Handling Forms and File uploads
Handling forms and file uploads is a fundamental aspect of building web applications. Whether you're developing a simple contact form, a user registration system, or a complex file-sharing platform, understanding how to manage form data and file uploads is crucial. In this chapter, we'll explore these concepts in detail using Express.js, from basic form handling to advanced file upload scenarios.
Why Handling Forms and File Uploads Matters
Forms are the primary way users interact with web applications, allowing them to submit data such as text, selections, and files. Handling these submissions efficiently and securely is essential to providing a good user experience and maintaining data integrity.
File uploads, on the other hand, allow users to share documents, images, and other types of content. Managing these uploads correctly ensures that your application can handle user files in a safe and organized manner.
Understanding HTML Forms
The Basics of HTML Forms
An HTML form is a structured collection of input fields that allows users to submit data to a server. The form is typically composed of various input elements such as text fields, checkboxes, radio buttons, and file upload fields.
Example 1: Basic HTML Form
<form action="/submit-form" method="POST">
<label for="name">Name:</label>
<input type="text" id="name" name="name" required>
<label for="email">Email:</label>
<input type="email" id="email" name="email" required>
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
</form>
Explanation:
- action: Specifies the URL where the form data will be sent upon submission.
- method: Defines the HTTP method (
GETorPOST) used to send the form data. - input fields: Collect user input, like text or email.
- button: Triggers the form submission.
How Form Data is Sent to the Server
When a form is submitted, the data entered by the user is sent to the server. Depending on the method used (GET or POST), the data is sent differently:
- GET Method: The form data is appended to the URL as query parameters. This method is useful for simple searches or data that is not sensitive.
- POST Method: The form data is sent in the body of the HTTP request, making it suitable for sensitive information like passwords.
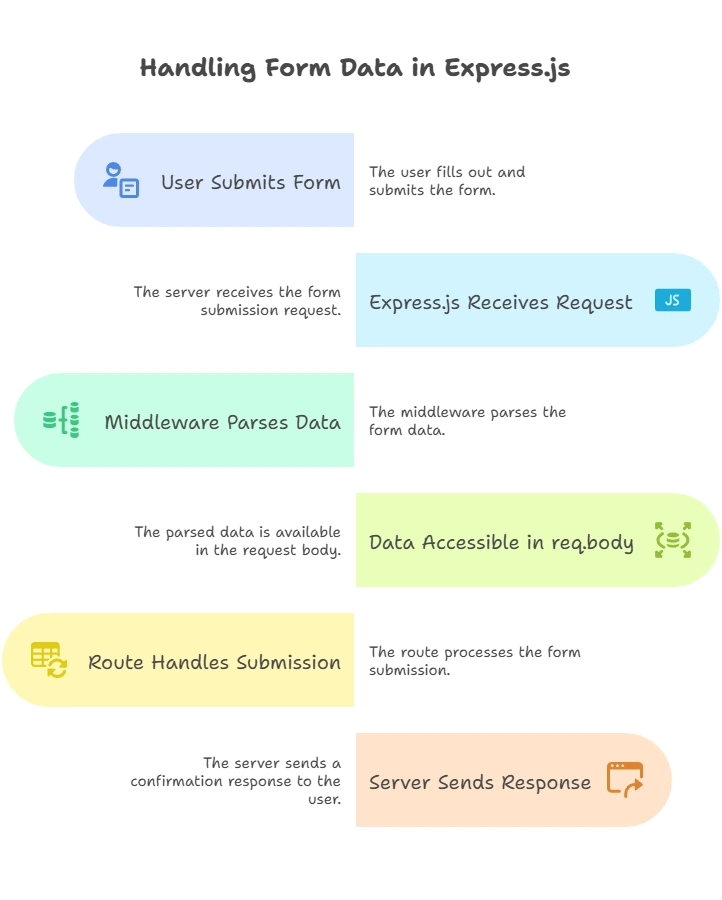
Handling Form Data in Express.js
Setting Up Express.js to Handle Form Data
To handle form data in Express.js, we need to parse the incoming data from the request. Express provides built-in middleware like express.urlencoded() to help with this.
Example 2: Handling Form Data in Express.js
File: app.js
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
const port = 3000;
// Middleware to parse URL-encoded form data
app.use(express.urlencoded({ extended: true }));
// Route to display the form
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.send(`
<form action="/submit-form" method="POST">
<label for="name">Name:</label>
<input type="text" id="name" name="name" required>
<label for="email">Email:</label>
<input type="email" id="email" name="email" required>
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
</form>
`);
});
// Route to handle form submission
app.post('/submit-form', (req, res) => {
const { name, email } = req.body;
res.send(`Thank you, ${name}! We have received your email: ${email}`);
});
app.listen(port, () => {
console.log(`Server running at http://localhost:${port}`);
});
Explanation:
- express.urlencoded({ extended: true }): This middleware parses the URL-encoded data from the form submission and makes it accessible in
req.body. - GET Route
/: Renders the HTML form for the user to fill out. - POST Route
/submit-form: Processes the submitted form data and sends a confirmation response.
Output:
When a user submits the form with their name and email, the server responds with:
Thank you, John Doe! We have received your email: john@example.com
Handling Different Form Submission Methods
Forms can be submitted using either GET or POST methods. Here’s how to handle both in Express.js:
Example 3: Handling GET and POST Form Submissions
File: app.js
// Route to display the form
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.send(`
<form action="/submit-form" method="POST">
<label for="name">Name:</label>
<input type="text" id="name" name="name" required>
<label for="email">Email:</label>
<input type="email" id="email" name="email" required>
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
</form>
<form action="/search" method="GET">
<label for="query">Search:</label>
<input type="text" id="query" name="query">
<button type="submit">Search</button>
</form>
`);
});
// POST route to handle form submission
app.post('/submit-form', (req, res) => {
const { name, email } = req.body;
res.send(`Thank you, ${name}! We have received your email: ${email}`);
});
// GET route to handle search query
app.get('/search', (req, res) => {
const { query } = req.query;
res.send(`You searched for: ${query}`);
});
Explanation:
- GET Method: The search form uses the
GETmethod to send the query as a URL parameter, accessible viareq.query. - POST Method: The form submission continues to use the
POSTmethod, sending data in the request body (req.body).
Output:
If the user searches for “Express.js”, the server responds with:
You searched for: Express.js
Handling File Uploads in Express.js
Introduction to File Uploads
File uploads are essential for web applications that need to handle user-generated content, like profile pictures, documents, or other media. Express.js handles file uploads through middleware like Multer, which processes multipart/form-data used for file uploads.
Setting Up Multer for File Uploads
Multer is a middleware that simplifies handling file uploads. It can store files on the disk or in memory, and it supports single or multiple file uploads.
Installation:
npm install multer
Basic Single File Upload
Let’s start with a simple example of handling a single file upload.
Example 4: Single File Upload with Multer
File: app.js
const express = require('express');
const multer = require('multer');
const app = express();
const port = 3000;
// Configure Multer to store uploaded files
const upload = multer({ dest: 'uploads/' });
// Route to display the file upload form
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.send(`
<form action="/upload" method="POST" enctype="multipart/form-data">
<label for="file">Upload a file:</label>
<input type="file" id="file" name="file" required>
<button type="submit">Upload</button>
</form>
`);
});
// Route to handle file upload
app.post('/upload', upload.single('file'), (req, res) => {
const file = req.file;
res.send(`File uploaded successfully: ${file.originalname}`);
});
app.listen(port, () => {
console.log(`Server running at http://localhost:${port}`);
});
Explanation:
- Multer Configuration: The files are stored in the
uploads/directory. - upload.single(‘file’): Middleware that handles the upload of a single file. The string
'file'corresponds to thenameattribute of the input field in the form. - POST Route
/upload: Handles the uploaded file and responds with a confirmation message.
Output:
After uploading a file, the server responds with:
File uploaded successfully: myfile.txt
Handling Multiple File Uploads
Multer also supports handling multiple file uploads at once.
Example 5: Multiple File Uploads with Multer
File: app.js
// Route to display the multiple file upload form
app.get('/multiple', (req, res) => {
res.send(`
<form action="/upload-multiple" method="POST" enctype="multipart/form-data">
<label for="files">Upload multiple files:</label>
<input type="file" id="files" name="files" multiple required>
<button type="submit">Upload</button>
</form>
`);
});
// Route to handle multiple file uploads
app.post('/upload-multiple', upload.array('files', 5), (req, res) => {
const files = req.files;
res.send(`Files uploaded successfully: ${files.map(file => file.originalname).join(', ')}`);
});
Explanation:
- upload.array(‘files’, 5): Middleware to handle multiple file uploads. The string
'files'must match the name attribute of the file input field, and5is the maximum number of files allowed. - The
/upload-multipleroute processes multiple files and responds with a success message.
Output:
After uploading multiple files, the server responds with:
Files uploaded successfully: file1.txt, file2.txt
File Upload with Custom Storage Configuration
Multer allows for custom storage configurations, such as defining file naming conventions or storing files in different locations.
Example 6: Custom Storage Configuration
File: app.js
// Configure custom storage
const storage = multer.diskStorage({
destination: (req, file, cb) => {
cb(null, 'custom-uploads/');
},
filename: (req, file, cb) => {
const uniqueSuffix = Date.now() + '-' + Math.round(Math.random() * 1E9);
cb(null, file.fieldname + '-' + uniqueSuffix + path.extname(file.originalname));
}
});
const uploadCustom = multer({ storage: storage });
// Route to handle file upload with custom storage
app.post('/upload-custom', uploadCustom.single('file'), (req, res) => {
const file = req.file;
res.send(`File uploaded successfully with custom naming: ${file.filename}`);
});
Explanation:
- multer.diskStorage(): Configures custom storage settings, including the destination directory and filename format.
- destination: Specifies the directory where files should be saved.
- filename: Defines how the file name should be formatted.
Output:
After uploading a file, the server responds with:
File uploaded successfully with custom naming: file-1632355552365-123456789.jpg
Handling File Upload Errors and Security
Handling Errors
Proper error handling is essential to provide a good user experience and to handle issues such as file size limits or invalid file types.
Example 7: Handling File Upload Errors
File: app.js
// Configure Multer with limits
const uploadLimited = multer({
storage: storage,
limits: { fileSize: 1 * 1024 * 1024 } // 1 MB limit
});
// Error-handling middleware
app.use((err, req, res, next) => {
if (err) {
return res.status(500).send(`Error: ${err.message}`);
}
next();
});
// Route to handle file upload with limits
app.post('/upload-limited', uploadLimited.single('file'), (req, res) => {
const file = req.file;
res.send(`File uploaded successfully: ${file.originalname}`);
});
Explanation:
- limits: { fileSize: 1 * 1024 * 1024 }: Sets a file size limit of 1 MB.
- Error-handling middleware: Catches and responds to any errors, such as file size exceeding the limit.
Output:
If a file larger than 1 MB is uploaded, the server will respond with an error message:
Error: File size limit exceeded
Security Considerations
When handling file uploads, it’s important to consider security risks such as malicious files or unauthorized access. Here are a few best practices:
- Validate File Types: Ensure that only allowed file types are uploaded.
- Sanitize File Names: Avoid using user-provided file names directly to prevent path traversal attacks.
- Limit File Size: Prevent excessively large files to avoid overwhelming the server.
Example 8: Validating File Types
File: app.js
// Configure Multer with file type validation
const fileFilter = (req, file, cb) => {
const allowedTypes = ['image/jpeg', 'image/png'];
if (allowedTypes.includes(file.mimetype)) {
cb(null, true);
} else {
cb(new Error('Invalid file type'), false);
}
};
const uploadFiltered = multer({
storage: storage,
fileFilter: fileFilter,
});
// Route to handle file upload with type validation
app.post('/upload-filtered', uploadFiltered.single('file'), (req, res) => {
const file = req.file;
res.send(`File uploaded successfully: ${file.originalname}`);
});
Explanation:
- fileFilter: Middleware function that validates the MIME type of uploaded files. Only files with
image/jpegorimage/pngtypes are allowed.
Output:
If a valid image is uploaded, the server responds with:
File uploaded successfully: image.jpg
If an invalid file type is uploaded, the server responds with:
Error: Invalid file type
In this chapter, we have covered the essentials of handling forms and file uploads in Express.js. Understanding how to process form submissions and manage file uploads is crucial for building robust and user-friendly web applications.Happy coding !❤️
