What is C ?
C is a general-purpose programming language originally developed by Dennis Ritchie at Bell Labs in the early 1970s. It is one of the most widely used programming languages of all time and has greatly influenced many other programming languages such as C++, Java, and Python.
History of C
- C was created by Dennis Ritchie at Bell Labs in the early 1970s.
- It emerged from the necessity to develop the Unix operating system.
- Ritchie aimed to design a language that provided low-level access to hardware while being portable and efficient.
- Inspired by languages like B and BCPL, Ritchie crafted C with a simple yet powerful syntax.
- The language gained popularity within Bell Labs and spread to other institutions and universities.
- In 1978, Brian Kernighan and Dennis Ritchie published “The C Programming Language“, commonly referred to as the “K&R C” book.
- The book served as the definitive guide to the language and contributed significantly to its widespread adoption.
- Throughout the 1980s, C became prevalent, especially in system programming, due to its control over computer resources and hardware.
- In 1989, the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) published the ANSI C standard, formalizing the language’s syntax and semantics.
- This standardization ensured consistency and compatibility among different implementations.
- C has remained a fundamental language in computer science and software development, influencing the design of numerous other programming languages.
Why C language ?
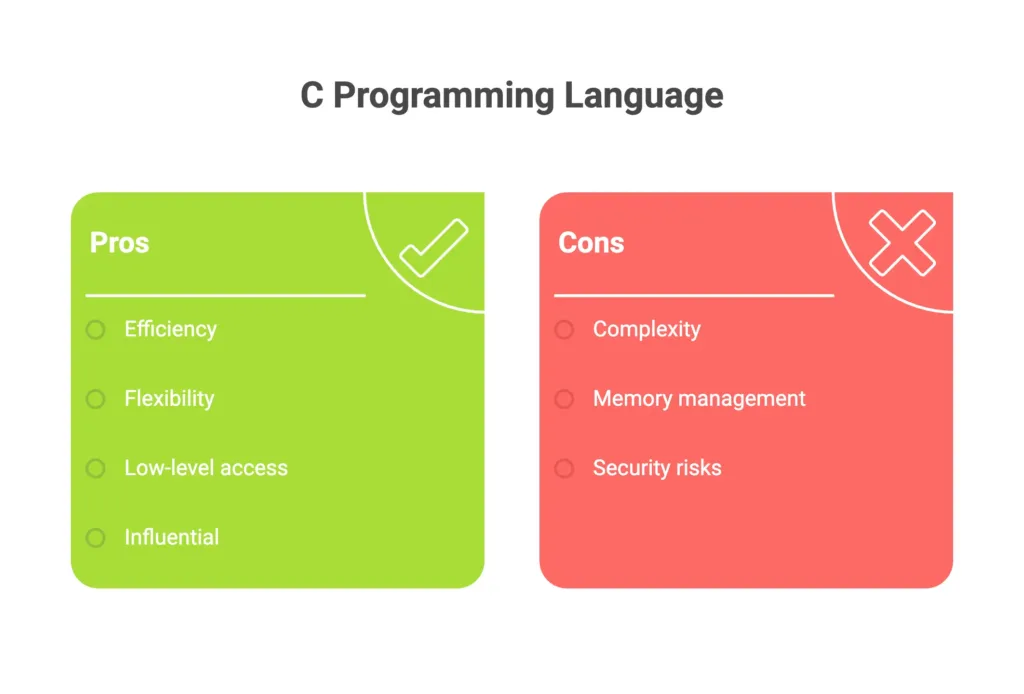
So, what’s so great about C? Well, it’s known for being really fast and flexible. People often use it to build things like operating systems and device drivers because it lets them get right down to the nitty-gritty of how computers work. But it’s not just for low-level stuff; you can use it for all sorts of applications where speed and efficiency are key.
One of the cool things about C is that it’s pretty simple to learn and use. The syntax is straightforward, and there aren’t too many fancy features to trip you up.
Another big plus is that C programs can run on lots of different types of computers without needing to be changed much. That’s because the language has been standardized, so as long as you’re writing code that follows the rules, it should work on any computer that has a C compiler.
C is also great for building modular programs. You can break your code up into smaller chunks called functions, which makes it easier to manage and reuse your code.
Because it’s been around for so long, there’s a huge library of existing code written in C that you can use in your own projects. This makes it easier to add cool features to your programs without having to start from scratch.
But C isn’t without its challenges. One big thing to watch out for is managing memory. If you’re not careful, you can end up with bugs like memory leaks or buffer overflows, which can cause your program to crash or behave unpredictably.
A General-Purpose Powerhouse
C is a general-purpose programming language, meaning it can be used to create a wide variety of applications, from simple scripts to complex operating systems. Its versatility stems from its ability to interact directly with a computer’s hardware, giving programmers fine-grained control over how the machine works
Efficiency at its Core
C is known for its speed and efficiency. It compiles directly into machine code, which the computer can execute very quickly. This makes C ideal for tasks where performance is critical, such as system programming, embedded systems, and game development.
Applications of C
C’s legacy lives on in various domains:
- Operating Systems: Major operating systems like Linux, Windows (partially), and macOS heavily rely on C for their core functionality.
- Device Drivers: The software that allows your computer to communicate with hardware devices like printers or graphics cards is often written in C.
- Embedded Systems: C’s efficiency makes it a popular choice for programming microcontrollers that power devices like smartphones, appliances, and industrial equipment.
- High-Performance Applications: When speed is paramount, C is often the go-to language for computationally intensive tasks like graphics rendering and scientific simulations.
Features
- Simplicity: C keeps things simple with its easy-to-understand syntax, making it a welcoming language for beginners to learn.
- Portability: C programs can smoothly run across different platforms without much tweaking, thanks to its standardized structure, which saves developers time and effort.
- Efficiency: C gives programmers direct access to computer memory and hardware, allowing for optimized resource management. This makes it a top choice for tasks where performance is crucial, like system programming.
- Modularity: With C, developers can break down their programs into smaller, reusable modules using functions and libraries. This not only promotes code reuse but also simplifies maintenance.
- Flexibility: C offers developers the freedom to use either procedural or structured programming styles, depending on what best fits their project’s needs. This flexibility empowers programmers to approach problem-solving in a way that makes sense to them.
- Standardization: C follows strict standards set by organizations like ISO and ANSI. This ensures that code written in C will be consistent and compatible across various platforms and compilers.
- Extensibility: C supports the integration of external libraries, enabling developers to enhance their programs by incorporating pre-existing code. This feature saves time and effort while expanding the functionality of C programs.
- High-performance computing: C is a go-to language for high-performance computing tasks such as scientific simulations and numerical computations. Its efficiency and speed make it well-suited for handling complex calculations and data processing.
- Embedded systems: C shines in the world of embedded systems, powering devices like IoT gadgets, microcontrollers, and firmware. Its ability to work closely with hardware makes it ideal for programming low-level applications.
- Legacy support: Many established software systems and libraries are written in C, making it crucial for developers to understand and interact with legacy codebases. This ensures the continued maintenance and improvement of existing software infrastructure.
The Building Block
C has profoundly influenced the creation of numerous other programming languages like C++, Java, and Python. Understanding C provides a solid foundation for learning these more modern languages, as they share many core concepts and syntax elements.
Despite these challenges, C remains one of the most important languages in computer science and software development. Its speed, flexibility, and wide range of applications make it a valuable tool for programmers everywhere.Happy coding !❤️
