Vue.js Instance
In this chapter, we'll dive deep into the heart of Vue.js – the Vue instance. Understanding the Vue instance is crucial as it forms the foundation of any Vue.js application. This chapter will guide you from the basics to advanced concepts, ensuring you have a comprehensive understanding of the Vue instance.
Introduction to Vue.js Instance
The Vue.js instance is the core of any Vue application. It serves as the connection between the View (DOM) and the Model (data). When you create a Vue instance, you bind it to a part of your DOM, enabling you to manage that part with Vue’s powerful reactivity system.
Creating a Vue Instance
Creating a Vue.js instance is simple. You use the new Vue constructor and pass in an options object.
<div id="app">{{ message }}</div> <script type="litespeed/javascript" data-src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2"></script> <script type="litespeed/javascript">var vm=new Vue({el:'#app',data:{message:'Hello Vue.js!'}})</script>
Explanation:
- el: Binds the Vue instance or Vue.js Instance to the DOM element with the id
app. - data: An object that contains the data properties for the instance. In this case,
message.
Output:
The content of the div with id app will be Hello Vue.js!.
Vue.js Instance Options
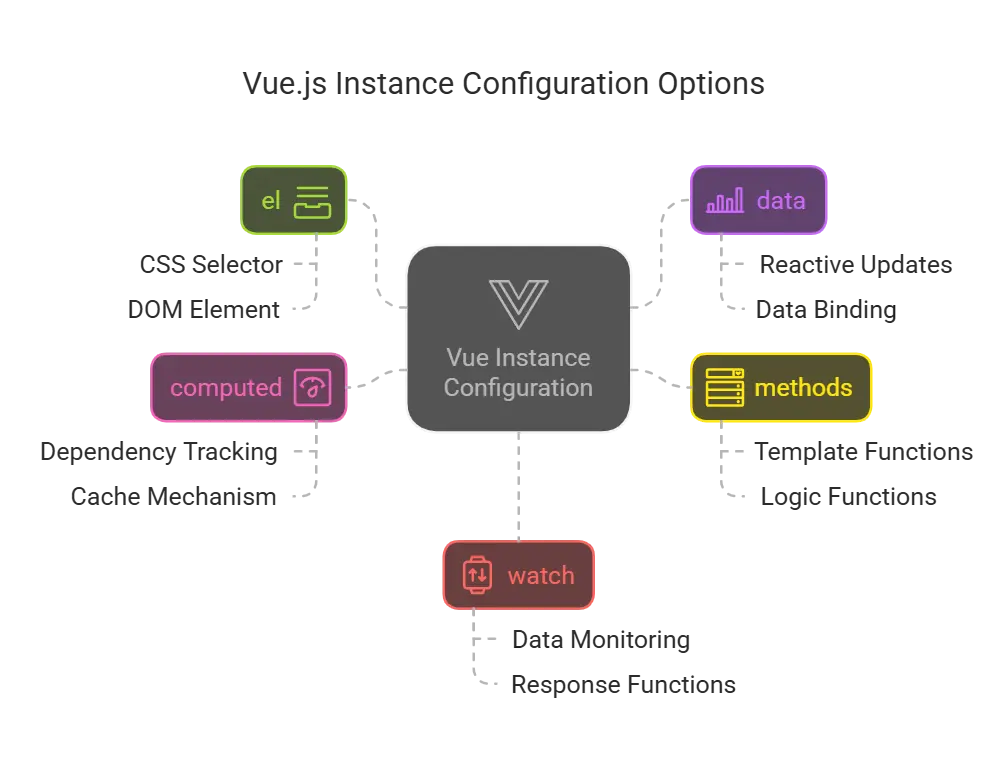
el
The 'el' option specifies the DOM element that the Vue.js instance will be mounted to. This can be a CSS selector or an actual DOM element.
<div id="app">{{ message }}</div> <script type="litespeed/javascript">new Vue({el:'#app',data:{message:'Hello Vue.js!'}})</script>
data
The 'data' option is an object that contains the data for the Vue.js instance. This data is reactive, meaning changes to the data will automatically update the DOM.
<div id="app">
<p>{{ message }}</p>
<button v-on:click="reverseMessage">Reverse Message</button>
</div> <script type="litespeed/javascript">new Vue({el:'#app',data:{message:'Hello Vue.js!'},methods:{reverseMessage:function(){this.message=this.message.split('').reverse().join('')}}})</script>
methods
The
'methods'option is an object where you can define methods for your Vue.js instance. These methods can be called from the DOM using directives like'v-on'.
<div id="app">
<p>{{ message }}</p>
<button v-on:click="reverseMessage">Reverse Message</button>
</div> <script type="litespeed/javascript">new Vue({el:'#app',data:{message:'Hello Vue.js!'},methods:{reverseMessage:function(){this.message=this.message.split('').reverse().join('')}}})</script>
computed
The
'computed'option is an object where you can define computed properties. These properties are cached based on their dependencies and are re-evaluated only when their dependencies change.
<div id="app">
<p>Original Message: {{ message }}</p>
<p>Reversed Message: {{ reversedMessage }}</p>
</div> <script type="litespeed/javascript">new Vue({el:'#app',data:{message:'Hello Vue.js!'},computed:{reversedMessage:function(){return this.message.split('').reverse().join('')}}})</script>
watch
The
'watch'option is an object where you can define watchers. Watchers are functions that will be called when the watched data properties change.
<div id="app">
<p>{{ message }}</p>
<input v-model="message">
</div> <script type="litespeed/javascript">new Vue({el:'#app',data:{message:'Hello Vue.js!'},watch:{message:function(newMessage,oldMessage){console.log('Message changed from',oldMessage,'to',newMessage)}}})</script>
Vue.js Instance Lifecycle
A Vue instance goes through a series of lifecycle events. You can hook into these events using lifecycle hooks to run code at specific stages.
Lifecycle Hooks:
- beforeCreate: Called before the instance is created.
- created: Called after the instance is created.
- beforeMount: Called before the instance is mounted.
- mounted: Called after the instance is mounted.
- beforeUpdate: Called before the data changes and the DOM re-renders.
- updated: Called after the data changes and the DOM re-renders.
- beforeDestroy: Called before the instance is destroyed.
- destroyed: Called after the instance is destroyed.
<div id="app">{{ message }}</div> <script type="litespeed/javascript">new Vue({el:'#app',data:{message:'Hello Vue.js!'},created:function(){console.log('Instance created')},mounted:function(){console.log('Instance mounted')},beforeDestroy:function(){console.log('Instance about to be destroyed')},destroyed:function(){console.log('Instance destroyed')}})</script>
Output:
In the console, you will see:
- “Instance created” when the instance is created.
- “Instance mounted” when the instance is mounted.
- “Instance about to be destroyed” and “Instance destroyed” when the instance is destroyed.
Accessing and Modifying the Vue Instance
You can access and modify the Vue instance using 'this' keyword within the instance’s methods and lifecycle hooks.
<div id="app">
<p>{{ message }}</p>
<button v-on:click="updateMessage">Update Message</button>
</div> <script type="litespeed/javascript">new Vue({el:'#app',data:{message:'Hello Vue.js!'},methods:{updateMessage:function(){this.message='Message Updated!'}}})</script>
Output:
Clicking the “Update Message” button will change the message to “Message Updated!”.
Vue Instance Methods
$mount
The
'$mount'method is used to manually mount an unmounted Vue instance.
<div id="app"></div> <script type="litespeed/javascript">var vm=new Vue({data:{message:'Hello Vue.js!'},template:'<p>{{ message }}</p>'});vm.$mount('#app')</script>
$destroy
The
'$destroy'method is used to destroy a Vue.js instance, cleaning up its connections and removing it from the DOM.
<div id="app">{{ message }}</div>
<button id="destroy">Destroy Instance</button> <script type="litespeed/javascript">var vm=new Vue({el:'#app',data:{message:'Hello Vue.js!'}});document.getElementById('destroy').addEventListener('click',function(){vm.$destroy()})</script>
Output:
Clicking the “Destroy Instance” button will destroy the Vue.js instance and remove it from the DOM.
$nextTick
The
$nextTickmethod is used to execute a callback function after the DOM has been updated.
<div id="app">
<p>{{ message }}</p>
<button v-on:click="updateMessage">Update Message</button>
</div> <script type="litespeed/javascript">new Vue({el:'#app',data:{message:'Hello Vue.js!'},methods:{updateMessage:function(){this.message='Message Updated!';this.$nextTick(function(){console.log('DOM updated')})}}})</script>
Output:
Clicking the “Update Message” button will log “DOM updated” to the console after the DOM is updated.
Vue’s reactivity system allows it to automatically update the DOM when the underlying data changes. This is achieved through getters and setters on the data properties.
<div id="app">
<p>{{ message }}</p>
<button v-on:click="updateMessage">Update Message</button>
</div> <script type="litespeed/javascript">new Vue({el:'#app',data:{message:'Hello Vue.js!'},methods:{updateMessage:function(){this.message='Message Updated!'}}})</script>
Explanation:
When updateMessage is called, the message property is updated, and Vue automatically re-renders the DOM to reflect the new value.
Working with Templates
Templates in Vue are used to define the HTML structure of your components. Vue uses a declarative syntax to bind data to the DOM.
<div id="app">
<p>{{ message }}</p>
<input v-model="message">
</div> <script type="litespeed/javascript">new Vue({el:'#app',data:{message:'Hello Vue.js!'}})</script>
Explanation:
'{{ message }}': This is an interpolation binding that displays the value of'message'.'v-model="message"': This is a two-way binding that keeps the input field and the'message'data property in sync.
Directives in Vue Instance
Directives are special tokens in the markup that tell the library to do something to a DOM element.
Common Directives
- v-bind: Binds an attribute to an expression.
- v-if: Conditionally renders an element.
- v-for: Renders a list of items.
- v-on: Attaches event listeners.
<div id="app">
<p v-if="seen">You can see me!</p>
<ul>
<li v-for="item in items">{{ item }}</li>
</ul>
<button v-on:click="toggleSeen">Toggle Seen</button>
</div> <script type="litespeed/javascript">new Vue({el:'#app',data:{seen:!0,items:['Apple','Banana','Cherry']},methods:{toggleSeen:function(){this.seen=!this.seen}}})</script>
Explanation:
v-if="seen": Conditionally renders the paragraph based on theseendata property.v-for="item in items": Renders a list item for each element in theitemsarray.v-on:click="toggleSeen": Attaches a click event listener to the button that calls thetoggleSeenmethod.
The Vue.js instance is the core of Vue.js and serves as the foundation for any Vue application. By understanding the various options, lifecycle hooks, methods, and reactivity system, you can effectively manage your application's state and behavior. This chapter provided a detailed overview of the Vue.js instance, from basic setup to advanced usage, ensuring you have a solid grasp of this fundamental concept in Vue.js.With this knowledge, you are now well-equipped to build dynamic, reactive applications using Vue.js. As you continue to explore and develop with Vue, keep these concepts in mind, as they will form the basis of your work. Happy Coding! ❤️
