data-no-optimize="1">window.litespeed_ui_events=window.litespeed_ui_events||["mouseover","click","keydown","wheel","touchmove","touchstart"];var urlCreator=window.URL||window.webkitURL;function litespeed_load_delayed_js_force(){console.log("[LiteSpeed] Start Load JS Delayed"),litespeed_ui_events.forEach(e=>{window.removeEventListener(e,litespeed_load_delayed_js_force,{passive:!0})}),document.querySelectorAll("iframe[data-litespeed-src]").forEach(e=>{e.setAttribute("src",e.getAttribute("data-litespeed-src"))}),"loading"==document.readyState?window.addEventListener("DOMContentLoaded",litespeed_load_delayed_js):litespeed_load_delayed_js()}litespeed_ui_events.forEach(e=>{window.addEventListener(e,litespeed_load_delayed_js_force,{passive:!0})});async function litespeed_load_delayed_js(){let t=[];for(var d in document.querySelectorAll('script[type="litespeed/javascript"]').forEach(e=>{t.push(e)}),t)await new Promise(e=>litespeed_load_one(t[d],e));document.dispatchEvent(new Event("DOMContentLiteSpeedLoaded")),window.dispatchEvent(new Event("DOMContentLiteSpeedLoaded"))}function litespeed_load_one(t,e){console.log("[LiteSpeed] Load ",t);var d=document.createElement("script");d.addEventListener("load",e),d.addEventListener("error",e),t.getAttributeNames().forEach(e=>{"type"!=e&&d.setAttribute("data-src"==e?"src":e,t.getAttribute(e))});let a=!(d.type="text/javascript");!d.src&&t.textContent&&(d.src=litespeed_inline2src(t.textContent),a=!0),t.after(d),t.remove(),a&&e()}function litespeed_inline2src(t){try{var d=urlCreator.createObjectURL(new Blob([t.replace(/^(?:<!--)?(.*?)(?:-->)?$/gm,"$1")],{type:"text/javascript"}))}catch(e){d="data:text/javascript;base64,"+btoa(t.replace(/^(?:<!--)?(.*?)(?:-->)?$/gm,"$1"))}return d}</script><script data-no-optimize="1">var litespeed_vary=document.cookie.replace(/(?:(?:^|.*;\s*)_lscache_vary\s*\=\s*([^;]*).*$)|^.*$/,"");litespeed_vary||fetch("/wp-content/plugins/litespeed-cache/guest.vary.php",{method:"POST",cache:"no-cache",redirect:"follow"}).then(e=>e.json()).then(e=>{console.log(e),e.hasOwnProperty("reload")&&"yes"==e.reload&&(sessionStorage.setItem("litespeed_docref",document.referrer),window.location.reload(!0))});</script><script data-optimized="1" type="litespeed/javascript" data-src="https://diginode.in/wp-content/litespeed/js/5ad5da7e80e1ecf64f3d75c5dab7ddb4.js?ver=da7aa"></script></body>
</html>
Running the Server
Run the server by executing the following command:
node server.js
Testing the Application
Static File Serving: Navigate to
http://localhost:3000/to see theindex.htmlfile served from thepublicdirectory.Request Logging: Check the terminal to see request logs generated by Morgan and the custom logging middleware.
JSON Body Parsing: Use Postman or any API testing tool to send a POST request to
http://localhost:3000/loginwith a JSON body:
{
"username": "admin",
"password": "password"
}
You should receive a response with a token if the credentials are correct.
Basic Authentication: Use the token received from the login endpoint to access the
/usersendpoint. Send a GET request tohttp://localhost:3000/userswith anAuthorizationheader set toBearer mysecrettoken. You should receive a list of users.Error Handling: If there is an error in the application, it will be caught by the error-handling middleware, and a 500 status response will be sent.
In this chapter, we explored middleware in Express.js from basics to advanced concepts. We discussed different types of middleware, how they work, and how to create and use them effectively. Middleware is a powerful feature in Express.js, enabling you to add a wide range of functionalities to your applications. By mastering middleware, you can build more robust, secure, and maintainable Express.js applications.Happy coding !❤️
